Abstract
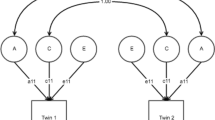
Adverse childhood experiences and substance use have been identified as potential causal risk factors for early-onset sexual intercourse. While it is possible that exposure to these risk factors directly increases the likelihood of engaging in early intercourse, an alternative explanation is that observed associations between these variables are due to shared familial confounds. These unmeasured confounds may increase the likelihood of being exposed to these risk factors and of engaging in early intercourse. Participants drawn from a population-based study of Swedish adult twins (ages 19–47 years; N = 12,126) reported on their history of exposure to early physical and sexual trauma, cigarette use, and cannabis use. We investigated the nature of the association between these risk factors and young age at first intercourse, using a comparison of twins differentially exposed to each risk factor. When compared to non-exposed, unrelated individuals, participants who reported adverse childhood experiences or who engaged in early cigarette use or cannabis use were more likely to engage in early intercourse. However, co-twin comparisons indicated that observed associations between these risk factors and early intercourse may be due to familial factors shared within twin pairs, and risk factor exposure may not lead directly to early intercourse. Our results suggest that preventing trauma exposure or preventing or delaying adolescents’ cigarette smoking or cannabis use may not effectively delay intercourse onset; instead, other aspects of the adolescent’s environment should be addressed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anda, R. F., Butchart, A., Felitti, V. J., & Brown, D. W. (2010). Building a framework for global surveillance of the public health implications of adverse childhood experiences. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 39, 93–98.
Anderson, B. J., & Stein, M. D. (2011). A behavioral decision model testing the association of marijuana use and sexual risk in young women. AIDS and Behavior, 15, 875–884.
Armour, S., & Haynie, D. L. (2007). Adolescent sexual debut and later delinquency. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 36, 141–152.
Bailey, J. A. (2009). Editorial: Addressing common risk and protective factors can prevent a wide range of adolescent risk behaviors. Journal of Adolescent Health, 45, 107–108.
Belsky, J., Steinberg, L., & Draper, P. (1991). Childhood experience, interpersonal development, and reproductive strategy: An evolutionary theory of socialization. Child Development, 62, 647–670.
Biglan, A., Mrazek, P. J., Carnine, D., & Flay, B. (2003). The integration of research and practice in the prevention of youth problem behaviors. American Psychologist, 58, 433–440.
Bricker, J. B., Stallings, M. C., Corley, R. P., Wadsworth, S. J., Bryan, A., Timberlake, D. S., et al. (2006). Genetic and environmental influences on age at sexual initiation in the Colorado Adoption Project. Behavior Genetics, 36, 820–832.
British Academy of Science Working Group. (2010). Social science and family policy. London: British Academy Policy Center.
Buston, K., Williamson, L., & Hart, G. (2007). Young women under 16 years with experience of sexual intercourse: Who becomes pregnant? Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 61, 221–225.
Capaldi, D. M., Crosby, L., & Stoolmiller, M. (1996). Predicting the timing of first intercourse for at-risk adolescent males. Child Development, 67, 344–359.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2007). Youth risk behavior surveillance: United States, 2007 [Occasional Report]. Atlanta, GA: Author.
Danielsson, M., Rogala, C., & Sundström, K. (2001). Teenage sexual and reproductive behavior in developed countries: Country report for Sweden [Occasional Report]. New York: Guttmacher Institute.
Dick, D. D., Johnson, J. K., Viken, R. J., & Rose, R. J. (2000). Testing between-family associations in within-family comparisons. Psychological Science, 11, 409–413.
Dunne, M. P., Martin, N. G., Statham, D. J., Slutske, W. S., Dinwiddie, S. H., Bucholz, K. K., et al. (1997). Genetic and environmental contributions to variance in age at first sexual intercourse. Psychological Science, 8, 211–216.
Fazel, S., & Grann, M. (2006). The population impact of severe mental illness on violent crime. American Journal of Psychiatry, 163, 1397–1403.
Frisell, T., Lichtenstein, P., Rahman, Q., & Långström, N. (2010). Psychiatric morbidity associated with same-sex sexual behavior: Influence of minority stress and familial factors. Psychological Medicine, 40, 315–324.
Furberg, H., Lichtenstein, P., Pedersen, N. L., Thornton, L., Bulik, C. M., Lerman, C., et al. (2008). The STAGE cohort: A prospective study of tobacco use among Swedish twins. Nicotine & Tobacco Research, 10, 1727–1735.
George, W. H., Davis, K. C., Norris, J., Heiman, J. R., Stoner, S. A., Schacht, R. L., et al. (2009). Indirect effects of acute alcohol intoxication on sexual risk-taking: The roles of subjective and physiological sexual arousal. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 38, 498–513.
Guo, G., & Tong, Y. (2006). Age at first sexual intercourse, genes, and social context: Evidence from twins and the dopamine D4 receptor gene. Demography, 43, 747–769.
Hansen, B. T., Kjær, S. K., Munk, C., Tryggvadottir, L., Sparén, P., Hagerup-Jenssen, M., et al. (2010). Early smoking initiation, sexual behavior and reproductive health: A large population-based study of Nordic women. Preventive Medicine, 51, 68–72.
Harden, K. P., Mendle, J., Hill, J. E., Turkheimer, E., & Emery, R. E. (2008). Rethinking timing of first sex and delinquency. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 37, 373–385.
Hollander, D. (2009). In the period before age 21, women, but not men, may have elevated STD risks. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 41, 129–130.
Jaffee, S. R., Caspi, A., Moffitt, T. E., Polo-Tomas, M., Price, T. S., & Taylor, A. (2004). The limits of child effects: Evidence for genetically mediated child effects on corporal punishment but not on physical maltreatment. Developmental Psychology, 40, 1047–1058.
Kaiser Family Foundation. (2008). Sexual health of adolescents and young adults in the United States [Occasional Report]. Washington, DC: Author.
Kendler, K. S., Bulik, C. M., Silberg, J., Hettema, J. M., Myers, J., & Prescott, C. A. (2000). Childhood sexual abuse and adult psychiatric and substance use disorders in women. Archives of General Psychiatry, 57, 953–959.
Kirby, D. (2003). Risk and protective factors affecting teen pregnancy and the effectiveness of programs designed to address them. In D. Romer (Ed.), Reducing adolescent risk: Toward an integrated approach (pp. 265–283). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Kirby, D., Laris, B. A., & Rolleri, L. A. (2007). Sex and HIV education programs: Their impact on sexual behaviors of young people throughout the world. Journal of Adolescent Health, 40, 206–217.
Kogan, S. M., Beach, S. R. H., Philibert, R. A., Brody, G. H., Chen, Y., & Lei, M. (2010). 5-HTTPLR status moderates the effect of early adolescent substance use on risky sexual behavior. Health Psychology, 29, 471–476.
Lahey, B. B., & D’Onofrio, B. M. (2010). All in the family: Comparing siblings to test causal hypotheses regarding environmental influences on behavior. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 19, 319–323.
Lahey, B. B., D’Onofrio, B. M., & Waldman, I. D. (2009). Using epidemiologic methods to test hypotheses regarding causal influences on child and adolescent mental disorders. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50, 53–62.
Lichtenstein, P., Sullivan, P. F., Cnattingius, S., Gatz, M., Johansson, S., Carlström, E., et al. (2006). The Swedish Twin Registry in the third millennium: An update. Twin Research and Human Genetics, 9, 875–882.
Maes, H. H., Woodard, C. E., Murrelle, L., Meyer, J. M., Silberg, J. L., Hewitt, J. K., et al. (1999). Tobacco, alcohol, and drug use in 8- to 16-year-old twins: The Virginia Twin Study of Adolescent Behavioral Development. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 60, 293–305.
McGue, M., Elkins, I., & Iacono, W. G. (2000). Genetic and environmental influences on adolescent substance use and abuse. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 96, 671–677.
McGue, M., Iacono, W. G., & Krueger, R. F. (2006). The association of early adolescent problem behavior and adult psychopathology: A multivariate behavioral genetic perspective. Behavior Genetics, 36, 591–602.
Mendle, J. M., Turkheimer, E., & Emery, R. E. (2007). Detrimental psychological outcomes associated with early pubertal timing in adolescent girls. Developmental Review, 27, 151–171.
Mustanski, B., Viken, R. J., Kaprio, J., Winter, T., & Rose, R. J. (2007). Sexual behavior in young adulthood: A population-based twin study. Health Psychology, 26, 610–617.
Muthén, L., & Muthén, B. (2010). Mplus user’s guide (6th ed.). Los Angeles: Author.
National Campaign to Prevent Teen Pregnancy. (2002). Halfway there: A prescription for progress in preventing teen pregnancy. Washington, DC: Author.
Nelson, E. C., Heath, A. C., Lynskey, M. T., Bucholz, K. K., Madden, P. A. F., Statham, D. J., et al. (2006). Childhood sexual abuse and risks for licit and illicit drug-related outcomes: A twin study. Psychological Medicine, 36, 1473–1483.
Neuhaus, J. M., & McCulloch, C. E. (2006). Separating between- and within-cluster covariate effects by using conditional and partitioning methods. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 68, 859–872.
Rhee, S. H., Hewitt, J. K., Young, S. E., Corley, R. P., Crowley, T. J., & Stallings, M. C. (2003). Genetic and environmental influences on substance initiation, use, and problem use in adolescents. Archives of General Psychiatry, 60, 1256–1264.
Roche, K. M., Mekos, D., Alexander, C. S., Astone, N. M., Bandeen-Roche, K., & Ensminger, M. E. (2005). Parenting influences on early sex initiation among adolescents: How neighborhood matters. Journal of Family Issues, 26, 32–54.
Rodgers, J. L., Rowe, D. C., & Buster, M. (1999). Nature, nurture and first sexual intercourse in the USA: Fitting behavioral genetic models to NLSY kinship data. Journal of Biosocial Science, 31, 29–41.
Rutter, M. (2007). Proceeding from observed correlation to causal inference: The use of natural experiments. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 2, 377–395.
Rutter, M., Belsky, J., Brown, G., Dunn, J., D’Onofrio, B. M., Eekelaar, J., et al. (2010). Social science and family policies. London: British Academy Policy Centre.
Rutter, M., & The Academy of Medical Sciences Working Group. (2007). Identifying the environmental causes of disease: How should we decide what to believe and when to take action?. London: The Academy of Medical Sciences.
Santelli, J., Carter, M., Orr, M., & Dittus, P. (2009). Trends in sexual risk behaviors, by nonsexual risk behavior involvement, U.S. high school students, 1991–2007. Journal of Adolescent Health, 44, 372–379.
Senn, T. E., Carey, M. P., & Vanable, P. A. (2008). Childhood and adolescent sexual abuse and subsequent sexual risk behavior: Evidence from controlled studies, methodological critique, and suggestions for research. Clinical Psychology Review, 28, 711–735.
Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Siebenbruner, J., Zimmer-Gembeck, M. J., & Egeland, B. (2007). Sexual partners and contraceptive use: A 16-year prospective study predicting abstinence and risk behavior. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 17, 179–206.
Snijders, T., & Bosker, R. (1999). Multilevel analysis: An introduction to basic and advanced multilevel modeling. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishers.
Statistics Sweden. (2011). Educational attainment of the population. Retrieved Feb 2, 2011 from http://www.scb.se/UF0506-EN.
Stein, M. B., Lang, K. L., Taylor, S., Vernon, P. A., & Livesley, W. J. (2002). Genetic and environmental influences on trauma exposure and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms: A twin study. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159, 1675–1681.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2000). Healthy people 2010: Understanding and improving health (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Verweij, K. J. H., Zietsch, B. P., Bailey, J. M., & Martin, N. G. (2009). Shared aetiology of risky sexual behaviour and adolescent misconduct: Genetic and environmental influences. Genes, Brain and Behavior, 8, 107–113.
Young-Wolff, K. C., Kendler, K. S., Ericson, M. L., & Prescott, C. A. (2011). Accounting for the association between childhood maltreatment and alcohol-use disorders in males: A twin study. Psychological Medicine, 41, 59–70.
Zimmer-Gembeck, M. J., & Helfand, M. (2008). Ten years of longitudinal research on U.S. adolescent sexual behavior: Developmental correlates of sexual intercourse, and the importance of age, gender, and ethnic background. Developmental Review, 28, 153–224.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by award numbers F31 DA 029376-01 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and T32 HD 007475 from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Kelly Donahue received the 2012 Sandra R. Leiblum Student Research Award from the Society for Sex Therapy and Research (SSTAR) in recognition of her work on this article. Portions of the article were presented at the March 2012 SSTAR meeting, Chicago, IL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donahue, K.L., D’Onofrio, B.M., Lichtenstein, P. et al. Testing Putative Causal Associations of Risk Factors for Early Intercourse in the Study of Twin Adults: Genes and Environment (STAGE). Arch Sex Behav 42, 35–44 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-012-9947-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-012-9947-1