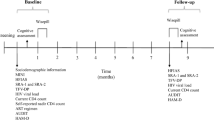
Cognitive deficits are associated with nonadherence to HIV medications. HIV-positive injecting drug users (IDUs) are at particular risk for nonadherence and cognitive barriers to adherence specific to this population should therefore be identified. The present study assessed the relation of three domains of cognitive functioning, executive functions, memory, and psychomotor speed, to self-reported antiretroviral adherence in a sample of HIV-positive IDUs. Depression, use of alcohol, heroin, cocaine/crack, or marijuana in the last week were also included in the models. Logistic regression analyses showed that only psychomotor slowing was significantly associated with nonadherence. Executive functions, memory, depression, and active alcohol and substance use were unrelated to adherence. No other studies to date have exclusively linked psychomotor slowing to nonadherence in HIV infection. Psychomotor slowing among our study sample was severe and suggests that when evident, such slowing may be a valuable determinant for antiretroviral adherence among IDUs.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ahmad, S., Ahmad, H., and Bindra, G. (1989). Cognitive impairment in chronic heroin addicts. Journal of Personality and Clinical Studies, 5, 237–240.
Albert, S. M., Weber, C. M., Todak, G., Polanco, C., Clouse,R., McElhiney, M., Rabkin, J., Stern, Y., Marder, K.(1999). An observed performance test of medication management ability in HIV: Relation to neuropsychological status and medication adherence outcomes. AIDS and Behavior, 3, 121–128.
Arnsten, J. H., Demas, P. A., Farzadegan, H., Grant, R. W., Gourevich, M. N., Chang, C., et al. (2001). Antiretroviral therapy adherence and viral suppression in HIV-infected drug users: Comparison of self-report and electronic monitoring. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 33, 1417–1423.
Arnsten, J. H., Demas, P. A., Grant, R. W., Gourevitch, M. N., Farzadegan, H., Howard, A. A., et al. (2002). Impact of active drug use on antiretroviral therapy adherence and viral suppression in HIV-infected drug users. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 17, 377–381.
Avants, S. K., Margolin, A., Warburton, L. A., Hawkins, K. A., and Shi, J. (2001). Predictors of nonadherence to HIV-related medication regimens during methadone stabilization. The American Journal on Addictions, 10, 69–78.
Bangsberg, D. R., Hecht, F. M., Charlebois, E. D., Zolopa, A. R., Holodniy, M., Sheiner, L., et al. (2000). Adherence to protease inhibitors, HIV-1 viral load, and development of drug resistance in an indigent population. AIDS, 14, 357–366.
Basso, M. R., and Bornstein, R. A. (2000). Neurobehavioral consequences of substance abuse and HIV infection. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 14, 228–237.
Beck, A. T., Ward, C. H., Mendelson, M., Mock, J., and Erbaugh, J. (1961). An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry, 4, 561–571.
Benton, A. L., Hamsher, K., and Sivan, A. B. (1983). Multilingual Aphasia Examination (3rd ed.). Iowa City, IA: AJA Associates.
Berry, J., van Gorp, W. G., Herzberg, D. S., Hinkin, C., Boone, K., Steinman, L., et al. (1993). Neuropsychological deficits in abstinent cocaine abusers: Preliminary findings after two weeks of abstinence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 32, 231–237.
Bono, G., Mauri, M., Sinforiani, E., Barbarini, G., Minoli, L., and Fea, M. (1996). Longitudinal neuropsychological evaluation of HIV-infected intravenous drug users. Addiction, 91, 263–268.
Bornstein, R. A., Pace, P., Rosenberger, P., Nasrallah, H. A., Para, M. F., Whitacre, C. C., et al. (1993). Depression and neuropsychological performance in asymptomatic HIV infection. American Journal of Psychiatry, 150, 922–927.
Carrieri, M. P., Chesney, M. A., Spire, B., Loundou, A., Sobel, A., Lepeu, G., Moatti, J. P., and the MANIF Study Group. (2003). Failure to maintain adherence to HAART in a cohort of French HIV-positive injecting drug users. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 10, 1–14.
Catz, S. L., Kelly, J. A., Bogart, L. M., Benotsch, E. G., and McAuliffe, T. L. (2000). Patterns, correlates and barriers to medication adherence among persons prescribed new treatments for HIV disease. Health Psychology, 19, 124–133.
Cohen, R. A., Boland, R., Paul, R., Tashima, K. T., Schoenbaum, E. E., Celentano, D. D., et al. (2001). Neurocognitive performance enhanced by highly active antiretroviral therapy in HIV infected women. AIDS, 15, 341–345.
Cummings, J. L., and Benson, D. F. (1992). Dementia: A clinical approach (2nd ed.). Boston: Butterworth Heinemann.
The Dana Consortium. (1996). Clinical confirmation of the American Academy of Neurology algorithm for HIV-1-associated cognitive/motor disorder. The Dana Consortium on Therapy for HIV Dementia and Related Cognitive Disorders. Neurology, 47, 1247–1253.
D’Elia, L., Satz, P., Uchiyama, C. L., and White, T. (1996). Color trails 1 and 2. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Ferrando, S., van Gorp, W., McElhiney, M., Goggin, K., Sewell, M., and Rabkin, J. (1998). Highly active antiretroviral treatment in HIV infection: Benefits for neuropsychological function. AIDS, 12, F65–F70.
First, M. B., Spitzer, R. L., Gibbon, M., and Williams, J. B. (1995). Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders, Patient Edition (Version 2.0). New York: New York State Psychiatric Institute.
Galea, S., and Vlahov, D. (2002). Social determinants and the health of drug users: Socioeconomic status, homeless, and incarceration. Public Health Reports, 117, S135–S145.
Gordillo, V., del Amo, J., Soriano, V., and Gonzalez-Lahoz, J. (1999). Sociodemographic and psychological variables influencing adherence to antiretroviral therapy. AIDS, 13, 1763–1769.
Grant, I., Adams, K. M., Carlin, A. S., Rennick, P. M., Judd, L. L., Schooff, K., et al. (1978). Neuropsychological effects of polydrug abuse. In D. R. Wesson, A. S. Carlin, K. M. Adams, and G. Beschner (Eds.), Polydrug abuse. The results of a national collaborative study (pp. 223–261). New York: Academic.
Grant, I., Atkinson, J. H., Hesselink, J. R., Kennedy, C. J., Richman, D. D., and Spector, S. A., et al. (1987). Evidence for early central nervous system involvement in the Acquired immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections. Annals of Internal Medicine, 107, 828–836.
Grant, I., and Martin, A. (1994). Neurocognitive disorders associated with HIV-1 infection. In I. Grant and A. Martin (Eds.), Neuropsychology of HIV-1 infection (pp. 3–19). New York: Oxford University Press.
Hinkin, C. H., Castellon, S. A., Durvasula, R. S., Hardy, D. J., Lam, M. N., and Mason, K. I., et al. (2002). Medication adherence among HIV+ adults. Neurology, 59, 1944–1950.
Hinkin, C. H., Hardy, D. J., Mason, K. I., Castellon, S. A., Durvasula, R. S., Lam, M. N., et al. (2004). Medication adherence in HIV-infected adults: Effect of patient, age, cognitive status, and substance abuse. AIDS, 18, S19–S25.
Howard, A. A., Arnsten, J. H., Lo, Y., Vlahov, D., Rich, J. D., Schuman, P., Stone, V. E., Smith, D. K., Schoenbaum, E. E., and the HER Study Group. (2002). A prospective study of adherence and viral load in a large multi-center cohort of HIV-infected women. AIDS, 16, 2175–2182.
Karon, J. M., Fleming, P. L., Steketee, R. W., and DeCock, K. M. (2001). HIV in the United States at the turn of the century. American Journal of Public Health, 91, 1060–1068.
Liu, H., Golin, C. E., Miller, L. G., Hays, R. D., Beck, C. K., Sanadaji, S., et al. (2001). A comparison study of multiple measures of adherence to HIV protease inhibitors. Annals of Internal Medicine, 134, 968–977.
Lucas, G. M., Cheever, L. W., Chaisson, R. E., and Moore, R. D. (2001). Detrimental effects of continued illicit drug use on the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 27, 251–259.
Mannheimer, S., Friedland, G., Matts, J., Child, C., and Chesney, M. (2002). The consistency of adherence to antiretroviral therapy predicts biologic outcomes for human immunodeficiency virus-infected persons in clinical trials. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 34, 1115–1121.
Martens, W. H. (2001). A review of physical and mental health in homeless persons. Public Health Review, 29, 13–33.
Meek, P. S., Clark, H. W., and Solana, V. L. (1989). Neurocognitive impairment: The unrecognized component of dual diagnoses in substance abuse treatment. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 21, 153–160.
Montaner, J. S. G., Reiss, P., Cooper, D., Vella, S., Harris, M., Conway, B., et al. (1998). A randomized, double-blind trial comparing combinations of nevirapine, didanosine and zidovudine for HIV-infected patients. JAMA, 279, 930–937.
Murphy, E. L., Collier, A. C., Kalish, L. A., Assmann, S. F., Para, M. F., Flanigan, T. P., et al. (2001). Highly active antiretroviral therapy decreases mortality and morbidity in patients with advanced HIV disease. Annals of Internal Medicince, 135, 17–26.
Navia, B. A., Jordan, B. D., and Price, R. W. (1986). The AIDS dementia complex: I. Clinical features. Annals of Neurology, 19, 517–524.
Paterson, D., Swindells, S., Mohr, J., Brestor, M., Vergis, R., Squier, C., et al. (2000). Adherence to protease inhibitor therapy and outcomes in patients with HIV infection. Annals of Internal Medicine, 133, 21–30.
Paterson, D. L., Potoski, B., and Capitano, B. (2002). Measurement of adherence to antiretroviral medications. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 31, S103–S106.
Sacktor, N., McDermott, M. P., Marder, K., Schiffito, G., Selnes, O. A., McArthur, J. C., et al. (2002). HIV-associated cognitive impairment before and after the advent of combination therapy. Journal of Neurovirology, 8, 136–142.
Sacktor, N., Skolasly, R. L., Tarwater, P. M., McArthur, J. C., Selnes, O. A., Becker, J., et al. (2003). Response to systemic HIV viral load suppression correlates with psychomotor speed performance. Neurology, 61, 567–569.
Sankoh, A. J., Huque, M. F., and Dubey, S. D. (1997). Some comments on frequently used multiple endpoint adjustments methods in clinical trials. Statistics in Medicine, 16, 2529–2542.
Selnes, O. A., Galai, N., McArthur, J. C., Cohn, S., Royal, W., Esposito, D., et al. (1997). HIV infection and cognition in intravenous drug users: Long-term follow-up. Neurology, 48, 223–230.
Smith, A. (2000). Symbol Digit Modalities Test: Manual. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Stern, R. A., Silva, S. G., Chaisson, N., and Evans, D. L. (1996). Influence of cognitive reserve on neuropsychological functioning in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection. Archives of Neurology, 53, 148–153.
Stevens, J. (1996). Applied Multivariate Statistics for the Social Sciences (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Strickland, T. L., Miller, B. L., Kowell, A., and Stein, R. (1993). Neurobiology of cocaine-induced organic brain impairment: Contribution from functional neuroimaging. Neuropsychology Review, 8, 1–9.
Suarez, S., Baril, L., Stankoff, B., Khellaf, M., Dubois, B., Lubetzki, C., et al. (2001). Outcome of patients with HIV-1-related cognitive impairment on highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS, 15, 195–200.
Tesoriero, J., French, T., Weiss, L., Waters, M., Finkelstein, R., and Agins, B. (2003). Stability of adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy over time among clients enrolled in the treatment adherence demonstration project. JAIDS: Journal of the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 33, 484–493.
Tiffin, J. (1968). Purdue Pegboard: Examiner manual. Chicago: Science Research Associates.
Tombaugh, T. N., Kozak, J., and Rees, L. (1996). Normative data for the controlled oral word association test. In O. Spreen and E. Strauss (Eds.), A compendium of neuropsychological tests: Administration, norms and commentary (2nd ed.). New York: Oxford.
Tucker, J. S., Burnam, A., Sherbourne, C. D., Kung, F. Y., and Gifford, A. L. (2003). Substance use and mental health correlates of nonadherence to antiretroviral medications in a sample of patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. The American Journal of Medicine, 114, 573–580.
Turner, B. J., Laine, C., Cosler, L., and Hauck, W. W. (2003). Relationship of gender, depression, and health care delivery with antiretroviral adherence in HIV-infected drug users. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 18, 248–257.
Wagner, G. J. (2002). Predictors of antiretroviral adherence as measured by self-report, electronic monitoring, and medication diaries. AIDS Patient Care and STDs, 16, 599–608.
Wainberg, M. A., and Friedland, G. (1998). Public health implications of antiretroviral therapy and HIV drug resistance. JAMA, 279, 1977–1983.
Wall, T. L., Sorensen, J. L., Batki, S. L., Delucchi, K. L., London, J. A., and Chesney, M. A. (1995). Adherence to zidovudine (AZT) among HIV-infected methadone patients: A pilot study of supervised therapy and dispensing compared to usual care. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 37, 261–269.
Wechsler, D. (1997). Wechsler adult intelligence scale Manual (3rd ed.). New York: The Psychological Corporation.
Wilkie, F. L., Eisdorfer, C., Morgan, R., Loewenstein, D. A., and Szapocznik, J. (1990). Cognition in early human immunodeficiency virus infection. Archives of Neurology, 47, 433–440.
Wilkinson, G. S. (1993). The Wide Range Achievement Test Administration Manual (3rd ed.). Wilmington, DE: Wide Range.
Yeudall, L. T., Fromm, D., Reddon, J. R., and Stefanyk, W. O. (1986). Normative data stratified by age and sex for 12 neuropsychological tests. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 42, 918–946.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by a Development Award from the Drug Abuse and AIDS Research Center (DAARC) at the University of Miami-School of Medicine, Department of Epidemiology, funded by NIDA P30 DA 13870. This study was also supported, in part, by research grants DA 12792 and DA 13550.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waldrop-Valverde, D., Ownby, R.L., Wilkie, F.L. et al. Neurocognitive Aspects of Medication Adherence in HIV-Positive Injecting Drug Users. AIDS Behav 10, 287–297 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-005-9062-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-005-9062-6