Abstract
Objectives
To assess the psychometric performance of proxy-reported EQ-5D-Y-5L (Y-5L) in comparisons with EQ-5D-Y-3L (Y-3L) administered by caregivers of patients with juvenile (JIS) or adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS).
Methods
A consecutive sample of caregivers of JIS or AIS patients were recruited. Redistribution property, ceiling effects, and discriminative power were examined. Known-group validity was determined by examining their ability to detect differences across clinical known groups. Test–retest reliability was assessed using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) for EQ-VAS score and Gwet’s agreement coefficient (GAC) and percentage agreement (PA) for dimension responses. Furthermore, subgroups were analyzed for comparing test–retest reliability.
Results
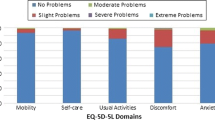
A total of 130 caregivers were involved in the study. Consistencies between proxy-reported Y-3L and Y-5L were very high for all dimensions (93.8–99.2%). The ceiling effect in the Y-5L was slightly reduced in four dimensions (AR: 0.8–2.3%) whereas increased in “Having pain/discomfort”. Greater informativity was found in the Y-5L than the Y-3L. In known-group comparisons of curvature magnitude, curvature type, and treatment modality, Y-5L and Y-3L dimension scales showed hypothesized results. For example, more full-health responses were found in the mild Cobb angle group (Y-5L: 63.1%; Y-3L: 62.2%) than the severe Cobb angle group (Y-5L: 55.6%, Y-3L: 55.6%). EQ-VAS score exhibited low test–retest reliability (ICC: 0.41), whereas dimension scales of both instruments showed satisfactory test–retest reliability (GAC ≥ 0.7 and PA ≥ 70% for all). In most known groups, hard-to-observe dimensions were more reliable for proxy-reported Y-5L than Y-3L.
Conclusion
Both the proxy-reported Y-5L and Y-3L are valid and reliable instruments for assessing the HRQoL of JIS or AIS patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
References
Weinstein, S.L., Dolan, L.A., Cheng, J.C., Danielsson, A., Morcuende, J.A.: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet 371, 1527–1537 (2008)
Kane, W.: Scoliosis prevalence: a call for a statement of terms. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 126, 43–46 (1977)
Vasiliadis, E., Grivas, T.B.: Quality of life after conservative treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 135, 409 (2008)
Asher, M., Burton, D.: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: natural history and long term treatment effects. Scoliosis 1(1), 2 (2006)
Cheung, P.W.H., Wong, C.K.H., Cheung, J.P.Y.: An insight into the health-related quality of life of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients who are braced, observed, and previously braced. Spine 44(10), E596–E605 (2019)
Han, J., Xu, Q., Yang, Y., Yao, Z., Zhang, C.: Evaluation of quality of life and risk factors affecting quality of life in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 4(1), 12–16 (2015)
Rowen, D., Rivero-Arias, O., Devlin, N., Ratcliffe, J.: Review of valuation methods of preference-based measures of health for economic evaluation in child and adolescent populations: where are we now and where are we going? Pharmacoeconomics 38(4), 325–340 (2020)
Rowen, D., Keetharuth, A.D., Poku, E., Wong, R., Pennington, B., Wailoo, A.: A review of the psychometric performance of selected child and adolescent preference-based measures used to produce utilities for child and adolescent health. Value Health 24(3), 443–460 (2021)
Thorrington, D., Eames, K.: Measuring health utilities in children and adolescents: a systematic review of the literature. PLoS ONE 10, e0135672 (2015)
Ravens-Sieberer, U., Wille, N., Badia, X., Bonsel, G., Burström, K., Cavrini, G., et al.: Feasibility, reliability, and validity of the EQ-5D-Y: results from a multinational study. Qual. Life Res. 19(6), 887–897 (2010)
Perez Sousa, M.Á., Olivares Sánchez-Toledo, P.R., Gusi Fuerte, N.: Parent-child discrepancy in the assessment of health-related quality of life using the EQ-5D-Y questionnaire. Archivos argentinos de pediatria 115(6), 541–546 (2017)
Noyes, J., Edwards, R.: EQ-5D for the assessment of health-related quality of life and resource allocation in children: a systematic methodological review. Value Health 14(8), 1117–1129 (2011)
Kind, P., Klose, K., Gusi, N., Olivares, P.R., Greiner, W.: Can adult weights be used to value child health states? Testing the influence of perspective in valuing EQ-5D-Y. Qual. Life Res. 24(10), 2519–2539 (2015)
Tamim, H., McCusker, J., Dendukuri, N.: Proxy reporting of quality of life using the EQ-5D. Med. Care 12(40), 1186–1195 (2002)
EuroQol Research Foundation. EQ-5D-3L User Guide, 2018. Available from: https://euroqol.org/publications/user-guides
Shiroiwa, T., Fukuda, T., Shimozuma, K.: Psychometric properties of the Japanese version of the EQ-5D-Y by self-report and proxy-report: reliability and construct validity. Quality of Life Res. 28, 3093–3105 (2019)
Verstraete, J., Lloyd, A., Scott, D., Jelsma, J.: How does the EQ-5D-Y proxy version 1 perform in 3, 4 and 5-year-old children? Health Qual. Life Outcomes 18, 1–10 (2020)
Bray, N., Noyes, J., Harris, N., Edwards, R.T.: Measuring the health-related quality of life of children with impaired mobility: examining correlation and agreement between children and parent proxies. BMC. Res. Notes 10(1), 1–8 (2017)
Varni, J.W., Burwinkle, T.M., Sherman, S.A., Hanna, K., Berrin, S.J., Malcarne, V.L., et al.: Health-related quality of life of children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: hearing the voices of the children. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 47(9), 592–597 (2005)
López-Bastida, J., López-Siguero, J.P., Oliva-Moreno, J., Vázquez, L.A., Aranda-Reneo, I., Reviriego, J. et al.: Health-related quality of life in type 1 diabetes mellitus pediatric patients and their caregivers in Spain: an observational cross-sectional study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 35, 1589–1595 (2019)
Lin, J., Wong, C.K.H., Cheung, P.W.H., Luo, N., Cheung, J.P.Y.: Feasibility of proxy-reported EQ-5D-3L-Y and its agreement in self-reported EQ-5D-3L-Y for patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 45(13), E799–E807 (2020)
Kreimeier, S., Åström, M., Burström, K., Egmar, A.C., Gusi, N., Herdman, M., et al.: EQ-5D-Y-5L: developing a revised EQ-5D-Y with increased response categories. Qual. Life Res. 28(7), 1951–1961 (2019)
Wong, C.K.H., Cheung, P.W.H., Luo, N., Cheung, J.P.Y.: A head-to-head comparison of five-level (EQ-5D-5L-Y) and three-level EQ-5D-Y questionnaires in paediatric patients. Eur. J. Health Econ. 20(5), 647–656 (2019)
Wong, C.K.H., Cheung, P.W.H., Luo, N., Lin, J., Cheung, J.P.Y.: Responsiveness of EQ-5D youth version 5-level (EQ-5D-5L-Y) and 3-level (EQ-5D-3L-Y) in patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 44(21), 1507–1514 (2019)
Kreimeier, S., Greiner, W.: EQ-5D-Y as a health-related quality of life instrument for children and adolescents: the instrument’s characteristics, development, current use, and challenges of developing its value set. Value Health 22(1), 31–37 (2019)
Østbye, T., Tyas, S., McDowell, I., Koval, J.: Reported activities of daily living: agreement between elderly subjects with and without dementia and their caregivers. Age Ageing 26(2), 99–106 (1997)
Shannon, C.E.: A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27(3), 379–423 (1948)
Janssen, M.F.B., Birnie, E., Bonsel, G.J.: Evaluating the discriminatory power of EQ-5D, HUI2 and HUI3 in a US general population survey using Shannon’s indices. Qual. Life Res. 16(5), 895–904 (2007)
Streiner, D.L., Norman, G.R., Cairney, J.: Health measurement scales: a practical guide to their development and use. Oxford University Press, USA (2015)
Cheung, P.W.H., Wong, C.K.H., Samartzis, D., Luk, K.D.K., Lam, C.L.K., Cheung, K.M.C., Cheung, J.P.Y.: Psychometric validation of the EuroQoL 5-dimension 5-level (EQ-5D-5L) in Chinese patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 11(1), 19 (2016)
Luo, N., Chew, L.H., Fong, K.Y., Koh, D.R., Ng, S.C., Yoon, K.H., Vasoo, S., et al.: Validity and reliability of the EQ-5D self-report questionnaire in Chinese-speaking patients with rheumatic diseases in Singapore. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 32(5), 685–690 (2003)
Mahesh, P.K.B., Gunathunga, M.W., Jayasinghe, S., Arnold, S.M., Senanayake, S., Senanayake, C., et al.: Construct validity and reliability of EQ-5D-3L for stroke survivors in a lower middle income setting. Ceylon Med. J. 64(2), 52–58 (2019)
Koo, T.K., Li, M.Y.: A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 15(2), 155–163 (2016)
Wongpakaran, N., Wongpakaran, T., Wedding, D., Gwet, K.L.: A comparison of Cohen’s Kappa and Gwet’s AC1 when calculating inter-rater reliability coefficients: a study conducted with personality disorder samples. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 13(1), 1–7 (2013)
Ungar, W.J.: Challenges in health state valuation in paediatric economic evaluation. Pharmacoeconomics 29(8), 641–652 (2011)
Janssen, M.F., Bonsel, G.J., Luo, N.: Is EQ-5D-5L better than EQ-5D-3L? : a head-to-head comparison of descriptive systems and value sets from seven countries. Pharmacoeconomics 36(6), 675–697 (2018)
Loomis, J.B.: Comparative reliability of the dichotomous choice and open-ended contingent valuation techniques. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 18(1), 78–85 (1990)
Zhou, W., Shen, A., Yang, Z., Wang, P., Wu, B., Herdman, M., et al.: Patient–caregiver agreement and test–retest reliability of the EQ-5D-Y-3L and EQ-5D-Y-5L in paediatric patients with haematological malignancies. Eur. J. Health Econ. 22, 1103–1113 (2021)
Rupel, V.P., Ogorevc, M.: EQ-5D-Y value set for Slovenia. PharmacoEconomics 39(4), 463–471 (2021)
Trudel, J.G., Rivard, M., Dobkin, P.L., Leclerc, J.M., Robaey, P.: Psychometric properties of the health utilities index mark 2 system in paediatric oncology patients. Qual. Life Res. 7(5), 421–432 (1998)
Hsu, C.N., Lin, H.W., Pickard, A.S., Tain, Y.L.: EQ-5D-Y for the assessment of health-related quality of life among Taiwanese youth with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 30(4), 298–305 (2018)
van Litsenburg, R.R., Kunst, A., Huisman, J., Ket, J.C., Kaspers, G.J., Gemke, R.J.: Health status utilities in pediatrics: a systematic review of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Med. Decis. Mak. 34(1), 21–32 (2014)
Kreimeier, S., Oppe, M., Ramos-Goñi, J.M., Cole, A., Devlin, N., Herdman, M., et al.: Valuation of EuroQol five-dimensional questionnaire, youth version (EQ-5D-Y) and EuroQol five-dimensional questionnaire, three-level version (EQ-5D-3L) health states: the impact of wording and perspective. Value Health 21(11), 1291–1298 (2018)
EuroQol Research Foundation. EQ-5D-Y User Guide, 2020. Available from: https://euroqol.org/publications/user-guides/
Konieczny, M.R., Senyurt, H., Krauspe, R.: Epidemiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Child. Orthop. 7(1), 3–9 (2013)
Funding
This study was supported by the EuroQol Research Foundation (Grant number: 20190250) and the General Research Fund of the Research Grants Council #17156416 and #17119518.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
Ethics approval for this study was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of the Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster/University of Hong Kong.
Informed consent
Written Informed consent to participate in the study was obtained from participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, J., Wong, C.K.H., Cheung, J.P.Y. et al. Psychometric performance of proxy-reported EQ-5D youth version 5-level (EQ-5D-Y-5L) in comparison with three-level (EQ-5D-Y-3L) in children and adolescents with scoliosis. Eur J Health Econ 23, 1383–1395 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-022-01435-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-022-01435-z