Abstract
Background
There is a growing interest in policy making for using utility measures and identifying algorithms to convert disease-specific measures into utilities.
Objectives
To analyse the relationship between EQ-5D, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) in psoriasis. To transform DLQI scores, and key clinical, demographic and health service utilisation variables into utilities.
Methods
A cross-sectional questionnaire survey of 200 consecutive adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis was carried out in two Hungarian university clinics. The relationship between the outcome measures were analysed with correlations and with the known-groups method. Bivariate and multivariate regression algorithms on EQ-5D scores were formulated.
Results
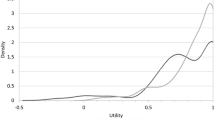
The mean age of respondents was 51 years (SD = 12.9), 68.5 % were male, and 51.5 % received biological therapy. Median EQ-5D, DLQI, and PASI scores were 0.73, 3.0, and 3.45, respectively. EQ-5D showed a moderate correlation with the DLQI and with the PASI (r s = −0.48 and −0.43, p < 0.05). Strong correlation was found between DLQI and PASI (r s = 0.81, p < 0.05). DLQI and PASI discriminated better among groups categorised by the localisation of the lesions than EQ-5D. Presence of psoriasis on the neck and/or décolletage was associated with the greatest health related quality of life (HRQOL) impairment. Ten variables were incorporated in a multivariate algorithm that accounted for 48.8 % of EQ-5D variance (ANOVA p < 0.001).
Conclusions
This study provided the first evidence that patients with visible psoriatic lesions have significantly worse HRQOL compared to those with non-visible lesions, measured not only with DLQI but also with EQ-5D. In addition to demographic and clinical variables, our model included health service utilisation variables related to psoriasis, and explained higher proportion of EQ-5D variance than any previous findings in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parisi, R., Symmons, D.P., Griffiths, C.E., Ashcroft, D.M.: Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J. Invest. Dermatol. 133(2), 377–385 (2013). doi:10.1038/jid.2012.339
de Korte, J., Sprangers, M.A., Mombers, F.M., Bos, J.D.: Quality of life in patients with psoriasis: a systematic literature review. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 9(2), 140–147 (2004). doi:10.1046/j.1087-0024.2003.09110.x
Ahn, C.S., Gustafson, C.J., Sandoval, L.F., Davis, S.A., Feldman, S.R.: Cost effectiveness of biologic therapies for plaque psoriasis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 14(4), 315–326 (2013). doi:10.1007/s40257-013-0030-z
Brodszky, V.: Systematic Review and Analysis of Evidences on Clinical Efficacy and Cost-Effectiveness of Biological Drugs for the Treatment of Prosiasis. Corvinus University of Budapest, Department of Health Economics, Budapest, Hungary (2013)
Bronsard, V., Paul, C., Prey, S., Puzenat, E., Gourraud, P.A., Aractingi, S., Aubin, F., Bagot, M., Cribier, B., Joly, P., Jullien, D., Le Maitre, M., Richard-Lallemand, M.A., Ortonne, J.P.: What are the best outcome measures for assessing quality of life in plaque type psoriasis? A systematic review of the literature. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 24(Suppl 2), 17–22 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03563.x
Lewis, V., Finlay, A.Y.: 10 years experience of the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 9(2), 169–180 (2004). doi:10.1111/j.1087-0024.2004.09113.x
Dakin, H.: Review of studies mapping from quality of life or clinical measures to EQ-5D: an online database. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 11, 151 (2013). doi:10.1186/1477-7525-11-151
Norlin, J.M., Steen Carlsson, K., Persson, U., Schmitt-Egenolf, M.: Analysis of three outcome measures in moderate to severe psoriasis: a registry-based study of 2450 patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 166(4), 797–802 (2012). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10778.x
Blome, C., Beikert, F.C., Rustenbach, S.J., Augustin, M.: Mapping DLQI on EQ-5D in psoriasis: transformation of skin-specific health-related quality of life into utilities. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 305(3), 197–204 (2013). doi:10.1007/s00403-012-1309-2
Currie, C.J., Conway, P.: Evaluation of the association between EQ5D utility and dermatology life quality index (DLQI) score in patients with psoriasis. Value Health 10(6), A470 (2007)
Hjortsberg, C., Bergman, A., Bjarnason, A., Heikkila, H., Hjelmgren, J., Svensson, A., Tennvall, G.R.: Are treatment satisfaction, quality of life, and self-assessed disease severity relevant parameters for patient registries? Experiences from Finnish and Swedish patients with psoriasis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 91(4), 409–414 (2011). doi:10.2340/00015555-1094
Dolan, P.: Modeling valuations for EuroQol health states. Med. Care 35(11), 1095–1108 (1997)
Finlay, A.Y., Khan, G.K.: Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI)—a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 19(3), 210–216 (1994)
Basra, M.K., Fenech, R., Gatt, R.M., Salek, M.S., Finlay, A.Y.: The Dermatology Life Quality Index 1994–2007: a comprehensive review of validation data and clinical results. Br. J. Dermatol. 159(5), 997–1035 (2008). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08832.x
Cohen, J.: A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 112, 155–159 (1992)
Balogh, O., Brodszky, V., Gulácsi, L., Herédi, E., Herszényi, K., Jókai, H., Kárpáti, S., Baji, P., Remenyik, É., Szegedi, A., Holló, P.: Cost-of-illness in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: a cross-sectional survey in Hungarian dermatological centres. Eur. J. Health Econ. (2014). doi:10.1007/s10198-014-0599-z
Mabuchi, T., Yamaoka, H., Kojima, T., Ikoma, N., Akasaka, E., Ozawa, A.: Psoriasis affects patient’s quality of life more seriously in female than in male in Japan. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 37(3), 84–88 (2012)
Nijsten, T., Meads, D.M., de Korte, J., Sampogna, F., Gelfand, J.M., Ongenae, K., Evers, A.W., Augustin, M.: Cross-cultural inequivalence of dermatology-specific health-related quality of life instruments in psoriasis patients. J. Invest. Dermatol. 127(10), 2315–2322 (2007). doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700875
Mattei, P.L., Corey, K.C., Kimball, A.B.: Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): the correlation between disease severity and psychological burden in patients treated with biological therapies. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. (2013). doi:10.1111/jdv.12106
Robinson, A., Kardos, M., Kimball, A.B.: Physician Global Assessment (PGA) and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI): why do both? A systematic analysis of randomized controlled trials of biologic agents for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 66(3), 369–375 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.01.022
Revicki, D.A., Jin, Y., Wilson, H.D., Chau, D., Viswanathan, H.N.: Reliability and validity of the psoriasis symptom inventory in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 25(1), 8–14 (2014). doi:10.3109/09546634.2013.769042
Dauden, E., Herrera, E., Puig, L., Sanchez-Carazo, J.L., Toribio, J., Caloto, M.T., Nocea, G., Roset, M., Lara, N.: Validation of a new tool to assess health-related quality of life in psoriasis: the PSO-LIFE questionnaire. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 10, 56 (2012). doi:10.1186/1477-7525-10-56
Brodszky, V., Pentek, M., Balint, P.V., Geher, P., Hajdu, O., Hodinka, L., Horvath, G., Koo, E., Polgar, A., Sesztak, M., Szanto, S., Ujfalussy, I., Gulacsi, L.: Comparison of the Psoriatic Arthritis Quality of Life (PsAQoL) questionnaire, the functional status (HAQ) and utility (EQ-5D) measures in psoriatic arthritis: results from a cross-sectional survey. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 39(4), 303–309 (2010). doi:10.3109/03009740903468982
Dauden, E., Herrera, E., Puig, L., Sanchez-Carazo, J.L., Toribio, J., Perulero, N.: Impact of active and stable psoriasis on health-related quality of life: the PSO-LIFE study. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 104(8), 685–693 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.adengl.2013.02.008
Pettey, A.A., Balkrishnan, R., Rapp, S.R., Fleischer, A.B., Feldman, S.R.: Patients with palmoplantar psoriasis have more physical disability and discomfort than patients with other forms of psoriasis: implications for clinical practice. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 49(2), 271–275 (2003)
Sampogna, F., Tabolli, S., Abeni, D.: Living with psoriasis: prevalence of shame, anger, worry, and problems in daily activities and social life. Acta Derm. Venereol. 92(3), 299–303 (2012). doi:10.2340/00015555-1273
Sampogna, F., Chren, M.M., Melchi, C.F., Pasquini, P., Tabolli, S., Abeni, D.: Age, gender, quality of life and psychological distress in patients hospitalized with psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 154(2), 325–331 (2006). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06909.x
Lesuis, N., Befrits, R., Nyberg, F., van Vollenhoven, R.F.: Gender and the treatment of immune-mediated chronic inflammatory diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and psoriasis: an observational study. BMC Med. 10, 82 (2012). doi:10.1186/1741-7015-10-82
Lu, G., Brazier, J.E., Ades, A.E.: Mapping from disease-specific to generic health-related quality-of-life scales: a common factor model. Value Health 16(1), 177–184 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jval.2012.07.003
Brazier, J.E., Yang, Y., Tsuchiya, A., Rowen, D.L.: A review of studies mapping (or cross walking) non-preference based measures of health to generic preference-based measures. Eur. J. Health Econ. 11(2), 215–225 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10198-009-0168-z
Shikiar, R., Willian, M.K., Okun, M.M., Thompson, C.S., Revicki, D.A.: The validity and responsiveness of three quality of life measures in the assessment of psoriasis patients: results of a phase II study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 4, 71 (2006). doi:10.1186/1477-7525-4-71
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by The Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (OTKA K108421, TÁMOP-4.2.2.A-11/1/KONV-2012-0023, TÁMOP-4.2.2.A-11/1/KONV-2012-0031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Emese Herédi and Fanni Rencz have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herédi, E., Rencz, F., Balogh, O. et al. Exploring the relationship between EQ-5D, DLQI and PASI, and mapping EQ-5D utilities: a cross-sectional study in psoriasis from Hungary. Eur J Health Econ 15 (Suppl 1), 111–119 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-014-0600-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-014-0600-x