Abstract
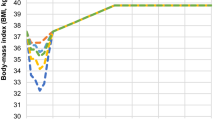
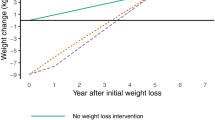
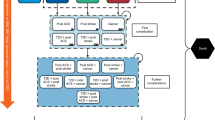
Obesity is associated with major health risks and a high economic burden impacting on health care systems. This study utilises the latest evidence from randomised clinical trials (RCTs) to explore and to assess the cost effectiveness of sibutramine in combination with diet and lifestyle advice compared to diet and lifestyle advice alone for the treatment of obese subjects without comorbidities at baseline in Germany. New evidence from recently published RCTs and post-marketing surveillance studies, including health economic data as well as quality of life (QoL) data, were used to model the long-term outcomes of weight management with sibutramine in German practice. German healthcare costs and new data from over 8,000 patients were analysed based on a recently published model. These new RCT data were used to model weight losses, proportion of responders to treatment, utilities by weight loss and variability in weight regain post-treatment. Costs and QoL benefits associated with weight loss (using SF-36 data from sibutramine trials), reduced incidence of coronary heart disease (using Framingham equations) and diabetes were used to estimate the cost per quality adjusted life year of sibutramine treatment. For 1,000 patients treated with sibutramine for 1 year, extrapolating outcomes over 4 further years, sibutramine is estimated to save 4.18 CHD events, 2.58 diabetes incident cases and give 51.5 more quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). The cost-utility analysis (CUA) estimates €13,706 per QALY gained. Results are sensitive to changes in weight loss, rate of weight regain and discounting rate. Although the non-pharmacological weight management programme in the comparator arm yielded higher weight losses than generally observed in clinical practice, these results demonstrate that additional sibutramine treatment is a cost effective therapy for an obese population without comorbidities in Germany. The CUA results are within the range generally accepted as cost effective and should be viewed as conservative when generalizing to settings offering standard non-pharmacological treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 8941: 253
Anderson KM, Wilson PW, Odell PM, Kannel WB (1991) An updated coronary risk profile. A statement for health professionals. Circulation 83: 356–362
Avenell A, Broom J, Brown TJ et al. (2004) Systematic review of the long-term effects and economic consequences of treatments for obesity and implications for health improvement. Health Technol Assess 8(21): 111–182
Bergmann KE, Mensink GB (1999) Anthropometric data and obesity (in German). Gesundheitswesen 61: 115–120
Brazier J, Roberts J, Tsuchiya A, Busschbach J (2004) A comparison of the EQ-5D and SF-6D across seven patient groups. Health Econ 13: 873–884
Brazier J, Usherwood T, Harper R, Thomas K (1998) Deriving a preference-based single index from the UK SF-36 Health Survey. J Clin Epidemiol 51: 1115–1128
Bundesministerium für Gesundheit und Soziale Sicherung und Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung. Body-Mass-Index – Prävalenzen. Bundes-Gesundheitssurvey 1998. Statistisches Bundesamt und Robert Koch-Institut . 2003. Electronic Citation
Büro für Informations Systeme (BIS) Christian de Haen (2004) Einheitlicher Bewertungsmassstab (EBM98). http://www e-bis de/ebm/Default htm
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ (2003) Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 348: 1625–1638
Esposito K, Pontillo A, Di Palo C et al. (2003) Effect of weight loss and lifestyle changes on vascular inflammatory markers in obese women: a randomized trial. JAMA 289: 1799–1804
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL (2002) Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 288: 1723–1727
Fontaine KR, Cheskin LJ, Barofsky I (1996) Health-related quality of life in obese persons seeking treatment. J Fam Pract 43: 265–270
Fontaine KR, Redden DT, Wang C et al. (2003) Years of life lost due to obesity. JAMA 289: 187–193
Hauner H, Meier M, Wendland G, Lauterbach K (2004) Weight reduction by sibutramine in obese subjects in primary care medicine: the S.A.T.study group. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 112: 201–207
Hazenberg BP (2000) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study of sibutramine in obese hypertensive patients. Cardiology 94: 152–158
Heitmann BL, Garby L (1999) Patterns of long-term weight changes in overweight developing Danish men and women aged between 30 and 60 years. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 23: 1074–1078
Hubert HB, Feinleib M, McNamara PM, Castelli WP (1983) Obesity as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: a 26-year follow-up of participants in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 67: 968–977
James WP, Astrup A, Finer N et al. (2000) Effect of sibutramine on weight maintenance after weight loss: a randomised trial. STORM Study Group. Sibutramine Trial of Obesity Reduction and Maintenance. Lancet 356: 2119–2125
Jönsson B (2002) Revealing the cost of Ttpe II diabetes in Europe. Diabetologia 45(7): S5–12
Kenchaiah S, Evans JC, Levy D et al. (2002) Obesity and the risk of heart failure. N Engl J Med 347: 305–313
Kind P, Dolan P, Gudex C, Williams A (1998) Variations in population health status: results from a United Kingdom national questionnaire survey. BMJ 316: 736–741
Klever-Deichert G, Hinzpeter B, Hunsche E, Lauterbach KW (1999) Costs of coronary heart diseases over the remaining life time in coronary heart disease cases – an analysis of the current status of coronary heart disease cases in Germany from the social perspective (in German). Z Kardiol 88: 991–1000
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE et al. (2002) Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med 346: 393–403
Kuntz KM, Tsevat J, Goldman L, Weinstein MC (1996) Cost-effectiveness of routine coronary angiography after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 94: 957–965
Kurscheid T, Lauterbach K (1998) The cost implications of obesity for health care and society. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 22 [Suppl 1]: S3–5
Narayan KM, Boyle JP, Thompson TJ et al. (2003) Lifetime risk for diabetes mellitus in the United States. JAMA 290: 1884–1890
Neter JE, Stam BE, Kok FJ et al. (2003) Influence of weight reduction on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hypertension 42: 878–884
Nisoli E, Carruba MO (2003) A benefit-risk assessment of sibutramine in the management of obesity. Drug Saf 26: 1027–1048
Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Johnson CL (2002) Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999–2000. JAMA 288: 1728–1732
Parker ED, Folsom AR (2003) Intentional weight loss and incidence of obesity-related cancers: the Iowa Women’s Health Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27: 1447–1452
Peeters A, Barendregt JJ, Willekens F et al. (2003) Obesity in adulthood and its consequences for life expectancy: a life-table analysis. Ann Intern Med 138: 24–32
Pickin DM, McCabe CJ, Ramsay LE et al. (1999) Cost effectiveness of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin) treatment related to the risk of coronary heart disease and cost of drug treatment. Heart 82: 325–332
Rexrode KM, Carey VJ, Hennekens CH et al. (1998) Abdominal adiposity and coronary heart disease in women. JAMA 280: 1843–1848
Rote Liste Service (2004) Rote Liste, Arzneimittelverzeichnis für Deutschland. http://www rote-liste de
Sander B, Bergemann R (2003) Economic burden of obesity and its complications in Germany. Eur J Health Econ 4: 248–253
Scholze J (2002) Sibutramine in clinical practice – a PMS-study with positive effects on blood pressure and metabolic parameters (in German). Dtsch Med Wochenschr 127: 606–610
Schwimmer JB, Burwinkle TM, Varni JW (2003) Health-related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. JAMA 289: 1813–1819
Seidell JC (2000) Obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes – a worldwide epidemic. Br J Nutr 83 [Suppl 1]: S5–8
Smith IG, Goulder MA (2001) Randomized placebo-controlled trial of long-term treatment with sibutramine in mild to moderate obesity. J Fam Pract 50: 505–512
Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG et al. (2001) Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 344: 1343–1350
Vasan RS (2003) Cardiac function and obesity. Heart 89: 1127–1129
Warren E, Brennan A, Akehurst R (2004) Cost-effectiveness of sibutramine in the treatment of obesity. Med Decis Making 24: 9–19
Williamson DF, Thompson TJ, Thun M et al. (2000) Intentional weight loss and mortality among overweight individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care 23: 1499–1504
Winkelmayer WC, Weinstein MC, Mittleman MA et al. (2002) Health economic evaluations: the special case of end-stage renal disease treatment. Med Decis Making 22: 417–430
Wirth A (2004) Anhaltende Gewichtsreduktion nach Beendigung der Adipositasbehandlung mit Sibutramin. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 129: 1002–1005
Wirth A, Krause J (2001) Long-term weight loss with sibutramine: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 286: 1331–1339
Zannad F, Gille B, Grentzinger A et al. (2002) Effects of sibutramine on ventricular dimensions and heart valves in obese patients during weight reduction. Am Heart J 144: 508–515
Acknowledgements
Financial support for this study was provided entirely by a grant from Abbott GmbH and Co. KG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brennan, A., Ara, R., Sterz, R. et al. Assessment of clinical and economic benefits of weight management with sibutramine in general practice in Germany. Eur J Health Econ 7, 276–284 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-006-0374-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-006-0374-x