Abstract
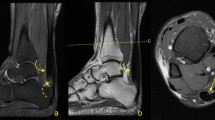
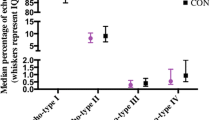
Previous research has shown that plantar fascia and Achilles tendon thickness is increased in diabetes. The aims of present study were to assess whether tendon changes can occur in the early stages of the disease and to evaluate the extent of the influence of body mass index (BMI). The study population included 51 recent-onset type II diabetic subjects, who were free from diabetic complications, divided according to BMI into three groups (normal weight, overweight, and obese). Eighteen non-diabetic, normal-weight subjects served as controls. Plantar fascia and Achilles tendon thickness was measured by means of sonography. The groups were well balanced for age and sex. In all the diabetic subjects, plantar fascia and Achilles tendon thickness was increased compared to the controls (p < 0.001, p = 0.01, p = 0.003, respectively). A significant relationship was found between plantar fascia thickness and BMI values (r = 0.749, p < 0.0001), while the correlation between BMI and Achilles tendon was weaker (r = 0.399, p = 0.004). This study shows that plantar fascia and Achilles tendon thickness is increased in the early stages of type II diabetes and that BMI is related more to plantar fascia than Achilles tendon thickness. Further longitudinal studies are needed to evaluate whether these early changes can overload the metatarsal heads and increase the stress transmitted to plantar soft tissues, thus representing an additional risk factor for foot ulcer development.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akturk M, Ozdemir A, Maral I, Yetkin I, Arslan M (2007) Evaluation of Achilles tendon thickening in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 115(2):92–96
Batista F, Nery C, Pinzur M, Monteiro AC, de Souza EF, Felippe FH, Alcântara MC, Campos RS (2008) Achilles tendinopathy in diabetes mellitus. Foot Ankle Int 29(5):498–501
Bolton NR, Smith KE, Pilgram TK, Mueller MJ, Bae KT (2005) Computed tomography to visualize and quantify the plantar aponeurosis and flexor hallucis longus tendon in the diabetic foot. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 20(5):540–546
Duffin AC, Lam A, Kidd R, Chan AK, Donaghue KC (2002) Ultrasonography of plantar soft tissues thickness in young people with diabetes. Diabet Med 19(12):1009–1113
Papanas N, Courcoutsakis N, Papatheodorou K, Daskalogiannakis G, Maltezos E, Prassopoulos P (2009) Achilles tendon volume in type 2 diabetic patients with or without peripheral neuropathy: MRI study. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 117(10):645–648
Giacomozzi C, D’Ambrogi E, Uccioli L, Macellari V (2005) Does the thickening of Achilles tendon and plantar fascia contribute to the alteration of diabetic foot loading? Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 20(5):532–539
D’Ambrogi E, Giurato L, D’Agostino MA, Giacomozzi C, Macellari V, Caselli A, Uccioli L (2003) Contribution of plantar fascia to the increased forefoot pressures in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 26(5):1525–1529
Association AD (2011) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 34(Suppl 1):S62–S69
Brach JS, Talkowski JB, Strotmeyer ES, Newman AB (2008) Diabetes mellitus and gait dysfunction: possible explanatory factors. Phys Ther 88(11):1365–1374
Bril V, Tomioka S, Buchanan RA, Perkins BA, mTCNS Study Group (2009) Reliability and validity of the modified Toronto Clinical Neuropathy Score in diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Diabet Med 26(3):240–246
Martinoli C, Bianchi S, Derchi LE (1999) Tendon and nerve sonography. Radiol Clin North Am 37(4):691–711, viii
Moraes do Carmo CC, Fonseca de Almeida Melão LI, Valle de Lemos Weber MF, Trudell D, Resnick D (2008) Anatomical features of plantar aponeurosis: cadaveric study using ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging. Skeletal Radiol 37(10):929–935
Heinemeier KM, Kjaer M (2011) In vivo investigation of tendon responses to mechanical loading. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 11(2):115–123
Parkinson J, Samiric T, Ilic MZ, Cook J, Handley CJ (2011) Involvement of proteoglycans in tendinopathy. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 11(2):86–93
Grant WP, Sullivan R, Sonenshine DE, Adam M, Slusser JH, Carson KA, Vinik AI (1997) Electron microscopic investigation of the effects of diabetes mellitus on the Achilles tendon. J Foot Ankle Surg 36(4):272–278
Abate M, Schiavone C, Pelotti P, Salini V (2011) Limited joint mobility (LJM) in elderly subjects with type II diabetes mellitus. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 53(2):135–140
Abate M, Schiavone C, Pelotti P, Salini V (2010) Limited joint mobility in diabetes and ageing: recent advances in pathogenesis and therapy. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 23(4):997–1003
Shoji T, Koyama H, Morioka T, Tanaka S, Kizu A, Motoyama K, Mori K, Fukumoto S, Shioi A, Shimogaito N, Takeuchi M, Yamamoto Y, Yonekura H, Yamamoto H, Nishizawa Y (2006) Receptor for advanced glycation end products is involved in impaired angiogenic response in diabetes. Diabetes 55(8):2245–2255
Alikhani Z, Alikhani M, Boyd CM, Nagao K, Trackman PC, Graves DT (2005) Advanced glycation end products enhance expression of pro-apoptotic genes and stimulate fibroblast apoptosis through cytoplasmic and mitochondrial pathways. J Biol Chem 280(13):12087–12095
Pascual Huerta J, García JM, Matamoros EC, Matamoros JC, Martínez TD (2008) Relationship of body mass index, ankle dorsiflexion, and foot pronation on plantar fascia thickness in healthy, asymptomatic subjects. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 98(5):379–385
Lago R, Gomez R, Otero M, Lago F, Gallego R, Dieguez C, Gomez-Reino JJ, Gualillo O (2008) A new player in cartilage homeostasis: adiponectin induces nitric oxide synthase type II and pro-inflammatory cytokines in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 16(9):1101–1109
D’Ambrogi E, Giacomozzi C, Macellari V, Uccioli L (2005) Abnormal foot function in diabetic patients: the altered onset of Windlass mechanism. Diabet Med 22(12):1713–1719
Rao S, Saltzman CL, Yack HJ (2010) Relationships between segmental foot mobility and plantar loading in individuals with and without diabetes and neuropathy. Gait Posture 31(2):251–255
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abate, M., Schiavone, C., Di Carlo, L. et al. Achilles tendon and plantar fascia in recently diagnosed type II diabetes: role of body mass index. Clin Rheumatol 31, 1109–1113 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-1955-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-1955-y