Abstract
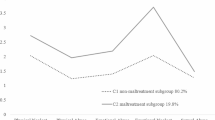
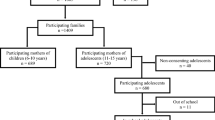
Child maltreatment has frequently been associated with impaired social skills and antisocial features, but there are still controversies about the effect of each type of maltreatment on social behaviour. The aim of this study was to compare the social functioning and psychopathic traits of maltreated adolescents (MTA) with a control group (CG) and to investigate what types of maltreatments and social skills were associated with psychopathic traits in both groups. The types and intensity of maltreatment were evaluated through the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire (CTQ) in 107 adolescents, divided into the MTA group (n = 66) and non-maltreated youths (n = 41), our CG. The Hare Psychopathy Checklist: Youth Version (PCL: YV) and a detailed inventory for evaluation of social skills in adolescents were also applied in all individuals. MTA presented more psychopathic traits than the CG, in all domains measured by PCL: YV, independently of IQ levels and the presence of psychiatric disorders. Interestingly, the groups did not differ significantly from each other on indicators of social skills. Multiple regression analysis revealed that emotional neglect was the only maltreatment subtype significantly associated with psychopathic traits, more specifically with the PCL: YV interpersonal factor (F1), and that some social skills (empathy, self-control and social confidence) were related to specific psychopathic factors. The results highlight that emotional neglect may be more detrimental to social behaviours than physical and sexual abuse, and that neglected children require more specific and careful attention.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (2006) Preventing child maltreatment: a guide to taking action and generating evidence. WHO Press, Genebra
Navalta CP, Polcari A, Webster DM, Boghossian A, Teicher MH (2006) Effects of childhood sexual abuse on neuropsychological and cognitive function in college women. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 18(1):45–53
De Oliveira PA, Scivoletto S, Cunha PJ (2010) Neuropsychological and neuroimaging studies associated with emotional stress during childhood and adolescence. Revista de Psiquiatria Clínica 37(6):260–269
Bücker J, Kapczinski F, Post R, Keila M, Ceresér KM, Szobot C, Yatham LN, Kapczinski NS, Kauer-Sant’Anna M (2012) Cognitive impairment in school-aged children with early trauma. Compr Psychiatry 53(6):758–764
Spann MN, Mayes LC, Kalmar JH, Guiney J, Womer FY, Pittman B, Mazure CM, Sinha R, Blumberg HP (2012) Childhood abuse and neglect and cognitive flexibility in adolescents. Child Neuropsychol 18(2):182–189
De Oliveira PA, Scarpari GK, Dos Santos B, Scivoletto S (2012) Intellectual deficits in Brazilian victimized children and adolescents: a psychosocial problem? Child Abuse Negl 36(7–8):608–610
Da Silva TF, Cunha PJ, Scivoletto S (2010) High rates of psychiatric disorders in a sample of Brazilian children and adolescents living under social vulnerability- urgent public policies implications. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria 32(2):195–196
Darwish D, Esquivel GB, Houtz JC, Alfonso VC (2001) Play and social skills in maltreated and non-maltreated preschoolers during peer interactions. Child Abuse Negl 25:13–31
Valentino K, Toth SL, Rogosch FA, Cicchetti D (2011) Mother–Child Play and Maltreatment: a longitudinal analysis of emerging social behavior from infancy to toddlerhood. Dev Psychol 47(5):1280–1294
Del Prette A, Del Prette ZAP (2009) Inventário de Habilidades Sociais para Adolescentes (IHSA-Del-Prette). Casa do Psicólogo, São Paulo
Fantuzzo JW, delGaudio Weiss A, Atkins M, Noone M (1998) A contextually relevant assessment of the impact of child maltreatment on the social competencies of low-income urban children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 66(12):1089
Kim J, Cicchetti D (2010) Longitudinal pathways linking child maltreatment, emotion regulation, peer relations and psychopathology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 51(6):706–716
Kinard EM (1999) Perceived social skills and social competence in maltreated children. Am J Orthopsychiatry 69(4):465–481
Alink LR, Cicchetti D, Kim J, Rogosch FA (2012) Longitudinal associations among child maltreatment, social functioning, and cortisol regulation. Dev Psychol 48(1):224–236
Cullerton-Sen C, Cassidy AR, Murray-Close D, Cicchetti D, Crick NR, Rogosch FA (2008) Childhood maltreatment and the development of relational and physical aggression: the importance of a gender-informed approach. Child Dev 79(6):1736–1751
Keyes KM, Eaton NR, Krueger RF, McLaughlin KA, Wall MM, Grant BF, Hasin DS (2012) Childhood maltreatment and the structure of common psychiatric disorders. Br J Psychiatry 200(2):107–115
Shaeffer A, Yates TM, Egeland BR (2009) The relation of emotional maltreatment to early adolescent competence: developmental processes in a prospective study. Child Abuse Negl 33(1):36–44
Bolger KE, Patterson C (2001) Developmental pathways from child maltreatment to peer rejection. Child Dev 72(2):549–568
Shonk SM, Cicchetti D (2001) Maltreatment, competency deficits, and risk for academic and behavioral maladjustment. Dev Psychol 37(1):3–17
McCabe KM, Lucchini SE, Hough RL, Yeh M, Hazen A (2005) The relation between violence exposure and conduct problems among adolescents: a prospective study. Am J Orthopsychiatry 75(4):575–584
Jonson-Reid M, Presnall N, Drake B, Fox L, Bierut L, Reich W, Kane P, Todd RD, Constantino JN (2010) Effects of child maltreatment and inherited liability on antisocial development: an official records study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49(4):321–332
Shi Z, Bureau JF, Easterbrooks MA, Zhao X, Lyons-Ruth K (2012) Childhood maltreatment and prospectively observed quality of early care as predictors of antisocial personality disorder features. Infant Ment Health J 33(1):55–96
Kolla NJ, Malcolm C, Attard S, Arevovich T, Blackwood N, Hodgins S (2013) Childhood maltreatment and aggressive behavior in violent offenders with psychopathy. Can J Psychiatry 58(8):487–494
Campbell MA, Porter S, Santor D (2004) Psychopathic traits in adolescent offenders: an evaluation of criminal history, clinical and psychosocial correlates. Behav Sci Law 22:23–47
Gao Y, Raine A, Chan F, Venables PH, Mednick SA (2010) Early maternal and paternal bonding, childhood physical abuse and adult psychopathic personality. Psychol Med 40:1007–1016
Graham N, Kimonis ER, Wasserman AL, Kline SM (2012) Associations among childhood abuse and psychopathy facets in male sexual offenders. Personal Disord 3(1):66–75
Jovev M, McKenzie T, Whittle S, Simmons JG, Allen NB, Chanen AM (2013) Temperament and maltreatment in the emergence of borderline and antisocial personality pathology during early adolescence. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 22(3):220–229
American Psychiatric Association (2002) DSM-IV-TR—manual diagnóstico e estatístico de transtornos mentais, 4th edn. Artmed, Porto Alegre
Hare RD, Neumann CS (2005) The structure of psychopathy. Curr Psychiatr Rep 7:1–32
Neumann CS, Kosson DS, Forth AE, Hare RD (2006) Factor structure of The Hare Psychopathy Checklist: Youth Version (PCL: YV) in incarcerated adolescents. Psychol Assess 18(2):142–154
Karpman B (1941) On the need of separating psychopathy into two distinct clinical types: the symptomatic and the idiopathic. J Crim Psychopathol 3:112–137
Poythress NG, Edens JF, Landfield K, Lilienfeld SO, Skeem JL, Douglas KS (2008) A critique of Carver and White’s (1994) behavioral inhibition scale (BIS) for investigating Lykken’s (1995) theory of primary psychopathy. Personal Individ Differ 45(4):269–275
Topitzes J, Mersky JP, Reynolds AJ (2012) From child maltreatment to violent offending: an examination of mixed-gender and gender-specific models. J Interpers Violence 27(12):2322–2347
Scivoletto S, da Silva TS, Rosenheck RA (2011) Child psychiatry takes to the streets: a developmental partnership between a university institute and children and adolescents from the streets of Sao Paulo, Brazil. Child Abuse Negl 35:89–95
Wechsler D (2002) WISC-III: Escala de Inteligência Wechsler para Crianças: Manual; Adaptação e Padronização de uma amostra Brasileira, 1a edn. Vera Lucia Marques de Figueiredo. São Paulo, Casa do Psicólogo
Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, Rao U, Flynn C, Moreci O, Williamson D, Ryan N (1997) Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): initial reliability and validity data. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36(7):980–988
Bernstein D, Fink L (1998) Childhood trauma questionnaire: a retrospective self-report. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Grassi-Oliveira R, Stein LM, Pezzi JC (2006) Translation and content validation of the childhood trauma questionnaire into Portuguese language. Revista de Saúde Pública 40(2):249–255
Forth A, Kosson DS, Hare RD (2003) The Psychopathy Checklist: Youth Version (PCL: YV). Multi-Health Systems, Toronto
De Almeida Rocca CC, de Macedo-Soares MB, Gorenstein C, Tamada RS, Issler CK, Dias RS, Schwartzmann AM, Lafer B (2008) Social dysfunction in bipolar disorder: pilot study. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 42(8):686–692
Suzigan LZ, de Paiva e Silva RB, Guerra-Júnior G, Marini SH, Maciel-Guerra AT (2011) Social skills in women with turner syndrome. Scand J Psychol 52(5):440–447
Del Prette, ZA, Teodoro M, Del Prette A (2014). Social skills of adolescents: convergent validity between IHSA-Del-Prette and MESSY. Estud. psicol. (Campinas) [online] 31 (1):15-24
Allen JP, Marsh P, McFarland C, McElhaney KB, Land DJ, Jodl KM, Peck S (2002) Attachment and autonomy as predictors of the development of social skills and delinquency during mid adolescence. J Consult Clin Psychol 70(1):56–66
Calkins SD, Keane SP (2009) Developmental origins of early antisocial behavior. Dev Psychopathol 21(4):1095–1109
Lockwood PL, Sebastian CL, McCrory EJ, Hyde ZH, Gu X, De Brito SA, Viding E (2013) Association of callous traits with reduced neural response to others’ pain in children with conduct problems. Curr Biol 23(10):901–905
Marsh AA, Finger EC, Fowler KA, Adalio CJ, Jurkowitz IT, Schechter JC, Pine DS, Decety J, Blair RJ (2013) Empathic responsiveness in amygdala and anterior cingulate cortex in youths with psychopathic traits. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 54(8):900–910
Moffitt TE, Arseneault L, Belsky D, Dickson N, Hancox RJ, Harrington HL, Houts R, Poulton R, Roberts BW, Ross S, Sears MR, Thomson WM, Caspi A (2011) A gradient of childhood self-control predicts health, wealth, and public safety. PNAS 108(7):2693–2698
Cicchetti D, Rogosch FA, Thibodeau E (2012) The effects of child maltreatment on early signs of antisocial behavior: genetic moderation by tryptophan hydroxylase, serotonin transporter, and monoamine oxidase-A-genes. Dev Psychopathol 24(3):907–928
Marshall E (2014) An experiment in zero parenting. Science 345:752–754
Bruns EJ, Pullmann MD, Weathers ES, Wirschem ML, Murphy JK (2012) Effects of a multidisciplinary family treatment drug court on child and family outcomes: results of a quasi-experimental study. Child Maltreatment 17(3):218–230
Thomas R, Zimmer-Gembeck MJ (2012) Parent-child interaction therapy: an evidence-based treatment for child maltreatment. Child Maltreatment 17(3):253–266
Lanier P, Kohl PL, Benz J, Swinger D, Drake B (2014) Preventing maltreatment with a community-based implementation of parent–child interaction therapy. J Child Fam Stud 23(2):449–460
Donohue B, Azrin NH, Bradshaw K, Van Hasselt VB, Cross CL, Urgelles J, Romero V, Hill HH, Allen DN (2014) A controlled evaluation of family behavior therapy in concurrent child neglect and drug abuse. J Consult Clin Psychol 82(4):706–720
Byrne S, Rodrigo MJ, Máiquez ML (2014) Patterns of individual change in a parenting program for child maltreatment and their relation to family and professional environments. Child Abuse Negl 38(3):457–467
Allin H, Wathen CN, MacMillan H (2005) Treatment of child neglect: a systematic review. Can J Psychiatry 50(8):497–504
Pane HT, White RS, Nadorff MR, Grills-Taquechel A, Stanley MA (2013) Multisystemic therapy for child non-externalizing psychological and health problems: a preliminary review. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 16(1):81–99
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all LIM-21 and Equilibrium Program’s staff and participants. This study was funded by FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo) Grants numbers 2010/15604-0 (Dr. Paulo Jannuzzi Cunha), 2010/15786-1 (Dr. Geraldo F. Busatto) and 2010/18374-6, 2011/19185-5 (Dra. Sandra Scivoletto). We also thank São Paulo Municipality for the support to the Equilibrium Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ometto, M., de Oliveira, P.A., Milioni, A.L. et al. Social skills and psychopathic traits in maltreated adolescents. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 25, 397–405 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-015-0744-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-015-0744-y