Abstract
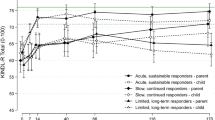
Quality of life (QoL) is a well-established outcome measure. In contrast to adult obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), little is known about the effects of treatment on QoL in children with OCD. This study aimed to assess QoL after cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) in children and adolescents with OCD compared with the general population and to explore factors associated with potential changes in QoL after treatment. QoL was assessed in 135 children and adolescents (ages 7–17; mean 13 [SD 2.7] years; 48.1 % female) before and after 14 CBT sessions, using self-report and a caregivers proxy report of the Questionnaire for Measuring Health-related Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents (KINDL-R). QoL was compared with an age- and gender-matched sample from the general population. Before treatment, QoL was markedly lower in children with OCD compared with the general population. QoL improved significantly in CBT responders (mean score change 7.4), to the same range as QoL in the general population. Non-responders reported no QoL changes after treatment, except for one patient. Comorbidity, family accommodation and psychosocial functioning were not associated with changes in QoL after treatment. To our knowledge, this is the first study of the changes in QoL after treatment of paediatric OCD. The assessment of QoL beyond symptoms and function in children with OCD has been shown to be reliable and informative. The results of this study support the application of QoL assessment as an additional measure of treatment outcome in children and adolescents with OCD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heyman I, Fombonne E, Simmons H, Ford T, Meltzer H, Goodman R (2001) Prevalence of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the British nationwide survey of child mental health. Br J Psychiatry 179(4):324–329. doi:10.1192/bjp.179.4.324
Valleni-Basile LA, Garrison CZ, Jackson KL, Waller JL, McKeown RE, Addy CL, Cuffe SP (1994) Frequency of obsessive-compulsive disorder in a community sample of young adolescents. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 33(6):782–791. doi:10.1097/00004583-199407000-00002
Verhulst FC, van der Ende J, Ferdinand RF, Kasius MC (1997) The prevalence of DSM-III-R diagnoses in a national sample of Dutch adolescents. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54(4):329–336
Micali N, Heyman I, Perez M, Hilton K, Nakatani E, Turner C, Mataix-Cols D (2010) Long-term outcomes of obsessive-compulsive disorder: follow-up of 142 children and adolescents. Br J Psychiatry 197(2):128–134. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.109.075317
Skoog G, Skoog I (1999) A 40-year follow-up of patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56(2):121–127
Stewart SE, Geller DA, Jenike M, Pauls D, Shaw D, Mullin B, Faraone SV (2004) Long-term outcome of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder: a meta-analysis and qualitative review of the literature. Acta Psychiatr Scand 110(1):4–13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2004.00302.x
Hanna GL (1995) Demographic and clinical feature of obsessive-compulsive disorder in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 34:19–27
Ivarsson T, Melin K, Wallin L (2008) Categorical and dimensional aspects of co-morbidity in obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 17(1):20–31. doi:10.1007/s00787-007-0626-z
Bejerot S, Nylander L, Lindstrom E (2001) Autistic traits in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nord J Psychiatry 55(3):169–176. doi:10.1080/08039480152036047
Cath DC, Ran N, Smit JH, van Balkom AJ, Comijs HC (2008) Symptom overlap between autism spectrum disorder, generalized social anxiety disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder in adults: a preliminary case-controlled study. Psychopathology 41(2):101–110. doi:10.1159/000111555
LaSalle VH, Cromer KR, Nelson KN, Kazuba D, Justement L, Murphy DL (2004) Diagnostic interview assessed neuropsychiatric disorder comorbidity in 334 individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Depress Anxiety 19(3):163–173. doi:10.1002/da.20009
Ivarsson T, Melin K (2008) Autism spectrum traits in children and adolescents with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). J Anxiety Disord 22(6):969–978. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.10.003
AACAP (2012) Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 51(1):98–113. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.09.019
Abramowitz JS, Whiteside SP, Deacon BJ (2005) The effectiveness of treatment for pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder: A meta-analysis. Behavior Therapy. Behavior Therapy 36:55–63. doi:10.1016/s0005-789428052980054-1
NICE (2005) Obsessive-compulsive disorder: core interventions in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder and body dysmorphic disorder. Clinical Guideline 31
Watson HJ, Rees CS (2008) Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled treatment trials for pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 49(5):489–498. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01875.x
Luhmann M, Hofmann W, Eid M, Lucas RE (2012) Subjective well-being and adaptation to life events: a meta-analysis. J Pers Soc Psychol 102(3):592–615. doi:10.1037/a0025948
Koot HM (2001) The study of quality of life: concepts and methods. In: Koot HM, Wallander JL (eds) Quality of Life in children and adolescent illness: Concepts, methods, and findings. Brunner-Routledge, East Essex, UK
EMEA (2004) Reflection paper on the regulatory guidance for the use of health-related quality of life (HRQL) measures in the evaluation of medicinal products European Medicines Agency London
FDA (2006) Guidance for industry: patient-reported outcome measures: use in medical product development to support labeling claims: draft guidance. Health Qual Life Outcomes 4:79. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-4-79
Eisen JL, Mancebo MA, Pinto A, Coles ME, Pagano ME, Stout R, Rasmussen SA (2006) Impact of obsessive-compulsive disorder on quality of life. Compr Psychiatry 47(4):270–275. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2005.11.006
Hollander E, Stein DJ, Fineberg NA, Marteau F, Legault M (2010) Quality of life outcomes in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: relationship to treatment response and symptom relapse. J Clin Psychiatry 71(6):784–792. doi:10.4088/JCP.09m05911blu
Koran LM (2000) Quality of life in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am 23(3):509–517
Macy AS, Theo JN, Kaufmann SC, Ghazzaoui RB, Pawlowski PA, Fakhry HI, Cassmassi BJ, IsHak WW (2013) Quality of life in obsessive compulsive disorder. CNS Spectr 18(1):21–33. doi:10.1017/S1092852912000697
Moritz S (2008) A review on quality of life and depression in obsessive-compulsive disorder. CNS Spectr 13(9 Suppl 14):16–22
Subramaniam M, Soh P, Vaingankar JA, Picco L, Chong SA (2013) Quality of life in obsessive-compulsive disorder: impact of the disorder and of treatment. CNS drugs 27(5):367–383. doi:10.1007/s40263-013-0056-z
Diefenbach GJ, Abramowitz JS, Norberg MM, Tolin DF (2007) Changes in quality of life following cognitive-behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Behav Res Ther 45(12):3060–3068. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2007.04.014
Moritz S, Rufer M, Fricke S, Karow A, Morfeld M, Jelinek L, Jacobsen D (2005) Quality of life in obsessive-compulsive disorder before and after treatment. Compr Psychiatry 46(6):453–459. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2005.04.002
Hertenstein E, Thiel N, Herbst N, Freyer T, Nissen C, Kulz AK, Voderholzer U (2013) Quality of life changes following inpatient and outpatient treatment in obsessive-compulsive disorder: a study with 12 months follow-up. Ann Gen Psychiatry 12(1):4. doi:10.1186/1744-859X-12-4
Tenney NH, Denys DA, van Megen HJ, Glas G, Westenberg HG (2003) Effect of a pharmacological intervention on quality of life in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 18(1):29–33. doi:10.1097/01.yic.0000047752.19914.a8
Arbuckle R, Abetz-Webb L (2013) “Not just little adults”: qualitative methods to support the development of pediatric patient-reported outcomes. Patient 6(3):143–159. doi:10.1007/s40271-013-0022-3
Jozefiak T (2014) Can we trust in parents’ report about their childrens well-being? In: Holte A et. al. The psychology of child well-being. In: Asher Ben-Arieh FC, Ivar Frønes, Jill E. Korbin (ed) Handbook of child well-being. Theories, methods and policies in global perspective. Springer Netherlands, pp 555–631
Sattoe JN, van Staa A, Moll HA (2012) The proxy problem anatomized: child-parent disagreement in health related quality of life reports of chronically ill adolescents. Health Qual Life Outcomes 10:10. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-10-10
Upton P, Lawford J, Eiser C (2008) Parent-child agreement across child health-related quality of life instruments: a review of the literature. Qual Life Res 17(6):895–913. doi:10.1007/s11136-008-9350-5
Casas F in A. Holte MMB, Bekkhus M, Borge AIH, Bowes L, Casas F, Friborg O, Grinde B, Headey B, Jozefiak T, Lekhal R, Marks N, Muffels R, Nes RB, Røysamb E, Thimm J, Torgersen S, Trommsdorff G, Veenhoven R, Vittersø J, Waaktaar T, Wagner GG, Wang CE, Wold B, Zachrisson HD (2014) Psychology of child well-being In: Ben-Arieh A, Casas F, Frønes I, Korbin JE (eds) Handbook of child well-being: theories, metods and policies in global perspective. Springer, pp 555–632
Palermo SD, Bloch MH, Craiglow B, Landeros-Weisenberger A, Dombrowski PA, Panza K, Smith ME, Peterson BS, Leckman JF (2011) Predictors of early adulthood quality of life in children with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 46(4):291–297. doi:10.1007/s00127-010-0194-2
Lack CW, Storch EA, Keeley ML, Geffken GR, Ricketts ED, Murphy TK, Goodman WK (2009) Quality of life in children and adolescents with obsessive-compulsive disorder: base rates, parent-child agreement, and clinical correlates. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 44(11):935–942. doi:10.1007/s00127-009-0013-9
Weidle B, Ivarsson T, Thomsen PH, Jozefiak T (2014) Quality of life in children with OCD with and without comorbidity. Health Qual Life Outcomes 12:152. doi:10.1186/s12955-014-0152-x
Ivarsson T, Thomsen PH, Dahl K, Valderhaug R, Weidle B, Nissen JB, Englyst I, Christensen K, Torp NC, Melin K (2010) The rationale and some features of the Nordic Long-term OCD Treatment Study (NordLOTS) in childhood and adolescence. Child Youth Care Forum 39(2):91–99
Thomsen PH, Torp NC, Dahl K, Christensen K, Englyst I, Melin KH, Nissen JB, Hybel KA, Valderhaug R, Weidle B, Skarphedinsson G, von Bahr PL, Ivarsson T (2013) The Nordic long-term OCD treatment study (NordLOTS): rationale, design, and methods. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health 7(1):41. doi:10.1186/1753-2000-7-41
Torp NC, Dahl K, Skarphedinsson G, Thomsen PH, Valderhaug R, Weidle B, Melin K, Hybel K, Nissen JB, Lenhard F, Wentzel-Larsen T, Franklin ME, Ivarsson T (2014) Effectiveness of cognitive behavior treatment for pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder: acute outcomes from the nordic long-term OCD Treatment Study (NordLOTS). Behav Res Ther Forthcom. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2014.11.005
March JS, Mulle K, Foa E, Kozak MJ (2000) Treatment of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder cognitive behavior therapy treatment manual
Piacentini J, Langley A, Roblek T (2007) Cognitive behavioral treatment of childhood OCD: it’s only a false alarm : therapist guide. Oxford University Press, New York
Hollingshead AB (2011) Four factor index of social status Yale. J Sociol 8:21–52
APA (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., text rev.). American Psychiatric Association, Washington. doi:10.1176/appi.books.9780890423349
Jozefiak T, Larsson B, Wichstrom L (2009) Changes in quality of life among Norwegian school children: a six-month follow-up study. Health Qual Life Outcomes 7:7. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-7-7
Jozefiak T, Larsson B, Wichstrom L, Mattejat F, Ravens-Sieberer U (2008) Quality of life as reported by school children and their parents: a cross-sectional survey. Health Qual Life Outcomes 6:34. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-6-34
Ravens-Sieberer U, Bullinger M (2000) KINDL-R. Questionnaire for measuring health-related quality of life in children and adolescents—Revised version 2000. http://kindl.org/english/manual/
Bullinger M, Brutt AL, Erhart M, Ravens-Sieberer U, Group BS (2008) Psychometric properties of the KINDL-R questionnaire: results of the BELLA study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 17(Suppl 1):125–132. doi:10.1007/s00787-008-1014-z
Solans M, Pane S, Estrada MD, Serra-Sutton V, Berra S, Herdman M, Alonso J, Rajmil L (2008) Health-related quality of life measurement in children and adolescents: a systematic review of generic and disease-specific instruments. Value Health 11(4):742–764. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00293.x
Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, Rao U, Flynn C, Moreci P, Williamson D, Ryan N (1997) Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): initial reliability and validity data. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36(7):980–988. doi:10.1097/00004583-199707000-00021
Axelson D, Birmaher B, Zelazny J, Kaufman J, Gill MK (2009) Kiddie-sads-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL) 2009 Working Draft. Department of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh. http://psychiatry.pitt.edu/research/tools-research/ksads-pl-2009-working-draft
Goodman WK, Price LH, Rasmussen SA, Mazure C, Fleischmann RL, Hill CL, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1989) The Yale-Brown obsessive compulsive scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46(11):1006–1011
Scahill L, Riddle MA, McSwiggin-Hardin M, Ort SI, King RA, Goodman WK, Cicchetti D, Leckman JF (1997) Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale: reliability and validity. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36(6):844–852. doi:10.1097/00004583-199706000-00023
Storch EA, Murphy TK, Geffken GR, Soto O, Sajid M, Allen P, Roberti JW, Killiany EM, Goodman WK (2004) Psychometric evaluation of the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale. Psychiatry Res 129(1):91–98. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2004.06.009
Calvocoressi L, Mazure CM, Kasl SV, Skolnick J, Fisk D, Vegso SJ, Van Noppen BL, Price LH (1999) Family accommodation of obsessive-compulsive symptoms: Instrument development and assessment of family behavior. J Nerv Ment Dis 187(10):636–642. doi:10.1097/00005053-199910000-00008
Geffken GR, Storch EA, Duke DC, Monaco L, Lewin AB, Goodman WK (2006) Hope and coping in family members of patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Anxiety Disord 20(5):614–629. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2005.07.001
Storch EA, Geffken GR, Merlo LJ, Jacob ML, Murphy TK, Goodman WK, Larson MJ, Fernandez M, Grabill K (2007) Family accommodation in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Clinic Child Adolesc Psychol 36(2):207–216
Shaffer D, Gould MS, Brasic J, Ambrosini P, Fisher P, Bird H, Aluwahlia S (1983) A Children’s Global Assessment Scale (CGAS). Arch Gen Psychiatry 40(11):1228–1231
Bird HR, Canino G, Rubio-Stipec M, Ribera JC (1987) Further measures of the psychometric properties of the Children’s Global Assessment Scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry 44(9):821–824
Rey JM, Starling J, Wever C, Dossetor DR, Plapp JM (1995) Inter-rater reliability of global assessment of functioning in a clinical setting. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 36(5):787–792. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1995.tb01329.x
Vivan Ade S, Rodrigues L, Wendt G, Bicca MG, Cordioli AV (2013) Quality of life in adolescents with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Revista brasileira de psiquiatria 35(4):369–374. doi:10.1590/1516-4446-2013-1135
Huppert JD, Simpson HB, Nissenson KJ, Liebowitz MR, Foa EB (2009) Quality of life and functional impairment in obsessive-compulsive disorder: a comparison of patients with and without comorbidity, patients in remission, and healthy controls. Depress Anxiety 26(1):39–45. doi:10.1002/da.20506
Davis E, Davies B, Waters E, Priest N (2008) The relationship between proxy reported health-related quality of life and parental distress: gender differences. Child Care Health Dev 34(6):830–837. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2214.2008.00866.x
Pallanti S, Hollander E, Bienstock C, Koran L, Leckman J, Marazziti D, Pato M, Stein D, Zohar J (2002) Treatment non-response in OCD: methodological issues and operational definitions. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 5(2):181–191. doi:10.1017/S1461145702002900
Tolin DF, Abramowitz JS, Diefenbach GJ (2005) Defining response in clinical trials for obsessive-compulsive disorder: a signal detection analysis of the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale. J Clin Psychiatry 66(12):1549–1557
Franklin ME, Sapyta J, Freeman JB, Khanna M, Compton S, Almirall D, Moore P, Choate-Summers M, Garcia A, Edson AL, Foa EB, March JS (2011) Cognitive behavior therapy augmentation of pharmacotherapy in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder: the pediatric OCD treatment study II (POTS II) randomized controlled trial. JAMA 306(11):1224–1232. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.1344
Bystritsky A, Liberman RP, Hwang S, Wallace CJ, Vapnik T, Maindment K, Saxena S (2001) Social functioning and quality of life comparisons between obsessive-compulsive and schizophrenic disorders. Depress Anxiety 14(4):214–218
Klassen AF, Miller A, Fine S (2004) Health-related quality of life in children and adolescents who have a diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 114(5):e541–e547. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-0844
Storch EA, Merlo LJ, Lack C, Milsom VA, Geffken GR, Goodman WK, Murphy TK (2007) Quality of life in youth with Tourette’s syndrome and chronic tic disorder. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 36(2):217–227. doi:10.1080/15374410701279545
Bernard BA, Stebbins GT, Siegel S, Schultz TM, Hays C, Morrissey MJ, Leurgans S, Goetz CG (2009) Determinants of quality of life in children with Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Mov Disord 24(7):1070–1073. doi:10.1002/mds.22487
Cutler D, Murphy T, Gilmour J, Heyman I (2009) The quality of life of young people with Tourette syndrome. Child Care Health Dev 35(4):496–504. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2214.2009.00983.x
Eddy CM, Cavanna AE, Gulisano M, Agodi A, Barchitta M, Cali P, Robertson MM, Rizzo R (2011) Clinical correlates of quality of life in Tourette syndrome. Mov Disord 26(4):735–738. doi:10.1002/mds.23434
Eddy CM, Rizzo R, Gulisano M, Agodi A, Barchitta M, Cali P, Robertson MM, Cavanna AE (2011) Quality of life in young people with Tourette syndrome: a controlled study. J Neurol 258(2):291–301. doi:10.1007/s00415-010-5754-6
Eddy CM, Cavanna AE, Gulisano M, Cali P, Robertson MM, Rizzo R (2012) The effects of comorbid obsessive-compulsive disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder on quality of life in tourette syndrome. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 24(4):458–462. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.11080181
Storch EA, Lewin AB, Farrell L, Aldea MA, Reid J, Geffken GR, Murphy TK (2010) Does cognitive-behavioral therapy response among adults with obsessive-compulsive disorder differ as a function of certain comorbidities? J Anxiety Disord 24(6):547–552. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2010.03.013
Lack CW, Yardley HL, Dalaya A (2013) Treatment of multiple co-morbid anxiety disorders. In: Storch EA, McKay D (eds) Handbook of treating variants and complications in anxiety disorders. Springer, New York
Storch EA, Merlo LJ, Larson MJ, Geffken GR, Lehmkuhl HD, Jacob ML, Murphy TK, Goodman WK (2008) Impact of comorbidity on cognitive-behavioral therapy response in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 47(5):583–592. doi:10.1097/CHI.0b013e31816774b1
Kugler BB, Lewin AB, Phares V, Geffken GR, Murphy TK, Storch EA (2013) Quality of life in obsessive-compulsive disorder: the role of mediating variables. Psychiatry Res 206(1):43–49. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2012.10.006
Hauschildt M, Jelinek L, Randjbar S, Hottenrott B, Moritz S (2010) Generic and illness-specific quality of life in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Behav Cogn Psychother 38(4):417–436. doi:10.1017/s1352465810000275
Cavanna AE, Luoni C, Selvini C, Blangiardo R, Eddy CM, Silvestri PR, Cali PV, Gagliardi E, Balottin U, Cardona F, Rizzo R, Termine C (2013) Disease-specific quality of life in young patients with tourette syndrome. Pediatr Neurol 48(2):111–114. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2012.10.006
Acknowledgments
This study was funded with support by the Norwegian Research Council and St. Olav’s Hospital, Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Trondheim. We wish to thank all patients, parents, and the participating clinics for their contribution to the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics
The study was approved by the Regional Committees for Medical and Health Research Ethics in Denmark, Norway and Sweden. All parents gave written informed consent and the permission for their children to participate before inclusion in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weidle, B., Ivarsson, T., Thomsen, P.H. et al. Quality of life in children with OCD before and after treatment. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 24, 1061–1074 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-014-0659-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-014-0659-z