Abstract
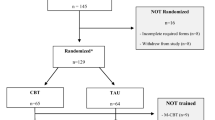
This observational study examined the changes during inpatient cognitive-behavioral treatment (CBT) of adolescents with chronic anxious-depressive school absenteeism with or without comorbid disruptive symptoms. 147 adolescents (aged 12–18 years) with a specific phobia or other anxiety disorder or a depressive episode or a mixed disorder of conduct and emotions and who had completely ceased to attend school or showed irregular school attendance underwent an inpatient cognitive-behavioral treatment. A further 16 patients aborted the treatment during the first day and were not included in the analyses. The treatment was manual guided and also included parents. Assessments were made pre-inpatient treatment, immediately post-inpatient treatment and at 2-month follow-up. School attendance was the primary outcome variable and secondary outcomes were composite scores of a range of adolescent- and parent-rated mental health problems. Overall, results show a considerable decline of school absenteeism and mental health problems during treatment and subsequent follow-up. Continuous school attendance was achieved by 87.1% of the sample at the end of inpatient treatment and by 82.3% at 2-month follow-up. Comorbid symptoms of anxiety, depression, disruptive and insufficient learning behavior were significantly reduced from pre to follow-up, with effect sizes for the composite scores ranging from 0.44 to 1.15 (p < 0.001). This large observational study in adolescents with school absenteeism and a mixture of emotional and disruptive symptoms is the first to show the benefits of inpatient therapy that included cognitive-behavioral therapy and access to a special school with expertise on teaching children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders. The results must be interpreted conservatively because of the lack of a control condition.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, Text Revision: DSM-IV-TR, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Arbeitsgruppe Deutsche Child Behavior Checklist (1998) Elternfragebogen über das Verhalten von Kindern und Jugendlichen: Deutsche Bearbeitung der Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL/4-18). Arbeitsgruppe Kinder-, Jugend- und Familiendiagnostik (KJFD), Köln
Arbeitsgruppe Deutsche Child Behavior Checklist (1998) Fragebogen für Jugendliche: Deutsche Bearbeitung der Youth Self Report Form der Child Behavior Checklist (YSR). [German version of the Youth self report form of the Child Behavior Checklist (YSR)]. Arbeitsgruppe Kinder-, Jugend- und Familiendiagnostik (KJFD), Cologne
Blagg NR, Yule W (1984) The behavioural treatment of school refusal—a comparative study. Behav Res Ther 22:119–127
Carr A (1999) The handbook of child and adolescent psychology. A contextual approach. Routledge, London
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Doepfner M, Berner W, Schmeck K, Lehmkuhl G, Poustka F (1995) Internal consistencies and validity of the CBCL and the TRF in a German sample: a cross-cultural comparison. In: Sergeant J (ed) Eunethydis: European approaches to hyperkinetic disorder. Fotorator, Egg, pp 51–81
Doepfner M, Goertz-Dorten A, Lehmkuhl G (2008) Diagnostik-System für psychische Störungen im Kindes- und Jugendalter nach ICD-10 und DSM-IV DISYPS-2 [Diagnostic system for mental disorders in child and adolescents according to ICD-10 and DSM-IV DISYPS-2]. Huber, Bern
Doepfner M, Lehmkuhl G (2002) DISYPS-KJ. Diagnostik-System für psychische Störungen im Kindes- und Jugendalter nach ICD-10 und DSM-IV [DISYPS-KJ. Diagnostic system for mental disorders in child and adolescents according to ICD-10 and DSM-IV]. Huber, Bern
Doepfner M, Schmeck K, Berner W, Lehmkuhl G, Poustka F (1994) Zur Reliabilität und faktoriellen Validität der Child Behavior Checklist: Eine Analyse in einer klinischen und einer Feldstichprobe [Reliability and factorial validity of the Child Behavior Checklist: an analysis of a clinical sample and a field sample]. Z Kinder Jugendpsychiatr Psychother 22:189–205
Doepfner M, Schnabel M, Goletz H, Ollendick TH (2006) Phobiefragebogen für Kinder und Jugendliche PHOKI [Phobia questionnaire for children and adolescents]. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Doepfner M, Walter D (2006) Schulverweigerung [School refusal]. In: Steinhausen HC (ed) Schule und psychische Störungen [School and mental health problems]. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart, pp 218–235
Egger HL, Costello EJ, Angold A (2003) School refusal and psychiatric disorders: a community study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42:797–807
Goertz-Dorten A, Doepfner M (2008) Diagnose-Checklisten aus dem Diagnostik-System für Psychische Störungen im Kindes- undJugendalter (DISYPS-II)—Gütekriterien und klinische Anwendung [Diagnostic-checklists of the diagnostic system for mental disorders in childhood and adolescence (DISYPS-II)—psychometric criteria and clinical application]. Klinische Diagn Eval 1:378–394
Ihle W, Jahnke D, Esser G (2003) Cognitive behavior therapy treatment approaches in non-dyssocial school refusal: school phobia and school anxiety. Prax Kinderpsychol Kinderpsychiatr 52:409–424
Kearney CA (2008) School absenteeism and school refusal behavior in youth: a contemporary review. Clin Psychol Rev 28:451–471
Kearney CA, Albano AM (2004) The functional profiles of school refusal behavior. Diagnostic aspects. Behav Modif 28:147–161
Kearney CA, Albano AM (2003) When children refuse school: a cognitive-behavioral therapy approach-parent workbook. Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Keller G, Thiel RD (1998) Lern- und Arbeitsverhaltensinventar LAVI [Learning and achievement behavior inventory]. Hogrefe, Göttingen
King N, Tonge BJ, Heyne D, Ollendick TH (2000) Research on the cognitive-behavioral treatment of school refusal: a review and recommendations. Clin Psychol Rev 20:495–507
King NJ, Bernstein GA (2001) School refusal in children and adolescents: a review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40:197–205
King NJ, Tonge BJ, Heyne D, Pritchard M, Rollings S, Young D, Myerson N, Ollendick TH (1998) Cognitive-behavioral treatment of school-refusing children: a controlled evaluation. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 37:395–403
Last CG, Hansen C, Franco N (1998) Cognitive-behavioral treatment of school phobia. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 37:404–411
McShane G, Walter G, Rey JM (2001) Characteristics of adolescents with school refusal. Aust NZ J Psychiatry 35:822–826
Pina A, Zerr A, Gonzales N, Ortiz C (2009) Psychosocial interventions for school refusal behavior in children and adolescents. Child Dev Perspect 3:11–20
Rettig M, Crawford J (2000) Getting past the fear of going to school. Educ Dig 65:54–59
Schmeck K, Poustka F, Doepfner M, Plück J, Berner W, Lehmkuhl G, Fegert JM, Lenz K, Huss M, Lehmkuhl U (2001) Discriminant validity of the Child Behavior Checklist CBCL-4/18 in German samples. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 10:240–247
Stiensmeier-Pelster J, Schuermann M, Duda K (2000) Depressions-Inventar für Kinder und Jugendliche (DIKJ) [Depression inventory for children and adolescents]. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Tyrrell M (2005) School phobia. J Sch Nurs 21:147–151
Walter D, Boyraz M, Lehmkuhl G, Doepfner M (2008) Die stationäre Behandlung von Jugendlichen mit emotional bedingtem Schulabsentismus - Eine Kasuistik [Inpatient treatment of adolescents with school refusal due to emotional distress. A case report]. Verhaltenstherapie 18:177–184
Walter D, Doepfner M (2009) Die Behandlung von Kindern und Jugendlichen mit Schulabsentismus—Konzept und Behandlungsempfehlungen [School absenteeism in children and adolescents—concept and treatment recommendations]. Verhaltenstherapie 19:153–160
Walter D, Rademacher C, Schuermann S, Doepfner M (2007) Grundlagen der Selbstmanagementtherapie mit Jugendlichen. Therapieprogramm für Jugendliche mit Selbstwert-, Leistungs- und Beziehungsstörungen (SELBST) [Basic principles of the self management therapy with adolescents. Treatment program for adolescents with problems in self esteem, achievement and relationships]. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Wieczerkowski W, Nickel H, Jankowski A, Fittkau B, Rauer W (1981) Angstfragebogen für Schüler AFS [Fear questionnaire for students]. Hogrefe, Göttingen
World Health Organization (1993) The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: Diagnostic criteria for research. World Health Organization, Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walter, D., Hautmann, C., Rizk, S. et al. Short term effects of inpatient cognitive behavioral treatment of adolescents with anxious-depressed school absenteeism: an observational study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 19, 835–844 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-010-0133-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-010-0133-5