Abstract
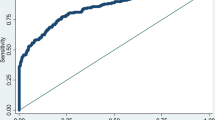
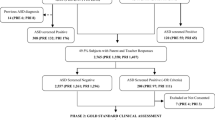
The aims of this study were, firstly, to study the association between parents’ and teachers’ ratings for the Finnish version of the Autism Spectrum Screening Questionnaire (ASSQ), secondly, to find out whether the original cut-off scores of the ASSQ identify primary school-aged children with Asperger syndrome (AS) or autism by using the Finnish ASSQ, and thirdly, to evaluate the validity of the ASSQ. Parents and/or teachers of higher-functioning (full-scale intelligence quotient ≥ 50) 8-year-old total population school children (n = 4,408) and 7–12-year-old outpatients with AS/autism (n = 47) completed the Finnish version of the ASSQ. Agreement between informants was slight. In the whole total population, low positive correlation was found between parents’ and teachers’ ratings, while in the sample of high-scoring children the correlation turned out to be negative. A cut-off of 30 for parents’ and teacher's summed score and 22 for teachers’ single score is recommended. A valid cut-off for parents’ single score could not been estimated. The clinicians are reminded that the ASSQ is a screening instrument, not a diagnosing instrument. The importance of using both parents’ and teachers’ ratings for screening in clinical settings is underlined.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach TM, McConaughy SH, Howell CT (1987) Child/adolescent behavioral and emotional problems: implications of cross-informant correlations for situational specificity. Psychol Bull 101:213–232
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Baird G, Simonoff E, Pickles A, Chandler S, Loucas T, Meldrum D, Charman T (2006) Prevalence of disorders of the autism spectrum in a population cohort of children in South Thames: the Special Needs and Autism Project (SNAP). Lancet 15:210–215
Baron-Cohen S, Allen J, Gillberg C (1992) Can autism be detected at 18 months? The needle, the haystack, and the CHAT. Br J Psychiatry 161:839–843
Baron-Cohen S, Cox A, Baird G, Swettenham J, Nightingale N, Morgan K, Drew A, Charman T (1996) Psychological markers in the detection of autism in infancy in a large population. Br J Psychiatry 168:158–163
Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S, Skinner R, Martin J, Clubley E (2001) The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ): evidence from Asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. J Autism Dev Disord 31:5–17
Berument SK, Rutter M, Lord C, Pickles A, Bailey A (1999) Autism screening questionnaire: diagnostic validity. Br J Psychiatry 175:444–451
Constantino JN, Davis SA, Todd RD, Schindler MK, Gross MM, Brophy SL, Metzger LM, Shoushtari CS, Splinter R, Reich W (2003) Validation of a brief quantitative measure of autistic traits: comparison of the social responsiveness scale with the autism diagnostic interview-revised. J Autism Dev Disord 33:427–433
Ehlers S, Gillberg C (1993) The epidemiology of Asperger syndrome. A total population study. J Child Psychol Psychiatr 34:1327–1350
Ehlers S, Gillberg C, Wing L (1999) A screening questionnaire for Asperger syndrome and other high-functioning autism spectrum disorders in school age children. J Autism Dev Disord 29:129–141
Howlin P, Asgharian A (1999) The diagnosis of autism and Asperger syndrome: findings from a survey of 770 families. Dev Med Child Neurol 41:834–839
Kadesjo B, Gillberg C, Hagberg B (1999) Brief report: autism and Asperger syndrome in seven year-old children: a total population study. J Autism Dev Disord 29:327–331
Krug DA, Arick J, Almond P (1980) Behavior checklist for identifying severely handicapped individuals with high levels of autistic behavior. J Child Psychol Psychiatr 21:221–229
Kumpulainen K, Rasanen E, Henttonen I, Moilanen I, Piha J, Puura K, Tamminen T, Almqvist F (1999) Children’s behavioural/emotional problems: a comparison of parents’ and teachers’ reports for elementary school-aged children. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 8:41–47
Lesinskiene S (2000) Vilniaus miesto vaiku autizmas, Vilniaus Universitetas, Daktaro disetacijos santrauka, Biomedicinos mokslai, medicina 07B, psichiatrija B650. Vilnius, Lithuania
Lord C, Rutter M, Le Couteur A (1994) Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: a revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 24:659–685
Lord C, Risi S, Lambrecht L, Cook EH Jr, Leventhal BL, DiLavore PC, Pickles A, Rutter M (2000) The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: a standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. J Autism Dev Disord 30:205–223
Mattila ML, Kielinen M, Jussila K, Linna SL, Bloigu R, Ebeling H, Moilanen I (2007) An epidemiological and diagnostic study of Asperger syndrome according to four sets of diagnostic criteria. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46:636–646
Posserud MB, Lundervold AJ, Gillberg C (2006) Autistic features in a total population of 7–9-year-old children assessed by the ASSQ (Autism Spectrum Screening Questionnaire). J Child Psychol Psychiatry 47:167–175
Risi S, Lord C, Gotham K, Corsello C, Chrysler C, Szatmari P, Cook EH Jr, Leventhal BL, Pickles A (2006) Combining information from multiple sources in the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 45:1094–1103
Rutter M, Bailey A, Lord C (2003) SCQ: social communication questionnaire. Western Psychological Services, Los Angeles, CA
Scott FJ, Baron-Cohen S, Bolton P, Brayne C (2002) The CAST (Childhood Asperger Syndrome Test): preliminary development of a UK screen for mainstream primary-school-age children. Autism 6:9–31
Sponheim E, Skjeldal O (1998) Autism and related disorders: epidemiological findings in a Norwegian study using ICD-10 diagnostic criteria. J Autism Dev Disord 28:217–227
Szatmari P, Archer L, Fisman S, Streiner DL (1994) Parent and teacher agreement in the assessment of pervasive developmental disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 24:703–717
Wechsler D (1991) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 3rd edition (WISC-III). Psychological Corporation, New York
Williams JG, Allison C, Scott FJ, Bolton PF, Baron-Cohen S, Matthews FE, Brayne C (2008) The Childhood Autism Spectrum Test (CAST): sex differences. J Autism Dev Disord 38:1731–1739
Williams J, Scott F, Stott C, Allison C, Bolton P, Baron-Cohen S, Brayne C (2005) The CAST (Childhood Asperger Syndrome Test): test accuracy. Autism 9:45–68
World Health Organisation (1993) International Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders (ICD-10). Diagnostic criteria for research. WHO, Geneva
Acknowledgments
We want to thank the children and their parents, the teachers and the entire staff of the schools for participating in this study. We thank chief psychologist Terttu Tapio and clinical psychologist Kati Wedman for their comments and help with this study. The Graduate School of Circumpolar Wellbeing, Health and Adaptation is acknowledged for their support. This study received financial support from Finland’s Slot Machine Association awarded to the Finnish Association for Autism and Asperger’s Syndrome and from the Child Psychiatric Research Foundation, Finland, awarded to the Eija and Veikko Lesonen Foundation, Oulu, Finland. Dr. Marja-Leena Mattila received research grants from the Rinnekoti Research Foundation, Espoo, Finland, the Alma and K. A. Snellman Foundation, Oulu, Finland, the Child Psychiatric Research Foundation, Finland, the Child Psychiatric Research Foundation, Oulu Area, Finland, and the Oulu Medical Research Foundation, Oulu, Finland. Psychologist Katja Jussila received a research grant from the Alma and K. A. Snellman Foundation, Oulu, Finland, and psychologist Sanna Kuusikko from the Alma and K. A. Snellman Foundation Oulu, Finland, and the Child Psychiatric Research Foundation, Finland. This particular study was also financially supported by a National Alliance for Autism Research (NAAR) grant awarded to professor David Pauls.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattila, ML., Jussila, K., Kuusikko, S. et al. When does the Autism Spectrum Screening Questionnaire (ASSQ) predict autism spectrum disorders in primary school-aged children?. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 18, 499–509 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-009-0044-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-009-0044-5