Abstract
Objective
To investigate the prevalence of behavioural problems and autism in a population-based group of children with hydrocephalus and to see whether learning disabilities, cerebral palsy (CP), epilepsy, myelomeningocele (MMC) or preterm birth increase the risk of these problems.
Method
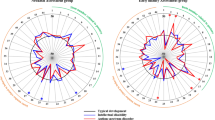
In the 107 children with hydrocephalus born in western Sweden in 1989–1993, behaviour was assessed using the Conners’ parent rating scales in 66 and the teacher’s rating scales in 57. Autism was investigated using the Childhood Autism Rating Scale.
Results
Parents rated 67% of the children and teachers 39% of the children as having behavioural problems (>1.5 SD, or T score >65). Learning disabilities increased the risk significantly and almost all the children with CP and/or epilepsy had behavioural problems. Autism was present in nine children (13%), in 20% of those without MMC and in one of 26 with MMC. Autism was significantly more frequent in children with learning disabilities (27% vs. 7%) and in children with CP and/or epilepsy (33% vs. 6%).
Conclusion
The majority of children with hydrocephalus have behavioural problems and many have autism. It is therefore important to assess and understand all the aspects of cognition and behaviour in these children in order to minimise disability and enhance participation for the child.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilenberg N, Lie HR (2001) Behavioural and emotional problems in children with myelomeningocele (MMC). Eur J Pediat Surgery 11(suppl I):544–546
Chakrabarti S, Fombonne E (2001) Pervasive developmental disorders in preschool children. Am Med Assoc 285:3093–3099
Connell HM, McConnel TS (1981) Psychiatric sequelae in children treated operatively for hydrocephalus in infancy. Develop Med Child Neurol 23:505–517
Conners CK (1989) Conners’ Rating Scales. Multi-Health Systems, New York
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (1994) American Psychiatric Association
De Bildt A, Sytema S, Krailer D, Minderaa R (2004) Prevalence of pervasive developmental disorders in children and adolescents with mental retardation. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 46, 3:275–286
Dekker M, Koot HM (2003) DSM-IV disorders in children with borderline to moderate intellectual disability. I: prevalence and impact. J Am Acad Child Adolescence Psychiatry 42:915–22
Dunn DW, Austin JK. (1999) Behavioural issues in pediatric epilepsy. Neurol 53(Suppl 2):96–100
Fernell E, Gillberg C, von Wendt L (1991) Autistic symptoms in children with infantile hydrocephalus. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 80:451–457
Fernell E, Gillberg C, von Wendt L (1991) Behavioural problems in children with infantile hydrocephalus. Develop Med Child Neurol 33:388–395
Fernell E, Hagberg G, Hagberg B. (1990) Infantile hydrocephalus-the impact of enhanced preterm survival. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 79:1080–1086
Fletcher JM, Brookshire BL, Landry SH, Bohan TP (1995) Behavioral adjustment of children with hydrocephalus: Relationships with etiology, neurological, and family status. J Pediat Psychol 20:109–125
Fombonne E (1999) The epidemiology of autism: a review. Psychol Med 29:769–786
Herzberg B, Herzberg L (1977) Brain damage and abnormal behaviour in children. Med J Aust 1:853–855
Kadesjö B, Gillberg C (1998) Attention deficits and clumsiness in Swedish 7-year-old children. Develop Med Child Neurol 40:796–804
Kielinen M, Rantala H, Timonen E, Linna S-L, Moilanen I (2004) Associated medical disorders and disabilities in children with autistic disorder. Autism 8:49–60
Lavigne JV, Nolan D, McLone DG (1988) Temperament, coping and psychological adjustment in young children with myelomeningocele. J Pediat Psychol 13: 363–378
Lindquist B, Carlsson G, Persson E-K, Uvebrant P (2005) Learning disabilities in a population-based group of children with hydrocephalus. Acta Paediatrica 94:1–8
Lumenta CHB, Skotaczak U (1995) Longterm follow-up in 233 patients with congenital hydrocephalus. Child’s Nervous Syst 11:173–175
Moilanen I, Meira L, Serlo W, von Wendt L (1985) Psychosocial adaptations of shunted hydrocephalic children. Zeitschrift für Kinderchirurgie 40(Supplement I):31–33
Persson E-K, Hagberg G, Uvebrant P (2005) Hydrocephalus: prevalence and outcome in a population-based cohort of children born 1989–1998. Acta Paediatrica 94:726–732
Rutter M (2005) Incidence of autism spectrum disorders: Changes over time and their meaning. Acta Paediatrica 94:2–15
Rutter M, Tizard J, Yule W, Graham P, Whitmore K (1976) Research report: Isle of Wight Studies, 1964–1974. Psychol Med 6:313–332
Rutter M, (1981) Psychological sequelae of brain damage in children. Am J Psychiatry 138:1533–1544
Schopler E, Reichler RJ, Rochen Renner B (1988) The childhood autism rating scale (CARS). Western Psychological Services
Stjernqvist K, Svenningsen NW (1999) Ten-year follow-up of children born before 29 gestational weeks: health, cognitive development, behaviour and school achievement. Acta Paediatrica 88:557–562
Vachha B, Adams R (2005) Myelomeningocele, Temperament Patterns, and Parental Perceptions. Pediatrics 115:58–63
Williams B, Lyttle S (1998) Mother and teacher reports of behaviour and perceived self-competence of children with hydrocephalus. Eur J Pediat Surgery 8:5–9
Acknowledgements
Financial support was obtained from the Sven Jerring, the Linnéa and Joseph Carlsson and the Folke Bernadotte Foundations and the Scientific Council, Province of Halland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindquist, B., Carlsson, G., Persson, EK. et al. Behavioural problems and autism in children with hydrocephalus. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 15, 214–219 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-006-0525-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-006-0525-8