Abstract
Purpose
To test the psychometric properties of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality of Life Questionnaire–Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (QLQ-CIPN20) using Rasch-based methods.
Methods
A secondary data analysis was performed using pooled QLQ-CIPN20 data from patients (N = 1008) who had participated in any of four multi-site chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) treatment and prevention trials. QLQ-CIPN20 responses were evaluated using a polytomous Rasch partial credit model. Data were assessed for person-item fit using the chi-square statistic, item scaling based on response proportions, threshold ordering using item characteristic curves and logit threshold locations, differential item response (DIF) (i.e., response bias) using likelihood ratio tests, and unidimensionality using cluster analysis.
Results
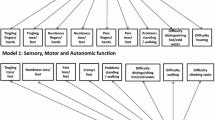
A statistically significant chi-square test indicated poor fit of the observed to the expected responses. More than 70% of the respondents reported a complete absence of six symptoms, reflecting significant floor effects and poor item scaling. Disordered/non-ordinal or narrow response thresholds were found for 11 of the 20 items. Item responses were significantly different by gender (p < 0.0001) and chemotherapy type (p < 0.0001). Cluster analysis findings suggest that the QLQ-CIPN20 is a unidimensional scale due to the absence of item clusters.
Conclusions
Rasch model testing revealed psychometric weaknesses that could be addressed by revising the QLQ-CIPN20’s problematic items and response options. Alternatively, perhaps the new gold standard CIPN measurement approach in future intervention trials should involve use of only the best items, which would also allow comparisons across previous trials that utilized the QLQ-CIPN20.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, Lavoie Smith EM, Bleeker J, Cavaletti G, Chauhan C, Gavin P, Lavino A, Lustberg MB, Paice J, Schneider B, Smith ML, Smith T, Terstriep S, Wagner-Johnston N, Bak K, Loprinzi CL (2014) Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol 32(18):1941–1967
Seretny M, Currie GL, Sena ES, Ramnarine S, Grant R, MacLeod MR, Colvin LA, Fallon M (2014) Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 155:2461–2470
Speck RM, Sammel MD, Farrar JT, Hennessy S, Mao JJ, Stineman MG, DeMichele A (2013) Impact of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy on treatment delivery in nonmetastatic breast cancer. J Oncol Pract 9:e234–e240
Tofthagen C, Overcash J, Kip K (2012) Falls in persons with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Support Care Cancer 20:583–589
Bao T, Basal C, Seluzicki C, Li SQ, Seidman AD, Mao JJ (2016) Long-term chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy among breast cancer survivors: prevalence, risk factors, and fall risk. Breast Cancer Res Treat 159:327–333
Tofthagen C, Donovan KA, Morgan MA, Shibata D, Yeh Y (2013) Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy's effects on health-related quality of life of colorectal cancer survivors. Support Care Cancer 21:3307–3313
Desaulniers GA (2011) Chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy and subjective sleep quality in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Nurs Forum 38:A56
Zanville NR, Nudelman KNH, Smith DJ, Von AD, McDonald BC, Champion VL, Saykin AJ (2016) Evaluating the impact of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy symptoms (CIPN-sx) on perceived ability to work in breast cancer survivors during the first year post-treatment. Support Care Cancer 24:4779–4789
Pike CT, Birnbaum HG, Muehlenbein CE, Pohl GM, Natale RB (2012) Healthcare costs and workloss burden of patients with chemotherapy-associated peripheral neuropathy in breast, ovarian, head and neck, and nonsmall cell lung cancer. Chemother Res Pract 2012:1–10
Reeves BN, Dakhil SR, Sloan JA, Wolf SL, Burger KN, Kamal A, Le-Lindqwister NA, Soori GS, Jaslowski AJ, Kelaghan J, Novotny PJ, Lachance DH, Loprinzi CL (2012) Further data supporting that paclitaxel-associated acute pain syndrome is associated with development of peripheral neuropathy: North Central Cancer Treatment Group trial N08C1. Cancer 118:5171–5178
Griffith K, Merkies ISJ, Hill E, Cornblath D (2010) Measures of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review of psychometric properties. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15:314–325
Cavaletti G, Frigeni B, Lanzani F, Mattavelli L, Susani E, Alberti P, Cortinovis D, Bidoli P (2010) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity assessment: a critical revision of the currently available tools. Eur J Cancer 46:479–494
Smith EM, Cohen JA, Pett MA, Beck SL (2010) The reliability and validity of a modified Total Neuropathy Score-reduced and neuropathic pain severity items when used to measure chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients receiving taxanes and platinums. Cancer Nurs 33:173–183
Smith EL, Beck SL, Cohen J (2008) The Total Neuropathy Score (TNS): a tool for measuring chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Oncol Nurs Forum 35:96–102
Alberti P, Rossi E, Cornblath DR, Merkies IS, Postma TJ, Frigeni B, Bruna J, Velasco R, Argyriou AA, Kalofonos HP, Psimaras D, Ricard D, Pace A, Galie E, Briani C, Dalla Torre C, Faber CG, Lalisang RI, Boogerd W, Brandsma D, Koeppen S, Hense J, Storey D, Kerrigan S, Schenone A, Fabbri S, Valsecchi MG, Cavaletti G, CI-PeriNomS Group (2014) Physician-assessed and patient-reported outcome measures in chemotherapy-induced sensory peripheral neurotoxicity: two sides of the same coin. Ann Oncol 25:257–264
Shimozuma K, Ohashi Y, Takeuchi A, Aranishi T, Morita S, Kuroi K, Ohsumi S, Makino H, Mukai H, Katsumata N, Sunada Y, Watanabe T, Hausheer FH (2009) Feasibility and validity of the Patient Neurotoxicity Questionnaire during taxane chemotherapy in a phase III randomized trial in patients with breast cancer: N-SAS BC 02. Support Care Cancer 17:1483–1491
Huang HQ, Brady MF, Cella D, Fleming G (2007) Validation and reduction of FACT/GOG-Ntx subscale for platinum/paclitaxel-induced neurologic symptoms: a gynecologic oncology group study. Int J Gynecol Cancer 17:387–393
Cella D, Peterman A, Hudgens S, Webster K, Socinski MA (2003) Measuring the side effects of taxane therapy in oncology: the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-taxane (FACT-taxane). Cancer 98:822–831
Postma TJ, Aaronson NK, Heimans JJ, Muller MJ, Hildebrand JG, Delattre JY, Hoang-Xuan K, Lanteri-Minet M, Grant R, Huddart R, Moynihan C, Maher J, Lucey R, EORTC Quality of Life G (2005) The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: the QLQ-CIPN20. Eur J Cancer 41:1135–1139
Kim HY, Kang JH, Youn HJ, So HS, Song CE, Chae SY, Jung SH, Kim SR, Kim JY (2014) Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Korean Acad Nurs 44:735–742
Cavaletti G, Cornblath DR, Merkies IS, Postma TJ, Rossi E, Frigeni B, Alberti P, Bruna J, Velasco R, Argyriou AA, Kalofonos HP, Psimaras D, Ricard D, Pace A, Galie E, Briani C, Dalla Torre C, Faber CG, Lalisang RI, Boogerd W, Brandsma D, Koeppen S, Hense J, Storey D, Kerrigan S, Schenone A, Fabbri S, Valsecchi MG, CI-PeriNomS Group (2013) The chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy outcome measures standardization study: from consensus to the first validity and reliability findings. Ann Oncol 24:454–462
Lavoie Smith EM, Barton DL, Qin R, Steen PD, Aaronson NK, Loprinzi CL (2013) Assessing patient-reported peripheral neuropathy: the reliability and validity of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-CIPN20 questionnaire. Qual Life Res 22:2787–2799
Kieffer JM, Postma TJ, van de Poll-Franse L, Mols F, Heimans JJ, Cavaletti G, Aaronson NK (2017) Evaluation of the psychometric properties of the EORTC chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy questionnaire (QLQ-CIPN20). Qual Life Res 26:2999–3010
Smith EML, Knoerl R, Yang JJ, Kanzawa-Lee G, Lee D, Bridges CM (2018) In search of a gold standard patient-reported outcome measure for use in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy clinical trials. Cancer Control 25:1–10
Smith EML, Banerjee T, Yang JJ, Bridges C, Alberti P, Sloan J, Loprinzi C (2018) Psychometric testing of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) QLQ-CIPN20 using pooled Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Outcome Measures Standardization (CI-PeriNomS) and Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology (Alliance) A151408 study data. Cancer Nurs:1. https://doi.org/10.1097/NCC.0000000000000596
Smith EML, Haupt R, Kelly J, Lee D, Kanzawa-Lee G, Knoerl R, Bridges C, Alberti P, Prasertsri N, Donohoe C (2017) The content validity of a chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy patient-reported outcome measure. Oncol Nurs Forum 44:580–588
Mols F, van de Poll-Franse LV, Vreugdenhil G, Beijers AJ, Kieffer JM, Aaronson NK, Husson O (2016) Reference data of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) QLQ-CIPN20 questionnaire in the general Dutch population. Eur J Cancer 69:28–38
Le-Rademacher J, Kanwar R, Seisler D, Pachman DR, Qin R, Abyzov A, Ruddy KJ, Banck MS, Lavoie Smith EM, Dorsey SG, Aaronson NK, Sloan J, Loprinzi CL, Beutler AS (2017) Patient-reported (EORTC QLQ-CIPN20) versus physician-reported (CTCAE) quantification of oxaliplatin- and paclitaxel/carboplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in NCCTG/Alliance clinical trials. Support Care Cancer 25:3537–3544
Cappelleri JC, Jason Lundy J, Hays RD (2014) Overview of classical test theory and item response theory for the quantitative assessment of items in developing patient-reported outcomes measures. Clin Ther 36:648–662
Merkies ISJ, Lauria G, Faber CG (2012) Outcome measures in peripheral neuropathies: requirements through statements. Curr Opin Neurol 25:556–563
Tennant A, Conaghan PG (2007) The Rasch measurement model in rheumatology: what is it and why use it? When should it be applied, and what should one look for in a Rasch paper? Arthritis Rheum 57:1358–1362
Pallant JF, Tennant A (2007) An introduction to the Rasch measurement model: an example using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Br J Clin Psychol 46:1–18
Loprinzi CL, Reeves BN, Dakhil SR, Sloan JA, Wolf SL, Burger KN, Kamal A, Le-Lindqwister NA, Soori GS, Jaslowski AJ, Novotny PJ, Lachance DH (2011) Natural history of paclitaxel-associated acute pain syndrome: prospective cohort study NCCTG N08C1. J Clin Oncol 29:1472–1478
Loprinzi CL, Qin R, Dakhil SR, Fehrenbacher L, Flynn KA, Atherton P, Seisler D, Qamar R, Lewis GC, Grothey A (2013) Phase III randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of intravenous calcium and magnesium to prevent oxaliplatin-induced sensory neurotoxicity (N08CB/Alliance). J Clin Oncol 32:997–1005
Barton DL, Wos EJ, Qin R, Mattar BI, Green NB, Lanier KS, Bearden JD 3rd, Kugler JW, Hoff KL, Reddy PS, Rowland KM, Jr RM, Christensen B, Loprinzi CL (2011) A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a topical treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: NCCTG trial N06CA. Support Care Cancer 19:833–841
Leal AD, Qin R, Atherton PJ, Haluska P, Behrens RJ, Tiber CH, Watanaboonyakhet P, Weiss M, Adams PT, Dockter TJ, Loprinzi CL, for the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology (2014) North Central Cancer Treatment Group/Alliance trial N08CA-the use of glutathione for prevention of paclitaxel/carboplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: a phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cancer 120:1890–1897
Fayers PM, Aaronson NK, Bjordal K, Groenvold M, Curran D, Bottomley A, on behalf of the EORTC Quality of Life Group (2001) The EORTC QLQ-C30 Scoring Manual, 3rd edn. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer, Brussels
Mair P, Hatzinger R (2007) Extended Rasch modeling: the eRm package for the application of IRT models in R. J Stat Softw 20:1–20
Mair P, Hatzinger R (2007) CML based estimation of extended Rasch models with the eRm package in R. Psychol Sci 49:26–43
van Nes SI, Vanhoutte EK, van Doorn PA, Hermans M, Bakkers M, Kuitwaard K, Faber CG, Merkies ISJ (2011) Rasch-built Overall Disability Scale (R-ODS) for immune-mediated peripheral neuropathies. Neurology 76:337–345
Binda D, Vanhoutte EK, Cavaletti G, Cornblath DR, Postma TJ, Frigeni B, Alberti P, Bruna J, Velasco R, Argyriou AA, Kalofonos HP, Psimaras D, Ricard D, Pace A, Galie E, Briani C, Dalla Torre C, Lalisang RI, Boogerd W, Brandsma D, Koeppen S, Hense J, Storey D, Kerrigan S, Schenone A, Fabbri S, Rossi E, Valsecchi MG, Faber CG, Merkies ISJ, CI-PeriNomS study group, Galimberti S, Lanzani F, Mattavelli L, Piatti ML, Bidoli P, Cazzaniga M, Cortinovis D, Lucchetta M, Campagnolo M, Bakkers M, Brouwer B, Boogerd W, Grant R, Reni L, Piras B, Pessino A, Padua L, Granata G, Leandri M, Ghignotti I, Plasmati R, Pastorelli F, Heimans JJ, Eurelings M, Meijer RJ, Grisold W, Lindeck Pozza E, Mazzeo A, Toscano A, Russo M, Tomasello C, Altavilla G, Penas Prado M, Dominguez Gonzalez C, Dorsey SG (2013) Rasch-built Overall Disability Scale for patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN-R-ODS). Eur J Cancer 49:2910–2918
Binda D, Cavaletti G, Cornblath DR, Merkies ISJ, CI-PeriNomS study group (2015) Rasch-transformed Total Neuropathy Score clinical version (RT-TNSc(©) ) in patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 20:328–332
Draak THP, Vanhoutte EK, van Nes SI, Gorson KC, Van der Pol W, Notermans NC, Nobile-Orazio E, Lewis RA, Leger J, Van den Bergh PY, Lauria G, Bril V, Katzberg H, Lunn MPT, Pouget J, van der Kooi AJ, Hahn AF, van den Berg LH, van Doorn PA, Cornblath DR, Faber CG, ISJ M, PeriNomS Study Group (2015) Comparing the NIS vs MRC and INCAT sensory scale through Rasch analyses. J Peripher Nerv Syst 20:277–288
Sadjadi R, Reilly MM, Shy ME, Pareyson D, Laura M, Murphy S, Feely SME, Grider T, Bacon C, Piscosquito G, Calabrese D, Burns TM (2014) Psychometrics evaluation of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Neuropathy Score (CMTNSv2) second version, using Rasch analysis. J Peripher Nerv Syst 19:192–196
Vanhoutte EK, Faber CG, van Nes SI, Cats EA, Van der Pol W, Gorson KC, van Doorn PA, Cornblath DR, van den Berg LH, Merkies ISJ, PeriNomS Study Group (2015) Rasch-built Overall Disability Scale for multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN-RODS(©)). J Peripher Nerv Syst 20:296–305
Funding
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health under the Award Number UG1CA189823 (Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology NCORP Grant), U10CA180790, U10CA180795, and R03 CA186183-02. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers: NCT00516503 (N06CA); NCT00860041 (N08C1); NCT02311907 (N08CA); NCT01099449 (N08CB)
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, E.M.L., Zanville, N., Kanzawa-Lee, G. et al. Rasch model-based testing of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality of Life Questionnaire–Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (QLQ-CIPN20) using Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology (Alliance) A151408 study data. Support Care Cancer 27, 2599–2608 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4553-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4553-y