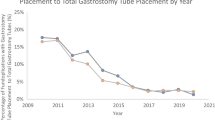
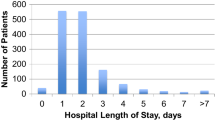
Abstract
Introduction
A gastrostomy placement is frequently performed in pediatric patients who require long-term enteral tube feeding. However, data on efficacy, perioperative complications and postoperative gastroesophageal reflux (GER) after laparoscopic gastrostomy (LAG) placement is limited.
The aim of this study is to evaluate long-term efficacy and adverse events after LAG in a large cohort and determine whether routine preoperative 24-h pH monitoring should be used to predict postoperative GER.
Method
A retrospective observational cohort study was performed including 300 patients (75 % neurologically impaired) that underwent LAG.
Results
After a median follow-up of 2.63 years, feeding was successful in 95.9 % of patients. Weight-for-length z-scores significantly increased (p < 0.0005). Major complications were seen in only 6 patients (2.0 %), but minor complications occurred frequently (73.6 %). Overall incidence of GER remained unchanged after LAG. Sensitivity and specificity of preoperative pH monitoring were 17.5 and 76.9 %, respectively.
Conclusion
LAG placement in pediatric patients leads to successful feeding in 96 % of patients and serious adverse events are rare. However, the minor complication rate is high. Overall incidence of GER does not increase after LAG. Preoperative 24-h pH monitoring is not a reliable tool to predict postoperative GER. This invasive investigation technique should therefore not be routinely performed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Srinivasan R, Irvine T, Dalzell M (2009) Indications for PEG and procedure-related outcome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol 49:584–588
Fortunato JE, Troy AL, Cuffari C, Davis JE, Loza MJ, Oliva-Hemker M, Schwarz KB (2010) Outcome after PEG in children and young adults. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 50:390–393
Khattak IU, Kimber C, Kiely EM, Spitz L (1998) PEG in paediatric practice: complications and outcome. J Pediatr Surg 33:67–72
Tomicic JT, Luks FI, Shalon L, Tracy TF (2002) LAG in infants and children. Eur J Pediatr Surg 12:107–110
Wragg RC, Salminen H, Pachl M, Singh M, Lander A, Jester I, Parikh D, Jawaheer G (2012) Gastrostomy insertion in the 21st century: PEG or laparoscopic? Report from a large single-centre series. Pediatr Surg Int 28:443–448
Zamakhshary M, Jamal M, Blair GK, Murphy JJ, Webber EM, Skarsgard ED (2005) Laparoscopic vs PEG tube insertion: a new pediatric gold standard? J Pediatr Surg 40:859–862
Rempel GR, Colwell SO, Nelson RP (1988) Growth in children with cerebral palsy fed via gastrostomy. Pediatrics 82:857–862
Corwin DS, Isaacs JS, Georgeson KE, Bartolucci AA, Cloud HH, Craig CB (1996) Weight and length increases in children after gastrostomy placement. J Am Diet Assoc 96:874–879
Samson-Fang L, Butler C, O’Donnell M (2003) Effects of gastrostomy feeding in children with cerebral palsy: an AACPDM evidence report. Dev Med Child Neurol 45:415–426
Brewster BD, Weil BR, Ladd AP (2012) Prospective determination of PEG complication rates in children: still a safe procedure. Surgery 152:714–719
Crosby J, Duerksen D (2005) A retrospective survey of tube-related complications in patients receiving long-term home enteral nutrition. Dig Dis Sci 50:1712–1717
Mollitt DL, Golladay ES, Seibert JJ (1985) Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux following gastrostomy in neurologically impaired patients. Pediatrics 75:1124–1126
Sulaeman E, Udall JN Jr, Brown RF, Mannick EE, Loe WA, Hill CB, Schmidt-Sommerfeld E (1998) Gastroesophageal reflux and Nissen fundoplication following PEG in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 26:269–273
Wilson GJ, van der Zee DC, Bax NM (2006) Endoscopic gastrostomy placement in the child with gastroesophageal reflux: is concomitant ARS indicated? J Pediatr Surg 41:1441–1445
Razeghi S, Lang T, Behrens R (2002) Influence of PEG on gastroesophageal reflux: a prospective study in 68 children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 35:27–30
Thomson M, Rao P, Rawat D, Wenzl TG (2011) PEG and gastro-oesophageal reflux in neurologically impaired children. World J Gastroenterol 17:191–196
TNO Groeicalculator voor de vijfde landelijke Groeistudie. 2013. Ref Type : Internet Communication
Richter JE, Bradley LA, DeMeester T, Wu WC (1992) Normal 24-h ambulatory esophageal pH values. Influence of study center, pH electrode, age and gender. Dig Dis Sci 37:849–856
Smout AJ, Breedijk M, van der Zouw C, Akkermans LM (1989) Physiological gastroesophageal reflux and esophageal motor activity studied with a new system for 24-h recording and automated analysis. Dig Dis Sci 34:372–378
Kang A, Zamora SA, Scott RB, Parsons HG (1998) Catch-up growth in children treated with home enteral nutrition. Pediatrics 102:951–955
Walker SP, Golden MH (1988) Growth in length of children recovering from severe malnutrition. Eur J Clin Nutr 42:395–404
Lantz M, Hultin LH, Arnbjornsson E (2010) Literature review comparing laparoscopic and percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomies in a pediatric population. Int J Pediatr 2010:507616
Arnbjornsson E, Larsson LT, Lindhagen T (1999) Complications of laparoscopy-aided gastrostomies in pediatric practice. J Pediatr Surg 34:1843–1846
Thorne SE, Radford MJ (1998) A comparative longitudinal study of gastrostomy devices in children. West J Nurs Res 20:145–159 discussion 159–65
Lintula H, Juvonen P, Hämynen I, Heikkinen M, Eskelinen M (2013) Severe gastro-oesophageal reflux necessitating fundoplication after percutaneous endoscopic and open gastrostomy in children. Langenbecks Arch Surg 398:703–707
Noble LJ, Dalzell AM, El-Matary W (2012) The relationship between PEG and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children: a systematic review. Surg Endosc 26:2504–2512
Hassall E (2005) Decisions in diagnosing and managing chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease in children. J Pediatr 146:S3–S12
Vandenplas Y, Sacre-Smits L (1987) Continuous 24-h esophageal pH monitoring in 285 asymptomatic infants 0–15 months old. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 6:220–224
Vandenplas Y, Goyvaerts H, Helven R, Sacre L (1991) Gastroesophageal reflux, as measured by 24-h pH monitoring, in 509 healthy infants screened for risk of sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatrics 88:834–840
Acknowledgments
F.A. Mauritz is supported by a Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital Grant and NutsOhra. No other sources of support were used.
Disclosures
J. Franken, F.A. Mauritz, N. Suksamanapun, C.C.C. Hulsker, D.C. van der Zee, and M.Y.A. van Herwaarden-Lindeboom have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franken, J., Mauritz, F.A., Suksamanapun, N. et al. Efficacy and adverse events of laparoscopic gastrostomy placement in children: results of a large cohort study. Surg Endosc 29, 1545–1552 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3839-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3839-5