Abstract
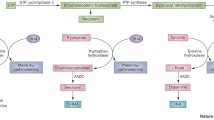
This report concerns one new mutation in the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) gene in three patients originating from three unrelated Dutch families with autosomal recessive L-DOPA-responsive dystonia (DRD). In this study, all exons of the TH gene were amplified by the polymerase chain reaction and subjected to analyses by single-strand conformation polymorphism. An aberrant migration pattern was observed for exon 6 of the TH gene in all patients. Direct sequencing of the coding region of exon 6 revealed the presence of one novel missense mutation. An a698g transition resulted in the substitution of the evolutionary conserved arginine 233 by a histidine (R233H). All patients were homozygous for the mutation. This new mutation in the TH gene was confirmed by restriction enzyme analysis with the restriction enzyme HhaI. Thus, a high proportion of defective TH alleles may be R233H in The Netherlands.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 July 1997 / Accepted: 10 February 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van den Heuvel, L., Luiten, B., Smeitink, J. et al. A common point mutation in the tyrosine hydroxylase gene in autosomal recessive L-DOPA-responsive dystonia in the Dutch population. Hum Genet 102, 644–646 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050756
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050756