Abstract
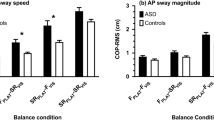
Given the known deficits in attention in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and the evidence suggesting that postural control requires attention, this study aimed to investigate the mechanisms of postural control of children with and without ADHD in single-(ST) and dual-task (DT) conditions. Postural sway and stabilogram diffusion analysis (SDA) were performed on the Center of Pressure trajectories on 24 ADHD children and 17 age–gender-matched healthy controls. The subjects were instructed to stand as stable as possible on a force platform in two task conditions: (1) single task (ST) and (2) dual task (DT)—an auditory-memory attention-demanding cognitive task. During ST and DT conditions, the ADHD children showed significantly greater ML-sway, short- and long-term effective diffusion coefficients, and critical displacement of SDA compared with controls. The effects of DT were somewhat unexpected; the control group indicated a significant decrease in ML-sway, AP-sway, sway area, and critical displacement of SDA; the ADHD group showed a significant decrease in ML-sway range and critical displacement. It is concluded that a greater sway displacement before closed-loop mechanisms is called into play in ADHD children. The DT enhanced balance control by reinforcing balance automaticity and minimizing sway in both healthy and ADHD children.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed. (DSM-IV). American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Anand V, Buckley JG, Scally A et al (2003) Postural stability in the elderly during sensory perturbations and dual tasking: the influence of refractive blur. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44(7):2885–2891
Bradley JD, Golden CJ (2001) Biological contributions to the presentation and understanding of attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder: a review. Clin Psychol Rev 21:907–929
Cheng J, Wang YF (2007) Comparison of postural control between normal and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder boys. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao 39:531–534, Abstract in Chinese
Christiansen A (2000) Persisting motor control problems in 11- to 12-year-old boys previously diagnosed with deficits in attention, motor control and perception (DAMP). Dev Med Child Neurol 42:4–7
Collins JJ, De Luca CJ (1993) Open-loop and closed-loop control of posture: a random walk analysis of center-of-pressure trajectories. Exp Brain Res 95:308–318
Collins JJ, De Luca CJ, Burrows A et al (1995) Age-related-changes in open-loop and closed-loop postural control mechanisms. Exp Brain Res 104:480–492
Conners CK, Sitarenios G, Parker JD et al (1998) The revised Conners’ Parent Rating Scale (CPRS-R): factor structure, reliability, and criterion validity. J Abnorm Child Psychol 26:257–268
Feng L, Wang YF, Cao QJ (2007) A pilot study on effect of methylphenidate on balance function of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao 39:304–309, Abstract in Chinese
Huxhold O, Li S-C, Schmiedek F et al (2006) Dual tasking postural control: aging and the effects of cognitive demand in conjunction with focus of attention. Brain Res Bull 69:294–305
Jacobi-Polishook T, Shorer Z, Melzer I (2009) The effect of methylphenidate on postural stability under single and dual task conditions in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder—a double blind randomized control trial. J Neurol Sci 280(1–2):15–21
Jucaite A, Fernell E, Forssberg H et al (2003) Deficient coordination of associated postural adjustments during a lifting task in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol 45:731–742
Kadesjö B, Gillberg C (1998) Attention deficit and clumsiness in Swedish 7-year-olds. Dev Med Child Neurol 40:796–804
Kadesjö B, Gillberg C (1999) Developmental coordination disorder in Swedish 7-year-old children. J Am Acad Child Ps 38:820–828
Lajoie Y, Teasdale N, Bard C et al (1993) Attentional demands for static and dynamic equilibrium. Exp Brain Res 97:139–144
Landgren M, Kjellman B, Gillberg C (2000) Deficits in attention, motor control and perception (DAMP): a simplified school entry examination. Acta Paediatr 89(3):302–309
Landgren M, Pettersson R, Kjellman B et al (1996) ADHD, DAMP and other neurodevelopmental/psychiatric disorders in 6-year-old children: epidemiology and comorbidity. Dev Med Child Neurol 38:891–906
Leitner Y, Barak R, Giladi N et al (2007) Gait in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: effects of methylphenidate and dual tasking. J Neurol 254:1330–1338
Levy F (1991) The dopamine theory of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Aust NZ J Psychiat 25:277–283
Melzer I, Benjuya N, Kaplanski J (2001) Age-related changes of postural control: effect of cognitive tasks. Gerontology 47:189–194
Mulas F, Mattos L, de la Osa-Langreo A et al (2007) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: in favour of the organic origin. Rev Neurol 44(3):S47–S49, Review. [Spanish]
Neumann O (1984) Automatic processing: a review of recent findings and a plea for an old theory. In: Prinz W, Sanders AF (eds) Cognition and motor processes. Springer, Berlin, pp 255–293
Pellecchia GL (2003) Postural sway increases with attentional demands of concurrent cognitive task. Gait Posture 18:29–34
Piek JP, Pitcher TM, Hay DA (1999) Motor coordination and kinaesthesis in boys with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Dev Med Child Neurol 41:159–165
Rankin JK, Woollacott MH, Shumway-Cook A et al (2000) Cognitive influence on postural stability: a neuromuscular analysis in young and older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 55(3):M112–M119
Rasmussen P, Gillberg C (2000) Natural outcome of ADHD with developmental coordination disorder at age 22 years: a controlled, longitudinal, community-based study. J Am Acad Child Psy 39:1424–1431
Riley MA, Baker AA, Schmit JM (2003) Inverse relation between postural variability and difficulty of a concurrent short-term memory task. Brain Res Bull 62(3):191–195
Schaefer S, Krampe RT, Lindenberger U et al (2008) Age differences between children and young adults in the dynamics of dual-task prioritization: body (balance) versus mind (memory). Dev Psychol 44(3):747–757
Scherder EJ, Rommelse NN, Bröring T et al (2008) Somatosensory functioning and experienced pain in ADHD-families: a pilot study. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 12(6):461–469, Epub 2008 Feb 8
Schmid M, Conforto S, Lopez L et al (2007) Cognitive load affects postural control in children. Exp Brain Res 179:375–385
Schoemaker MM, Ketelaars CE, van Zonneveld M, Minderaa RB, Mulder T (2005) Deficits in motor control processes involved in production of graphic movements of children with attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Dev Med Child Neurol 47:390–395
Sergeant JA, Piek JP, Oosterlaan J (2006) ADHD and DCD: a relationship in need of research. Hum Mov Sci 25:76–89
Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott M, Baldwin M et al (1997) The effects of cognitive demands on postural sway in elderly fallers and non fallers. J Gerontol 52:M232–M240
Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott M, Kerns KA et al (1997) The effect of two types of cognitive tasks on postural stability in older adults with and without a history of falls. J Gerontol 52A:232–240
Silk T, Vance A, Rinehart N et al (2005) Fronto-parietal activation in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, combined type: functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Brit J Psychiat 187:282–283
Swan L, Otani H, Loubert P et al (2004) Improving balance by performing a secondary cognitive task. Brit J Psychol 95:31–40
Taketomo CK (2005) Pediatric dosage handbook with international index, 12th edn. Lexi-Comp, Inc, Hudson, OH
Teicher MH, Ito Y, Glod CA et al (1996) Objective measurement of hyperactivity and attentional problems in ADHD. J Am Acad Child Psy 35:334–342
Tervo RC, Azuma S, Fogas B et al (2002) Children with ADHD and motor dysfunction compared with children with ADHD only. Dev Med Child Neurol 44:383–390
Whitmont S, Clark C (1996) Kinaesthetic acuity and fine motor skills in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a preliminary report. Dev Med Child Neurol 38:1091–1098
Wickens CD (1989) Attention and skilled performance. In: Holding DH (ed) Human skills. J Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 71–105
Woollacott M, Shumway-Cook A (2002) Attention and the control of posture and gait: a review of an emerging area of research. Gait Posture 16:1–14
Wulf G, McNevin N, Shea CH (2001) The automaticity of complex motor skill learning as a function of attentional focus. Q J Exp Psychol A 54:1143–1154
Yardley L, Gardner M, Leadbetter A et al (1999) Effect of articulatory and mental tasks on postural control. Neuroreport 10:215–219
Zametkin AJ, Liotta W (1998) The neurobiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Psychiat 59(Suppl 7):17–2
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests and no financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shorer, Z., Becker, B., Jacobi-Polishook, T. et al. Postural control among children with and without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in single and dual conditions. Eur J Pediatr 171, 1087–1094 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-012-1695-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-012-1695-7