Abstract
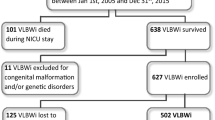
This study reports on the developmental outcome of a sample of pre-term children with a birth weight ≤1500 g born in 1994 and 1995 studied at the age of 5 to 6 years. The sample included 60 out of 81 surviving pre-term children (74.1%) of a German neonatal intensive care unit which was matched to a control group of 60 kindergarten children of the same region. The results show significant differences between term and pre-term children with regard to their intellectual development, language comprehension, attentiveness, and hyperactivity. Moreover, the pre-term children required more early intervention to compensate for developmental problems. The developmental deficits were intensified by the presence of biological risk factors like increasingly low birth weight, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and intraventricular haemorrhage. Conclusion: differences between term and pre-term children still exist, although the early 1990s witnessed fundamental changes in the treatment of pre-term children. The persistence of these differences is explained mainly by the increase in the survival rate of children with high biological risk factors.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPD :
-
bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- CBCL :
-
child behaviour checklist
- HKS :
-
questionnaire of hyperactivity symptoms
- IVH :
-
intraventricular haemorrhage
- K-ABC :
-
Kaufman assessment battery for children
- LOS :
-
Lincoln-Oseretzky scale
- MPC :
-
mental processing composite
- MSVK :
-
Marburg language comprehension test for children
- SED :
-
sequential informative processing score
- SGA :
-
small for gestational age
- SGD :
-
simultaneous information processing score
- VLBW :
-
very low birth weight
References
Achenbach TM (1991) Manual for the child behavior checklist/4–18 and profile. Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont, Burlington
Breslau N, Chilcoat HD, Johnson EO, Andreski P, Lucia VC (2000) Neurologic soft signs and low birthweight: their association and neuropsychiatric implications. Biol Psychiatry 1: 71–79
Dezoete JA, Macarthur BA (2000) Some influences on cognitive development in a group of very low birth weight infants at four years. N Z Med J 9: 207–210
Eggert D (1991) Lincoln-Oseretzky-Skala. Beltz Test GmbH, Weinheim
Elben CE, Lohaus A (2000) Marburger Sprachverständnistest für Kinder (MSVK). Hogrefe, Göttingen
Hack M, Fanaroff A (1999) Outcomes of children of extremely low birth weight and gestational age in the 1990's. Early Hum Dev 53: 193–218
Kaufman A, Kaufman N (1983) Kaufman assessment battery for children. Circle Pines, Minnesota, USA
Klein L (1993) Diagnostik und Therapie beim hyperkinetischen Syndrom. Beltz Test, Weinheim, Germany
Leonard CH, Piecuch RE (1997) School age outcomes in low birth weight preterm infants. Semin Perinatol 21: 240–253
Luoma L, Herrgard E, Martikainen A (1998) Neuropsychological analysis of the visuomotor problems in children born preterm ≤32 weeks gestation: a 5-year prospective follow-up. Dev Med Child Neurol 40: 21–30
Ouden LD, Rijken M, Brand R, Verloove-Vanhorick SP, Ruys JH (1991) Is it correct to correct? Developmental milestones in 555 "normal" preterm infants compared with term infants. J Pediatr 118: 399–404
Papile L, Burstein J, Burstein R (1978) Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weight less than 1500 grams. J Pediatr 92: 529–534
Salokorpi T, Rautio T, Sajaniemi N, Serenius-Sirve S, Tuomi H, Wendt L (2001) Neurological development up to the age of four years of extremely low birth weight infants born in Southern Finland in 1991–94. Acta Paediatr 90: 218–221
Singer L, Yamashita T, Lilien L, Collin M, Baley J (1997) A longitudinal study of developmental outcome of infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia and very low birthweight. Pediatrics 100: 987–993
Vohr B, Coll CG, Flanagan P, Oh W (1992) Effects of intraventricular hemorrhage and socioeconomic status on perceptual, cognitive and neurologic status of low birth weight infants at 5 years of age. J Pediatr 121: 280–285
Wolke D, Meyer R (1999) Cognitive status, language attainment, and prereading skills of 6-year-old very preterm children and their peers: the Bavarian Longitudinal Study. Dev Med Child Neurol 41: 94–104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanke, C., Lohaus, A., Gawrilow, C. et al. Preschool development of very low birth weight children born 1994–1995. Eur J Pediatr 162, 159–164 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-002-1127-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-002-1127-1