Abstract
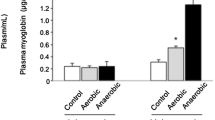
The aim of this study was to examine the expression pattern of myosin heavy chain (MHC) and myosin light chain (MLC) isoforms in single fibres from the rat soleus muscle under control (Cont) conditions and under conditions inducing slow-to-fast phenotype transitions. Two models of muscle phenotype modification, namely 2 weeks clenbuterol (CB) administration or hindlimb unloading (HU), were chosen to achieve a full range of appearance of hybrid fibres, i.e. fibres co-expressing slow and fast myosin isoforms. MHC and MLC compositions were analysed in parallel by one-dimensional-gel electrophoresis. We showed that (i) the slow-to-fast fibre type transitions at the MHC level were accompanied by exchanges of slow with fast MLC isoforms and (ii) that these transitions were characterized by increased proportions of hybrid profiles of both MHC and MLC isoforms, under both CB (27.5%) and HU (18%) conditions when compared with Cont (7%). This suggested a MHC-MLC coordinated program for myosin regulation during fibre type transitions. However, mismatched hybrid co-expression of MHC and MLC was also observed, probably resulting from differences in post-transcriptional regulation. Finally, in all the muscle fibre groups, specific favourable correlations between one MHC (IIa, IId or IIb) and one MLC (regulatory or essential) type were found.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bär A, Simoneau JA, Pette D (1989) Altered expression of myosin light-chain isoforms in chronically stimulated fast-twitch muscle of the rat. Eur J Biochem 178:591–594
Bortolotto SK, Stephenson DG, Stephenson GMM (1999) Fiber type populations and Ca-activation properties of single fibers in soleus muscles from SHR and WKY rats. Am J Physiol 276:C628–C637
Brown WE, Salmons S, Whalen RG (1983) The sequential replacement of myosin subunit isoforms during muscle type transformation induced by long term electrical stimulation. J Biol Chem 258:14686–14692
Caiozzo VJ, Baker MJ, Baldwin KM (1998) Novel transitions in MHC isoforms: separate and combined effects of thyroid hormone and mechanical unloading. J Appl Physiol 85:2237–2248
Criswell DS, Powers SK, Herb RA (1996) Clenbuterol-induced fiber type transition in the soleus of adult rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 74:391–396
Hämäläinen N, Pette D (1996) Slow-to-fast transitions in myosin expression of rat soleus muscle by phasic high-frequency stimulation. FEBS Lett 399:220–222
Härtner KT, Pette D (1990) Fast and slow isoforms of troponin I and troponin C. Distribution in normal rabbit muscles and effects of chronic stimulation. Eur J Biochem 188:261–267
Härtner KT, Kirschbaum BJ, Pette D (1989) The multiplicity of troponin T isoforms. Distribution in normal rabbit muscles and effects of chronic stimulation. Eur J Biochem 179:31–38
Kischel P, Bastide B, Stevens L, Mounier Y (2001) Expression and functional behavior of troponin C in soleus muscle fibers of rat after hindlimb unloading. J Appl Physiol 90:1095–1101
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lutz GJ, Bremner SN, Bade MJ, Lieber RL (2001) Identification of myosin light chains in Rana pipiens skeletal muscle and their expression patterns along single fibers. J Exp Biol 204:4237–4248
Mounier Y, Holy X, Stevens L (1989) Compared properties of the contractile system of skinned slow and fast rat muscle fibers. Pflugers Arch 415:136–141
Pette D, Staron RS (1997) Mammalian skeletal muscle fiber type transitions. Int Rev Cytol 170:143–223
Pette D, Staron RS (2000) Myosin isoforms, muscle fiber types and transitions. Microsc Res Tech 50:500–509
Poetter K, Jiang H, Hassanzadeh S, Master SR, Chang A, Dalakas MC, Rayment I, Sellers JR, Fananapazir L, Epstein ND (1996) Mutations in either the essential or regulatory light chains of myosin are associated with a rare myopathy in human heart and skeletal muscle. Nat Genet 13:63–69
Ricart-Firinga C, Stevens L, Canu MH, Nemiroskaya TL, Mounier Y (2000) Effects of β2-agonist clenbuterol on biochemical and contractile properties of unloaded soleus fibers of rat. Am J Physiol 278:C582–C588
Rivero JL, Serrano AL (1999) Skeletal myosin heavy chain composition and carriage training. Equine Vet J 30:318–323
Salviati G, Betto R, Danieli-Betto D (1992) Polymorphism of myofibrillar proteins of rabbit skeletal-muscle fibres. An electrophoretic study of single fibres. Biochem J 207:261–272
Schiaffino S, Reggiani C (1996) Molecular diversity of myofibrillar proteins: gene regulation and functional significance. Physiol Rev 76:371–423
Seedorf K, Seedorf U, Pette D (1983) Coordinate expression of alkali and DTNB myosin light chains during transformation of rabbit fast muscle by chronic stimulation. FEBS Lett 158:321–324
Stephenson GMM (2001) Hybrid skeletal muscle fibers: a rare or a common phenomenon? Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28:692–702
Stevens L, Mounier Y, Holy X, Falempin M (1990) Contractile properties of rat soleus muscle after 15 days hindlimb suspension. J Appl Physiol 68:334–340
Stevens L, Gohlsch B, Mounier Y, Pette D (1999) Changes in myosin heavy chain mRNA and protein isoforms in single fibers of unloaded rat soleus muscle. FEBS Lett 463:15–18
Stevens L, Sultan KR, Peuker H, Gohlsch B, Mounier Y, Pette D (1999) Time-dependent changes in myosin heavy chain mRNA and protein isoforms in unloaded soleus muscle of rat. Am J Physiol 277:C1044–C1049
Stevens L, Firinga C, Gohlsch B, Bastide B, Mounier Y, Pette D (2000) Effects of unweighting and clenbuterol on myosin light and heavy chains in fast and slow muscles of rat. Am J Physiol 279:C1558–C1563
Szczesna D (2003) Regulatory light chains of striated muscle myosin. Structure, function and malfunction. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord 3:187–197
Talmadge RJ, Roy RR, Edgerton VR (1999) Persistence of hybrid fibers in rat soleus after spinal cord transection. Anat Rec 255:188–201
Toursel T, Stevens L, Mounier Y (1999) Evolution of contractile and elastic properties of rat soleus muscle fibers under unloading conditions. Exp Physiol 84:93–107
Wahrman JP, Winand R, Rieu M (2001) Plasticity of skeletal myosin in endurance-trained rats (I). A quantitative study. Eur J Appl Physiol 84:367–372
Zak R, Martin AF, Prior G, Rabinowitz M (1977) Comparison of turnover of several myofibrillar proteins and critical evaluation of double isotope method. J Biol Chem 252:3430–3435
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to D. Pette for providing the antibodies against Troponin C and I. The “Laboratoire de Plasticité Neuromusculaire” was supported by French Ministry of Research (UPRES EA 1032-IFR118) and grants from the “Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales” (No. 3194) and the “Conseil Régional du Nord-Pas-de-Calais”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevens, L., Bastide, B., Bozzo, C. et al. Hybrid fibres under slow-to-fast transformations: expression is of myosin heavy and light chains in rat soleus muscle. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 448, 507–514 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-004-1287-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-004-1287-0