Abstract
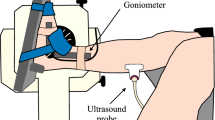
The aim of this study was to assess the predictability of in vivo, ultrasound-based changes in human tibialis anterior (TA) pennation angle from rest to maximum isometric dorsiflexion (MVC) using a planimetric model assuming constant thickness between aponeuroses and straight muscle fibres. Sagittal sonographs of TA were taken in six males at ankle angles of −15° (dorsiflexion direction), 0° (neutral position), +15° (plantarflexion direction) and +30° both at rest and during dorsiflexor MVC trials performed on an isokinetic dynamometer. At all four ankle angles scans were taken from the TA proximal, central and distal regions. TA architecture did not differ (P > 0.05) neither between its two unipennate parts nor along the scanned regions over its length at a given ankle angle and state of contraction. Comparing MVC with rest at any given ankle angle, pennation angle was larger (62–71%, P < 0.01), fibre length smaller (37–40%, P < 0.01) and muscle thickness unchanged (P > 0.05). The model used estimated accurately (P > 0.05) changes in TA pennation angle occurring in the transition from rest to MVC and therefore its use is encouraged for estimating the isometric TA ankle moment and force generating capacity using musculoskeletal modelling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 25 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maganaris, C., Baltzopoulos, V. Predictability of in vivo changes in pennation angle of human tibialis anterior muscle from rest to maximum isometric dorsiflexion. Eur J Appl Physiol 79, 294–297 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050510
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050510