Abstract.
Background and objectives:
Self-reported health status measures reflect disease impact from the patient’s perspective. However, such measures are not designed for individual patient use and are rarely used to guide clinical practice. Nevertheless, if strong predictors of health status can be demonstrated in large datasets, these could be used to identify people at risk of poor health states and help target interventions. The aim of this study was to examine the predictive value of routinely collected socio-demographic variables on health status.
Method:
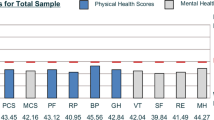
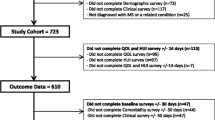
Data for 638 patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) on the eight health dimensions of the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) were collected either by a postal survey or hospital attendance and analysed by multiple regression analyses.
Results:
Several sociodemographic variables, such as unemployment and manual social class had some predictive value on health status, but the effect was not strong (maximum cumulative variance explained 53 %).
Conclusions:
Sociodemographic variables that we studied were limited predictors of health status in MS and are of limited value in guiding clinical practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riazi, A., Hobart, J.C., Fitzpatrick, R. et al. Socio-demographic variables are limited predictors of health status in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 250, 1088–1093 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-003-0160-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-003-0160-y