Abstract
Background
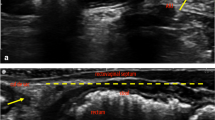
Anal ultrasound is helpful in assessing organic anorectal lesions, but its role in functional disease is still questionable. The purpose of the present study is to assess anal–vaginal–dynamic perineal ultrasonographic findings in patients with obstructed defecation (OD) and healthy controls.
Materials and methods
Ninety-two consecutive patients (77 women; mean age 51 years; range 21–71) with symptoms of OD were retrospectively evaluated. All patients underwent digital exploration, endoanal and endovaginal ultrasound (US) with rotating probe. Forty-one patients underwent dynamic perineal US with linear probe. Anal manometry and defaecography were performed in 73 and 43 patients, respectively. Ultrasonographic findings of 92 patients with symptoms of OD were compared to 22 healthy controls. Anismus was defined on US when the difference in millimetres between the distance of the inner edge of the puborectalis muscle posteriorly and the probe at rest and on straining was less then 5 mm. Sensitivity and specificity were calculated by assuming defaecography as the gold standard for intussusception and rectocele and proctoscopy for rectal internal mucosal prolapse. Since no gold standard for the diagnosis of anismus was available in the literature, the agreement between anal US and all other diagnostic procedures was evaluated.
Results
The incidence of anismus resulted significantly higher (P < 0.05) in OD patients than healthy controls on anal (48 vs 22%), vaginal (44 vs 21%), and dynamic perineal US (53 vs 22%). A significantly higher incidence of rectal internal mucosal prolapse was observed in OD patients when compared to healthy controls on both anal (61.9 vs 13.6%, P < 0.0001) and dynamic perineal US (51.2 vs.9% P = 0.001). For the diagnosis of rectal internal mucosal prolapse, anal US had a 100% sensitivity and specificity. For diagnosis of rectal intussusception, anal US had an 83.3% sensitivity and 100% specificity and perineal US had a 66.6% sensitivity and 100% specificity. In the diagnosis of anismus, anal ultrasonography resulted in agreement with perineal and vaginal US, manometry, defaecography, and digital exam (P < 0.05). Other lesions detected by US in patients with OD include solitary rectal ulcer, rectocele and enterocele. Damage of internal and/or external sphincter was diagnosed at anal US in 19/92 (20%) patients, all continent and with normal manometric values.
Conclusion
Anal, vaginal and dynamic perineal ultrasonography can diagnose or confirm many of the abnormalities seen in patients with OD. The value of the information obtained by this non-invasive test and its role in the diagnostic algorithm of OD is yet to be defined.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karlbom U, Lundin E, Graf W, Pahlman L (2004) Anorectal physiology in relation to clinical subgroups of patients with severe constipation. Colorectal Dis 6:343–349
Klingele CJ, Bharucha AE, Fletcher JG, Gebhart JB, Riederer SG, Zinsmeister AR (2005) Pelvic organ prolapse in defecatory disorders. Obstet Gynecol 106:315–320
Devroede G (1990) Irritable bowel syndrome: intestinal disease or personality disturbance? Gastroenterol Clin Biol 14:3C–4C
Dodi G, Pietroletti R, Milito G, Binda G, Pescatori M (2003) Bleeding, incontinence, pain and constipation after STARR transanal double stapling rectotomy for obstructed defecation. Tech Coloproctol 7:148–153
Roman H, Michot F (2005) Long-term outcomes of transanal rectocele repair. Dis Colon Rectum 48:510–517
Wexner SD, Zbar AP, Pescatori M (eds) (2005) Complex anorectal disorders. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Sultan AH, Loder PB, Bartram CI, Kamm MA, Hudson CN (1994) Vaginal endosonography. New approach to image the undisturbed anal sphincter. Dis Colon Rectum 37:1296–1299
Beer-Gabel M, Teshler M, Barzilai N, Lurie Y, Malnick S, Bass D et al (2002) Dynamic transperineal ultrasound in the diagnosis of pelvic floor disorders: pilot study. Dis Colon Rectum 45:239–248
Bouchoucha M, Devroede G, Arsac M (2004) Anismus: a marker of multi-site functional disorders? Int J Colorectal Dis 19:374–379
Chen HH, Iroatulam A, Alabaz O, Weiss EG, Nogueras JJ, Wexner SD (2001) Associations of defecography and physiologic findings in male patients with rectocele. Tech Coloproctol 5:157–161
Bartram CI (1992) Anal endosonography. Ann Gastroenterol Hepatol (Paris) 28:185–189
Rao SS, Mudipalli RS, Stessman M, Zimmerman B (2004) Investigation of the utility of colorectal function tests and Rome II criteria in dyssynergic defecation (Anismus). Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:589–596
Hosie GP, Spitz L (1997) Idiopathic constipation in childhood is associated with thickening of the internal anal sphincter. J Pediatr Surg 32:1041–1044
Fransioli A, Weber B, Cunningham M, Roche B, Marti MC, Hadengue A (1996) Dynamic valuation of puborectalis muscle function by external perineal sonography. Tech Coloproctol 4:125–129
Bouchoucha M, Devroede G, Renard P, Arhan P, Barbier JP, Cugnenc PH (1995) Compartmental analysis of colonic transit reveals abnormalities in constipated patients with normal transit. Clin Sci 89:129–135
Pescatori M, Maria G, Anastasio G, Rinallo L (1989) Anal manometry improves the outcome of surgery for fistula-in-ano. Dis Colon Rectum 32:588–592
Mahieu P, Pringot J, Bodart P (1984) Defecography: II. Contribution to the diagnosis of defecation disorders. Gastrointest Radiol 9:253–261
Halligan S, Bartram CI, Park HJ, Kamm MA (1995) Proctographic features of anismus. Radiology 197:679–682
Park UC, Choi SK, Piccirillo MF, Verzaro R, Wexner SD (1996) Patterns of anismus and the relation to biofeedback therapy. Dis Colon Rectum 39:768–773
Maria G, Sganga G, Civello IM, Brisinda G (2002) Botulinum neurotoxin and other treatments for fissure-in-ano and pelvic floor disorders. Br J Surg 89:1620–1621
Voderholzer WA, Neuhaus DA, Klauser AG, Tzavella K, Muller-Lissner SA, Schindlbeck NE (1997) Paradoxical sphincter contraction is rarely indicative of anismus. Gut 41:258–262
Roche B, Deleaval J, Fransioli A, Marti MC (2001) Comparison of transanal and external perineal ultrasonography. Eur Radiol 11:1165–1170
Pescatori M, Boffi F, Russo A, Zbar AP (2006) Complications and recurrence after excision of rectal internal mucosal prolapse for obstructed defaecation. Int J Colorectal Dis 21:160–165
Solomon MJ, Rex J, Eyers AA, Stewart P, Roberts R (2000) Biofeedback for fecal incontinence using transanal ultrasonography: novel approach. Dis Colon Rectum 43:788–792
Piloni V, Spazzafumo L (2005) Evacuation sonography. Tech Coloproctol 9:119–126
Beer Gabel M, Teshler M, Schechtman E, Zbar AP (2004) Dynamic tranperineal ultrasound vs. defecography in patients with evacuatory difficulty: a pilot study. Int J Colorectal Dis 19:60–67
Nielsen MB, Rasmussen OO, Pedersen JF, Christiansen J (1993) Anal endosonographic findings in patients with obstructed defecation. Acta Radiol 34:35–38
Marshall M, Halligan S, Fotheringham T, Bartram CI, Nicholls RJ (2002) Predictive value of internal anal sphincter thickness for diagnosis of rectal intussusception in patients with solitary rectal ulcer syndrome. Br J Surg 89:1281–1285
Dvorkin LS, Chan CL, Knowles CH, Williams NS, Lunniss PJ, Scott SM (2004) Anal sphincter morphology in patients with full-thickness rectal prolapse. Dis Colon Rectum 47:198–203
Cola B, Cuicchi D, Dalla Via B, Lecce F (2005) Endosonographic pattern of solitary polypoid rectal ulcer. Tech Coloproctol 1:71–72
Bollard RC, Gardiner A, Lindow S, Phillips RKS, Duthie GS (2002) Normal female anal sphincter: difficulties in interpretation explained. Dis Colon Rectum 45:171–175
Sultan AH, Kamm MA, Hudson CN, Thomas JM, Bartram CI (1993) Anal-sphincter disruption during vaginal delivery. N Engl J Med 329:1905–1911
Tjandra JJ, Lim JF, Hiscock R, Rajendra P (2004) Injectable silicone biomaterial for fecal incontinence caused by internal anal sphincter dysfunction is effective. Dis Colon Rectum 47:2138–2146
Senagore A, Gallagher T, Hull T, Ferrara A (2005) A shor-term assessment of the efficacy of the STARR procedure for obstructed defecation syndrome. Dis Colon Rectum 48:634
Halligan S, Bartram CI, Hall C, Wingate DJ (1996) Enterocele revealed by simultaneous evacuation proctografy and peritoneography: does “defecation blok” exist? Am J Roentgenol 167:461–466
Lienemann A, Anthuber CJ, Baron A, Reiser M (1996) Dynamic MR colpocystorectography. A new methods for evaluating pelvic floor descent and genital prolapse. Aktuelle Radiol 6:182–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brusciano, L., Limongelli, P., Pescatori, M. et al. Ultrasonographic patterns in patients with obstructed defaecation. Int J Colorectal Dis 22, 969–977 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-006-0250-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-006-0250-2