Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to quantify the severity of late effects by a simple numerical score (late effects severity score, LESS) in patients who received radiochemotherapy for medulloblastoma or ependymoma. The LESS was correlated with neurocognitive and quality of life (QoL) outcomes.
Patients and methods
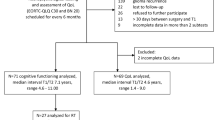
The LESS was calculated by assigning 0, 1, or 2 points within each of four different categories (neurology, endocrine, visual/auditory, others). Twenty-three patients with medulloblastoma (n = 18) or ependymoma (n = 5) underwent extensive neurocognitive and QoL testing at a median of 56 months (range, 1–174) after the end of treatment. Eight patients with low-grade glioma (LGG) who underwent tumor resection only served as control group.
Results
Patients with medulloblastoma/ependymoma had significantly higher LESS and significantly lower Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)/Wechsler Intelligence Scales for Children (WISC) scores compared to patients with LGG. There was no statistically significant correlation between neurocognitive performance and QoL. The total LESS was negatively correlated with WAIS/WISC, attention, concentration, and verbal learning scores. Comparison of QoL and late effects in patients with medulloblastoma/ependymoma demonstrated a significant negative correlation only for neurological late effects and the KINDL score suggesting that younger patients with more severe late effects reported on a worse QoL.
Conclusions
This LESS seems to be a simple and practical tool to quantify late effects in former brain tumor patients. Although both groups differ significantly with regard to neurocognitive parameters and severity of late effects, this does not apply for all QoL outcomes. Neurological late effects seem to be most predictive for an impaired QoL in younger children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, Filiberti A, Flechtner H, Fleishman SB, de Haes JC, Kaasa S, Klee MC, Osoba D, Razavi D, Rofe PB, Schraub S, Sneeuw KC, Sullivan M, Takeda F (1993) The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:365–376
Allen JC (1978) The effects of cancer therapy on the nervous system. J Pediatr 93:903–909
Benesch M, Lackner H, Sovinz P, Suppan E, Schwinger W, Eder HG, Dornbusch HJ, Moser A, Triebl-Roth K, Urban C (2006) Late sequela after treatment of childhood low-grade gliomas: a retrospective analysis of 69 long-term survivors treated between 1983 and 2003. J Neurooncol 78:199–205
Bhat SR, Goodwin TL, Burwinkle TM, Lansdale MF, Dahl GV, Huhn SL, Gibbs IC, Donaldson SS, Rosenblum RK, Varni JW, Fisher PG (2005) Profile of daily life in children with brain tumors: an assessment of health-related quality of life. J Clin Oncol 23:5493–5500
Brickenkamp R (1983) Test d2. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Buchanan GR, Adix L (2002) Grading of hemorrhage in children with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Pediatr 141:683–688
Calaminus G, Kiebert G (1999) Studies on health-related quality of life in childhood cancer in the European setting: an overview. Int J Cancer (Suppl) 12:83–86
Copeland DR, deMoor C, Moore BD 3rd, Ater JL (1999) Neurocognitive development of children after a cerebellar tumor in infancy: a longitudinal study. J Clin Oncol 17:3476–3486
Danoff BF, Cowchock FS, Marquette C, Mulgrew L, Kramer S (1982) Assessment of the long-term effects of primary radiation therapy for brain tumors in children. Cancer 49:1580–1586
Gajjar A, Chintagumpala M, Ashley D, Kellie S, Kun LE, Merchant TE, Woo S, Wheeler G, Ahern V, Krasin MJ, Fouladi M, Broniscer A, Krance R, Hale GA, Stewart CF, Dauser R, Sanford RA, Fuller C, Lau C, Boyett JM, Wallace D, Gilbertson RJ (2006) Risk-adapted craniospinal radiotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy and stem-cell rescue in children with newly diagnosed medulloblastoma (St Jude Medulloblastoma-96): long-term results from a prospective, multicenter trial. Lancet Oncol 7:813–820
George AP, Kuehn SM, Vassilyadi M, Richards PM, Parlow SE, Keene DL, Ventureyra EC (2003) Cognitive sequelae in children with posterior fossa tumors. Pediatr Neurol 28:42–47
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, Sanz M, Vallespi T, Hamblin T, Oscier D, Ohyashiki K, Toyama K, Aul C, Mufti G, Bennett J (1997) International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 89:2079–2088
Grill J, Renaux VK, Bulteau C, Viguier D, Levy-Piebois C, Sainte-Rose C, Dellatolas G, Raquin MA, Jambaqué I, Kalifa C (1999) Long-term intellectual outcome in children with posterior fossa tumors according to radiation doses and volumes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45:137–145
Helmstaedter C, Durwen HF (1990) VLMT: Verbaler Lern- und Merkfähigkeitstest. Ein praktikables und differenziertes Instrumentarium zur Prüfung der verbalen Gedächtnisleistung. Schweiz Arch Neurol Psychiatr 141:21–30
Hoppe-Hirsch E, Renier D, Lellouch-Tubiana A, Sainte-Rose C, Pierre-Kahn A, Hirsch JF (1990) Medulloblastoma in childhood: progressive intellectual deterioration. Childs Nerv Syst 6:60–65
Horzic M, Kopljar M, Cupurdija K, Bielen DV, Vergles D, Lackovic Z (2007) Comparison of P-POSSUM and Cr-POSSUM scores in patients undergoing colorectal cancer resection. Arch Surg 142:1043–1048
Johnson DL, McCabe MA, Nicholson HS, Joseph AL, Getson PR, Byrne J, Brasseux C, Packer RJ, Reaman G (1994) Quality of long-term survival in young children with medulloblastoma. J Neurosurg 80:1004–1010
Kessler J, Schaaf A, Mielke R (1993) Der fragmentierte Bildertest. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Kleihues P, Burger PC, Scheithauer BW (1993) Histological typing of tumours of the central nervous system, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Kortmann RD, Kühl J, Timmermann B, Mittler U, Urban C, Budach V, Richter E, Willich N, Flentje M, Berthold F, Slavc I, Wolff J, Meisner C, Wiestler O, Sörensen N, Warmuth-Metz M, Bamberg M (2000) Postoperative neoadjuvant chemotherapy before radiotherapy as compared to immediate radiotherapy followed by maintenance chemotherapy in the treatment of medulloblastoma in childhood: results of the German prospective randomized trial HIT ’91. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:269–279
Lackner H, Benesch M, Schagerl S, Kerbl R, Schwinger W, Urban C (2000) Prospective evaluation of late effects after childhood cancer therapy with a follow-up over 9 years. Eur J Pediatr 159:750–758
Li FP, Winston KR, Gimbrere K (1984) Follow-up of children with brain tumors. Cancer 54:135–138
Maddrey AM, Bergeron JA, Lombardo ER, McDonald NK, Mulne AF, Barenberg PD, Bowers DC (2005) Neuropsychological performance and quality of life of 10 year survivors of childhood medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 72:245–253
Maunsell E, Pogany L, Barrera M, Shaw AK, Speechley KN (2006) Quality of life among long-term adolescent and adult survivors of childhood cancer. J Clin Oncol 43:2527–2535
Mostow EN, Byrne J, Connelly RR, Mulvihill JJ (1991) Quality of life in long-term survivors of CNS tumors of childhood and adolescence. J Clin Oncol 9:592–599
Mulhern RK, Kepner JL, Thomas PR, Armstrong FD, Friedman HS, Kun LE (1998) Neuropsychologic functioning of survivors of childhood medulloblastoma randomized to receive conventional or reduced-dose craniospinal irradiation: a Pediatric Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 16:1723–1728
Mulhern RK, Merchant TE, Gajjar A, Reddick WE, Kun LE (2004) Late neurocognitive sequelae in survivors of brain tumors in childhood. Lancet Oncol 5:399–408
Needle MN, Goldwein JW, Grass J, Cnaan A, Bergman I, Molloy P, Sutton L, Zhao H, Garvin JH Jr, Phillips PC (1997) Adjuvant chemotherapy for the treatment of intracranial ependymoma of childhood. Cancer 80:341–347
Packer RJ, Gurney JG, Punyko JA, Donaldson SS, Inskip PD, Stovall M, Yasui Y, Mertens AC, Sklar CA, Nicholson HS, Zeltzer LK, Neglia JP, Robison LL (2003) Long-term neurologic and neurosensory sequelae in adult survivors of a childhood brain tumor: Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J Clin Oncol 21:3255–3261
Peris-Bonet R, Martínez-García C, Lacour B, Petrovich S, Giner-Ripoll B, Navajas A, Steliarova-Foucher E (2006) Childhood central nervous system tumours—incidence and survival in Europe (1978–1997): report from Automated Childhood Cancer Information System project. Eur J Cancer 42:2064–2080
Ravens-Sieberer U, Bullinger M (1998) Assessing health-related quality of life in chronically ill children with the German KINDL: first psychometric and content analytical results. Qual Life Res 7:399–407
Ribi K, Relly C, Landolt MA, Alber FD, Boltshauser MA, Grotzer MA (2005) Outcome of medulloblastoma in children: long-term complications and quality of life. Neuropediatrics 36:357–365
Robertson PL, Zeltzer PM, Boyett JM, Rorke LB, Allen JC, Geyer JR, Stanley P, Li H, Albright AL, McGuire-Cullen P, Finlay JL, Stevens KR Jr, Milstein JM, Packer RJ, Wisoff J (1998) Survival and prognostic factors following radiation therapy and chemotherapy for ependymomas in children: a report of the Children’s Cancer Group. J Neurosurg 88:695–703
Rousseau P, Habrand JL, Sarrazin D, Kalifa C, Terrier-Lacombe MJ, Rekacewicz C, Rey A (1994) Treatment of intracranial ependymomas of children: review of a 15-year experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 28:381–386
Tewes U (1994) Hamburg-Wechsler Intelligenztest für Erwachsene-Revision 1991. HAWIE-R. 2. korrigierte Auflage. Hans Huber, Bern
Tewes U (1983) Hamburg-Wechsler Intelligenztest für Kinder, Revision 1983. Hans Huber, Bern
Timmermann B, Kortmann RD, Kühl J, Meisner C, Slavc I, Pietsch T, Bamberg M (2000) Combined postoperative irradiation and chemotherapy for anaplastic ependymomas in childhood: results of the German prospective trials HIT 88/89 and HIT 91. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:287–295
Walter AW, Mulhern RK, Gajjar A, Heideman RL, Reardon D, Sanford RA, Xiong X, Kun LE (1999) Survival and neurodevelopmental outcome of young children with medulloblastoma at St Jude Children’s Research Hospital. J Clin Oncol 17:3720–3728
Zeltzer PM, Boyett JM, Finlay JL, Albright AL, Rorke LB, Milstein JM, Allen JC, Stevens KR, Stanley P, Li H, Wisoff JH, Geyer JR, McGuire-Cullen P, Stehbens JA, Shurin SB, Packer RJ (1999) Metastasis stage, adjuvant treatment, and residual tumor are prognostic factors for medulloblastoma in children: conclusions from the Children’s Cancer Group 921 randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 17:832–838
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Katharina Spiegl and Anita Winter contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benesch, M., Spiegl, K., Winter, A. et al. A scoring system to quantify late effects in children after treatment for medulloblastoma/ependymoma and its correlation with quality of life and neurocognitive functioning. Childs Nerv Syst 25, 173–181 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0742-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0742-1