Abstract
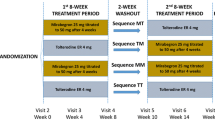
Overactive bladder (OAB) has a significant impact on a patient’s health-related quality of life (HRQoL). This study assessed the HRQoL of Japanese OAB patients following 12 weeks’ treatment with tolterodine extended release (ER) or oxybutynin. A total of 293 patients with symptoms of OAB were randomized for treatment with tolterodine ER 4 mg once daily (n=114), oxybutynin 3 mg three times daily (n=122) or a placebo (n=57). Treatment efficacy and safety assessments were made over the 12-week period. HRQoL was assessed using the King’s Health Questionnaire (KHQ). Patients receiving tolterodine ER or oxybutynin showed a significant (P<0.05) improvement in the Incontinence Impact, Role Limitations and most other KHQ domains compared with the placebo. These changes in HRQoL corresponded with significant (P<0.05) improvements in micturition diary variables for patients receiving tolterodine ER and oxybutynin compared with placebo. Our findings demonstrate that Japanese OAB patients receiving tolterodine ER or oxybutynin experienced overall improvement in their quality of life.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams P, Kelleher CJ, Kerr LA, Rogers RG (2000) Overactive bladder significantly affects quality of life. Am J Managed Care 6 [Suppl]:S580–590
Bullinger M, Alonso J, Apolone G, Leplege A, Sullivan M, Wood-Dauphinee S, Gandek B, Wagner A, Aaronson N, Bech P, Fukuhara Kaasa S, Ware JEJr (1998) Translating health status questionnaires and evaluating their quality: the IQOLA Project approach. International Quality of Life Assessment. J Clin Epidemiol 51:913–923
Coyne K, Revicki D, Hunt T, Corey R, Stewart W, Bentkover J, Kurth H, Abrams P (2002) Psychometric validation of an overactive bladder symptom and health-related quality of life questionnaire: the OAB-q. Qual Life Res 11:563–574
Drutz HP, Appell RA, Gleason D, Klimberg I, Radomski S (1999) Clinical efficacy and safety of tolterodine compared to oxybutynin and placebo in patients with overactive bladder. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 10:283–289
Homma Y, Gotoh M, Ando T, Fukuhara S (1999) Development of Japanese version of QOL questionnaires for urinary incontinence. Jpn J Neurogenic Bladder 10:225–236
Homma Y, Ando T, Yoshida M, Takei M, Momokazu G, Ohkawa A, Kageyama S, Fukihara S (2002) Validation of Japanese version of QoL questionnaires for urinary incontinence. Jpn J Neurogenic Bladder 13:247–257
Homma Y, Paick JS, Lee JG, Kawabe K (2003) Clinical efficacy and tolerability of extended-release tolterodine and immediate-release oxybutynin in Japanese and Korean patients with overactive bladder: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. BJU Int 92:741–748
Kelleher CJ, Cardozo LD, Khullar V, Salvatore S (1997) A new questionnaire to assess the quality of life of urinary incontinent women. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 104:1374–1379
Kelleher CJ, Kreder KJ, Pleil AM, Burgess SM, Reese PR (2002) Long-term health-related quality of life of patients receiving extended release tolterodine for overactive bladder. Am J Man Care 8 [Suppl]:S616-S630
Kelleher CJ, Reese PR, Pleil AM, Okano GJ (2002) Health-related quality of life of patients receiving extended release tolterodine for overactive bladder. Am J Man Care 8 [Suppl]:S608-S615
Kobelt G, Kirchberger I, Malone-Lee J (1999) Quality-of-life aspects of the overactive bladder and the effect of treatment with tolterodine. BJU Int 83:583–590
Lee JG, Hong JY, Choo M-S, Kwon HY, Chung DY, Lee KS, Lee JY, Lee T (2002) Tolterodine: as effective but better tolerated than oxybutynin in Asian patients with symptoms of overactive bladder. Int J Urol 9:19–24
Nilvebrant L (2000) The mechanism of action of tolterodine. Rev Contemp Pharmacother 11:13–27
Pleil AM, Reese PR, Kelleher CJ, Okano GJ (2001) Health-related quality of life of patients with overactive bladder receiving immediate-release tolterodine. Health Econ Prev Care 2:69–75
Pleil AM, Reese PR, Slayton T, Okano GJ (2001) Minimally perceived difference of the King’s Health Questionnaire: a comparison of results from two studies. Drug Information Association Quality of Life Conference, Hilton Head, South Carloina, March 2001, Abstract
Reese PR, Pleil AM, Slayton T, Okano GJ (2003) Multinational study of the reliability and validity of the King’s Health Questionnaire in patients with overactive bladder. QoL Res (in press)
Sankoh AJ, Huque MF, Dubey SD (1997) Some comments on frequently used multiple endpoint adjustment methods in clinical trials. Stat Med 16:2529–2542
Stewart W, Herzog R, Wein A, Cundiff G, Norton P, Corey R, on behalf of the NOBEL Program Research Team (2001) Prevalence and impact of overactive bladder in the U.S.: results from the NOBLE program. 22nd Annual Meeting of the American Urogynecologic Society, Chicago, 25–27 October 2001, Abstract
Van der Vaart CH, De Leeuw JRJ, Roovers JPWR, Heintz AP (2002) The effects of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder symptoms on quality of life in young women. BJU Int 90:544–549
Van Kerrebroeck P, Kreder K, Jonas U, Zinner N, Wein A, on behalf of the Tolterodine Study Group (2001) Tolterodine once-daily: superior efficacy and tolerability in the treatment of the overactive bladder. Urology 57:414–421
Wein AJ, Rovner ES (1999) The overactive bladder: an overview for primary care health providers. Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud 44:56–66
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a grant from Pfizer Inc NY, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Homma, Y., Kawabe, K. Health-related quality of life of Japanese patients with overactive bladder treated with extended-release tolterodine or immediate-release oxybutynin: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. World J Urol 22, 251–256 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-004-0455-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-004-0455-3