Abstract
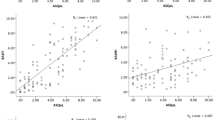
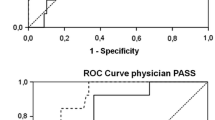
The aim of this study was to compare the performance characteristics of two answer modalities for BASDAI and BASFI in patients with AS and to show validity and reliability of NRS in Turkish version. BASDAI and BASFI were simultaneously employed with a 10-cm VAS and an 11-point NRS. Internal consistency was assessed by using Cronbach’s alpha coefficients. Testing was performed on baseline and next day under standardized conditions. Construct validity was determined by association of these measures with ASDAS, DFI, global disease activity, pain scores, ASQOL, HAQ, and SF-36. We also tested the ability of NRS version of BASDAI and BASFI to detect changes. A total 114 patients with AS according to the modified New York criteria were included. There was a good agreement between the total scores of each instrument on day 0 (ICC values were 0.894–0.934). Scores of the both answering modality of each instrument were correlated with ASDAS-CRP, and the scores of DFI, patient global assessment of disease activity and patient-reported pain, ASQOL, HAQ. Response time for BASDAI and BASFI was significantly shorter in NRS answer modality (P < 0.001). Our patients found NRS modality more comprehensible and easier to understand (P < 0.001). Our results showed the validity of NRS version of BASDAI and BASFI and provided an evidence for using these questionnaires in 11-point NRS answer modality in Turkish AS patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Linden S, van der Heijde D (1998) Ankylosing spondylitis. Clinical features. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 24(4):663–676, vii
Khan M (1998) Ankylosing spondylitis: clinical aspects. In: Calin A (ed) The spondyloarthritides. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 27–40
Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A (1994) A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol 21(12):2286–2291
Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, Kennedy LG, O’Hea J, Mallorie P et al (1994) A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol 21(12):2281–2285
Hawker GA, Mian S, Kendzerska T, French M (2011) Measures of adult pain: visual analog scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63(Suppl 11):S240–S252
McCormack HM, Horne DJ, Sheather S (1988) Clinical applications of visual analogue scales: a critical review. Psychol Med 18(4):1007–1019
Rodriguez CS (2001) Pain measurement in the elderly: a review. Pain Manag Nurs 2(2):38–46
Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, Brandt J, Braun J, Burgos-Vargas R et al (2009) The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) handbook: a guide to assess spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68(Suppl 2):ii1–ii44
Van Tubergen A, Debats I, Ryser L, Londono J, Burgos-Vargas R, Cardiel MH et al (2002) Use of a numerical rating scale as an answer modality in ankylosing spondylitis-specific questionnaires. Arthritis Rheum 47(3):242–248
Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guillemin F, Ferraz MB (2000) Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25(24):3186–3191
Akkoc Y, Karatepe AG, Akar S, Kirazli Y, Akkoc N (2005) A Turkish version of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index: reliability and validity. Rheumatol Int 25(4):280–284
Karatepe AG, Akkoc Y, Akar S, Kirazli Y, Akkoc N (2005) The Turkish versions of the bath ankylosing spondylitis and dougados functional indices: reliability and validity. Rheumatol Int 25(8):612–618
van der Heijde D, Lie E, Kvien TK, Sieper J, Van den Bosch F, Listing J et al (2009) ASDAS, a highly discriminatory ASAS-endorsed disease activity score in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 68(12):1811–1818
Doward LC, Spoorenberg A, Cook SA, Whalley D, Helliwell PS, Kay LJ et al (2003) Development of the ASQoL: a quality of life instrument specific to ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 62(1):20–26
Ware JE, Kosinski M, Bayliss MS, McHorney CA, Rogers WH, Raczek A (1995) Comparison of methods for the scoring and statistical analysis of SF-36 health profile and summary measures: summary of results from the Medical Outcomes Study. Med Care 33(4 Suppl):AS264–AS279
Fries JF, Spitz P, Kraines RG, Holman HR (1980) Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 23(2):137–145
Streiner DL, Norman GR (eds) (1989) Health measurement scales: a practical guide to their development and use. Oxford Medical Publications, Oxford
Centor RM (1991) Signal detectability: the use of ROC curves and their analyses. Med Decis Making 11(2):102–106
Liao JJ (2010) Sample size calculation for an agreement study. Pharm Stat 9(2):125–132
Zochling J (2008) Assessment and treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: current status and future directions. Curr Opin Rheumatol 20(4):398–403
van der Heijde D, Calin A, Dougados M, Khan MA, van der Linden S, Bellamy N (1999) Selection of instruments in the core set for DC-ART, SMARD, physical therapy, and clinical record keeping in ankylosing spondylitis. Progress report of the ASAS Working Group. Assessments in Ankylosing Spondylitis. J Rheumatol 26(4):951–954
Price DD, McGrath PA, Rafii A, Buckingham B (1983) The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain 17(1):45–56
Scott J, Huskisson EC (1976) Graphic representation of pain. Pain 2(2):175–184
Scott JM, Anchor KN (1977) Male homosexual behavior and ego function strategies in the group encounter. J Clin Psychol 33(4):1079–1084
Williamson A, Hoggart B (2005) Pain: a review of three commonly used pain rating scales. J Clin Nurs 14(7):798–804
Kremer E, Atkinson JH, Ignelzi RJ (1981) Measurement of pain: patient preference does not confound pain measurement. Pain 10(2):241–248
Dixon JS (1986) Agreement between horizontal and vertical visual analogue scales. Br J Rheumatol 25(4):415–416
Jensen MP, Karoly P, Braver S (1986) The measurement of clinical pain intensity: a comparison of six methods. Pain 27(1):117–126
Snow S, Kirwan JR (1988) Visual analogue scales: a source of error. Ann Rheum Dis 47(6):526
Ogon M, Krismer M, Sollner W, Kantner-Rumplmair W, Lampe A (1996) Chronic low back pain measurement with visual analogue scales in different settings. Pain 64(3):425–428
Paice JA, Cohen FL (1997) Validity of a verbally administered numeric rating scale to measure cancer pain intensity. Cancer Nurs 20(2):88–93
Bird HA, Dixon JS (1987) The measurement of pain. Bailliere’s clinical rheumatology. 1(1):71–89
Hjermstad MJ, Fayers PM, Haugen DF, Caraceni A, Hanks GW, Loge JH et al (2011) Studies comparing Numerical Rating Scales, Verbal Rating Scales, and Visual Analogue Scales for assessment of pain intensity in adults: a systematic literature review. J Pain Symptom Manag 41(6):1073–1093
Madsen OR, Rytter A, Hansen LB, Suetta C, Egsmose C (2010) Reproducibility of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Indices of disease activity (BASDAI), functional status (BASFI) and overall well-being (BAS-G) in anti-tumour necrosis factor-treated spondyloarthropathy patients. Clin Rheumatol 29(8):849–854
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Mr. Sabri Erdem, PhD, Dokuz Eylul University Entrepreneurship, Business and economics Application and Research Centre for his assistance in improving our data analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This study was conducted with the approval of the local ethic committee at the study center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akad, K., Solmaz, D., Sari, I. et al. Performance of response scales of activity and functional measures of ankylosing spondylitis: numerical rating scale versus visual analog scale. Rheumatol Int 33, 2617–2623 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2789-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2789-x