Abstract
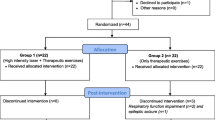
The aim of this clinical trial was to evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic MD on pain, functional capacity, muscle strength, quality of life, and depression in patients with subacromial impingement syndrome (SIS). A total of 40 inpatient subjects with definite SIS were included in this study. These patients were sequentially randomized into 2 groups. Group 1 (n = 20) received therapeutic MD. Group 2 (n = 20) was served as control group and received sham MD. Superficial heat and exercise program were given to both groups. Both of the programs were performed 5 times weekly for 3 weeks. Patients were assessed before treatment (BT), after treatment (AT), and at a 1-month follow-up (F). Outcome measures included visual analogue scale, goniometry, Shoulder Pain and Disability Index, Shoulder Disability Questionnaire, shoulder isokinetic muscle testing, handgrip strength, Short Form 36, and Beck Depression Index. The patients with SIS in each group had significant improvements in pain, shoulder ROM, disability, shoulder muscles and grip strength, quality of life, and depression AT and F when compared with their initial status (P < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference between the groups according to all the parameters regarding the change scores between AT–BT test and F–BT test (P > 0.05). A 2,450-MHz MD regimen showed no beneficial effects in patients with SIS, so the superficial heat and exercise program, as it is efficient, may be preferable for the treatment of SIS, alone.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van der Windt DA, Koes BW, de Jong BA, Bouter LM (1995) Shoulder disorders in general practice: incidence, patient characteristics, and management. Ann Rheum Dis 54:959–964
Ludewig PM, Cook TM (2000) Alterations in shoulder kinematics and associated muscle activity in people with symptoms of shoulder impingement. Phys Ther 80:276–291
Phadke V, Camargo PR, Ludewig PM (2009) Scapular and rotator cuff muscle function during arm elevation: a review of normal function and alterations with shoulder impingement. Rev Bras Fisioter 13:1–9
Camargo PR, Haik MN, Filho RB, Mattiello-Rosa SM, Salvini TF (2008) Bilateral deficits in muscle contraction parameters during shoulder scaption in patients with unilateral subacromial impingement syndrome. Isokinet Exerc Sci 16:93–99
MacDermid JC, Ramos J, Drosdowech D, Faber K, Patterson S (2004) The impact of rotator cuff pathology on isometric and isokinetic strength, function, and quality of life. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 13:593–598
Kamkar A, Irrgang JJ, Whitney SL (1993) Nonoperative management of secondary shoulder impingement syndrome. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 17:212–224
Bigliani LU, Levine WN (1997) Subacromial impingement syndrome. J Bone Jt Surg Am 79:1854–1868
American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (2001) AAOS clinical guideline on shoulder pain: support document. American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons, Rosemont
Uhl T, Carver TJ, Mattacola CG (2003) Shoulder musculature activation during upper extremity weight-bearing exercise. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 33:109–117
McClure PW, Bialker J, Neff N, Williams G, Karduna A (2004) Shoulder function and 3-dimensional kinematics in people with shoulder impingement syndrome before and after a 6-week exercise program. Phys Ther 84:832–848
Weber DC, Hoppe KM (2007) Physical agents modalities. In: Braddom RL (ed) Physical medicine and rehabilitation, 3rd edn. Saunders Elsevier, China, pp 459–477
Basford JR (1993) Physical agents. In: DeLisa JA, Gans BM (eds) Rehabilitation medicine: principles and practice, 2nd edn. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, pp 404–424
Huskisson EC, Jones J, Scott PJ (1976) Application of visual analogue scales to the measurement of functional capacity. Rheumatol Rehabil 15:185–187
Riddle DL, Rothstein JM, Lamb RL (1987) Goniometric reliability in a clinical setting: shoulder measurements. Phys Ther 67:668–673
Biçer A, Ankarali H (2010) Shoulder pain and disability index: a validation study in Turkish women. Singapore Med J 51(11):865–870
Van der Windt DA, Van der Heijden GJ, de Winter AF, Koes BW, Deville W, Bouter LM (1998) The responsiveness of the shoulder disability questionnaire. Ann Rheum Dis 57:82–87
David G, Magarey ME, Jones MA, Dvir Z, Turker KS, Sharpe M (2000) EMG and strength correlates of selected shoulder muscles during rotations of the glenohumeral joint. Clin Biomech 15:95–102
Dwyer GB, Davis SE (2005) ACSM’s Health-Related Physical Fitness Assessment Manual. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Kocyigit H, Aydemir O, Fisek G, Olmez N, Memis A (1999) Validity and reliability of Turkish version of Short form 36: a study of a patients with rheumatoid disorder. J Drug Ther 12:102–106
Hisli N (1988) The reliability and validity study of the beck depression inventory in a Turkish sample. Psikoloji Dergisi 6:118–122 (In Turkish)
Giombini A, Casciello GF, Di Cesare MC, Di Cesare A, Dragoni S, Sorrenti D (2001) A controlled study on the effects of hyperthermia at 434 MHz and conventional ultrasound upon muscle injuries in sport. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 41:521–527
Giombini A, Di Cesare A, Casciello GF, Sorrenti D, Dragoni S, Gabriele P (2002) Hyperthermia at 434 MHz in the treatment of overuse sport tendinopathies: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Int J Sports Med 23:207–211
Giombini A, Di Cesare A, Safran MR, Ciatti R, Maffulli N (2006) Short term effectiveness of hyperthermia for supraspinatus tendinopathy in athletes: A short term randomized controlled study. Am J Sports Med 34:1247–1253
Di Cesare A, Giombini A, Dragoni S, Agnello L, Ripani M, Saraceni VM, Maffulli N (2008) Calcific tendinopathy of the rotator cuff. Conservative management with 434 MHz local microwave diathermy (hyperthermia): a case study. Disabil Rehabil 30(20–22):1578–1583
Giombini A, Giovannini V, Di Cesare A, Pacetti P, Ichinoseki-Sekine N, Shiraishi M, Naito H, Maffulli N (2007) Hyperthermia induced by microwave diathermy in the management of muscle and tendon injuries. Br Med Bull 83:379–396
Spiegel TM, Hirschberg J, Taylor J, Paulus HE, Furst DE (1987) Heating rheumatoid knees to an intra-articular temperature of 42.1ºC. Ann Rheum Dis 46:716–719
Weinberger A, Abramonvici A, Fadilah R, Levy A, Giler S, Lev A (1990) The effect of local deep microwave hyperthermia on experimental zymosan-induced arthritis in rabbits. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 69:239–244
Giombini A, Di Cesare A, Ripani M, Maffulli N (2011) Localized hyperthermia induced by microwave diathermy in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:980–987
Neer CS (1983) Impingement lesions. Clin Orthop 173:70–77
Camargo PR, Avila MA, Oliveira AB, Asso NA, Benze BG, Salvini TF (2009) Shoulder abduction torque steadiness is preserved in subacromial impingement syndrome. Eur J Appl Physiol 106:381–387
Erol O, Ozcakar L, Celiker R (2008) Shoulder rotator strength in patients with stage I-II subacromial impingement: relationship to pain, disability, and quality of life. J Should Elbow Surg 17:893–897
Ludewig PM, Cook TM (2000) Alterations in shoulder kinematics and associated muscle activity in people with symptoms of shoulder impingement. Phys Ther 80:276–291
Phadke V, Camargo PR, Ludewig PM (2009) Scapular and rotator cuff muscle function during arm elevation: a review of normal function and alterations with shoulder impingement. Rev BrasFisioter 13:1–9
Tyler TF, Nahow RC, Nicholas SJ, McHugh MP (2005) Quantifying shoulder rotation weakness in patients with shoulder impingement J Should Elbow Surg 14:570–574
Asghari A, Julaeiha S, Godarsi M (2008) Disability and depression in patients with chronic pain: pain or pain-related beliefs? Arch Iran Med 11:263–269
Lombardı I Jr, Magrı AG, Fleury AM, Silva AC, Natour J (2008) Progressive resistance training in patients with shoulder impingement syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 59:615–622
Celik D, Akyuz G, Yeldan I (2009) Comparison of the effects of two different exercise program on pain in subacromial impingement syndrome. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 43(6):504–509
Michener LA, Walsworth MK, Burnet EN (2004) Effectiveness of rehabilitation for patients with subacromial impingement syndrome: a systematic review. J Hand Ther 17:221–223
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akyol, Y., Ulus, Y., Durmus, D. et al. Effectiveness of microwave diathermy on pain, functional capacity, muscle strength, quality of life, and depression in patients with subacromial impingement syndrome: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical study. Rheumatol Int 32, 3007–3016 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2097-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2097-2