Abstract
Purpose
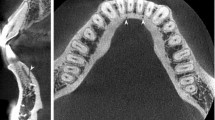
To investigate buccal perimandibular neurovascularisation associated with the mandibular accessory buccal foramina (ABF) which were detected using a limited cone-beam computed tomography (limited CBCT).
Methods
Five Japanese cadaveric mandibles had been examined using helical CT to investigate the presence or absence of ABF. Two mandibles indicating the presence of AMF were examined more minutely using a limited CBCT. Following the three-dimensional radiological observation of ABF, the mandibles were removed from the cadavers and dissected with referring to the findings of AMF on the limited CBCT images.
Results
Four ABF of the three mandibular sides, which were depicted with limited CBCT, had different perimandibular neurovascularisation. Three accessory foramina were associated with the following arteries: a branch of the submental, facial, and buccal artery, and one was associated with a branch of the mental nerve. A branch of the mental nerve re-entered the mandible through the accessory foramen after it exited from a mental foramen.
Conclusion
Limited CBCT is useful for pre-operative three-dimensional assessment of mandible since high-resolution analysis demonstrates not only the skeletal conditions but also the assessment and suggestions of perimandibular neurovascularisation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agthong S, Huanmanop T, Chentaez V (2005) Anatomical variations of the supraorbital, infraorbital, and mental foramina related to gender and side. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:800–804
Conception M, Rankow HJ (2000) Accessory branch of the mental nerve. J Endod 26:619–620
Cotton TP, Geisler TM, Holden DT, Schwartz SA, Schindler WG (2007) Endodontic applications of cone-beam volumetric tomography. J Endod 33:1121–1132
Estrela C, Bueno MR, Azevedo BC, Azevedo JR, Pécora JD (2008) A new periapical index based on cone beam computed tomography. J Endod 34:1325–1331
Flanagan D (2003) Important arterial supply of the mandible, control of an arterial hemorrhage and report of a hemorrhagic incident. J Oral Implantol 29:165–173
Gahleitner A, Hofschneider, Tepper G, Pretterklieber M, Schick S, Zauza K, Watzek G (2001) Lingual vascular canals of the mandible: evaluation with dental-CT. Radiology 220:186–189
Gershenson A, Nathan H, Luchansky E (1986) Mental foramen and mental nerve: changes with age. Acta Anat 126:21–28
Hamada Y, Kondoh T, Noguchi K, Iino M, Isono H, Ishii H, Mishima A, Kobayashi K, Seto K (2005) Application of limited cone beam computed tomography to clinical assessment of alveolar bone grafting: a preliminary report. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 42:128–137
Hanihara T, Ishida H (2001) Frequency variations of discrete cranial traits in major human populations. Vessel and nerve related variations. J Anat 199:273–287
Hu KS, Yun HS, Hur MS, Kwon HJ, Abe S, Kim HJ (2007) Branching patterns and intraosseous course of the mental nerve. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:2288–2294
Ilgüy D, Ilgüy M, Fisekcioglu E, Bayirli G (2009) Detection of jaw and root fractures using cone beam computed tomography: a case report. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 38:169–173
Jacobs R, Mraiwa N, vanSteenberghe D, Gijbels F, Quirynen M (2002) Appearance, location, course, and morphology of the mandibular incisive canal: an assessment on spiral CT scan. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 31:322–327
Jacobs R, Lambrichts I, Liang X, Martens W, Mraiwa N, Adriaesens P, Elan J (2007) Neurovascularization of the anterior jaw bones revised using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103:683–693
Kalpidis CD, Konstanrinidis AB (2005) Critical hemorrhage in the floor of the mouth during implant placement in the first mandibular premolar position: a case report. Implant Dent 14:117–123
Kalpidis CD, Setayesh RM (2004) Hemorrhaging associated with endosseous implant placement in the anterior mandible: a review of the literature. J Periodontol 75:631–645
Katakami K, Shimoda S, Kobayashi K, Kawasaki K (2008) Histological investigation of osseous changes of mandibular condyles with backscattered electron images. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 37:330–339
Katakami K, Mishima A, Shiozaki K, Shimoda S, Hamada Y, Kobayashi K (2008) Characteristics of accessory mental foramina observed on limited cone-beam CT images. J Endod 34:1441–1445
Katakami K, Mishima A, Kuribayashi A, Shimoda S, Hamada Y, Kobayashi K (2009) Anatomical characteristics of the mandibular lingual foramina observed on limited cone-beam CT images. Clin Oral Implants Res 20:386–390
Kawai T, Sato I, Yosue T, Takamori H, Sunohara M (2006) Anastomosis between the inferior alveolar artery branches and submental artery in human mandible. Surg Radiol Anat 28:130–308
Liang X, Jacobs R, Lambrichts I, Vandewalle G (2007) Lingual foramina on the mandibular midline revisited: a macroanatomical study. Clin Anat 20:246–251
Mardinger O, Manor Y, Mijiritsky E, Hirshberg A (2007) Lingual perimandibular vessels associated with life-threatening bleeding: an anatomic study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 22:127–131
Naitoh M, Hiraiwa Y, Aimiya H, Gotoh K, Ariji E (2009) Accessory mental foramen assessment using cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107:289–294
Patel S, Dawood A, Pitt Ford T, Whaites E (2007) The potential applications of cone beam computed tomography in the management of endodontic problems. Int Endod J 40:818–830
Przystańska A, Bruska M (2010) Accessory mandibular foramina: histological and immunohistochemical studies of their contents. Arch Oral Biol 55:77–80
Sawyer DR, Kiely ML, Pyle MA (1998) The frequency of accessory mental foramina in four ethnic groups. Arch Oral Biol 43:417–420
Serman NJ (1989) The mandibular incisive foramen. J Anat 167:195–198
Shankland WE 2nd (1994) The position of the mental foramen in Asian Indians. J Oral Implantol 20:118–123
Toh H, Kodama J, Ohmori T (1992) Anatomical study of the accessory mental foramen and the distribution of its nerve. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 69:85–88
Trikeriotis D, Paravalou E, Diamantopoulos P, Nikolaou D (2008) Anterior mandible canal communications: a potential portal of entry for tumour spread. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 37:125–129
Vandewalle G, Liang X, Jacobs R, Lambrichts I (2006) Macroanatomic and radiologic characteristics of the superior genial spinal foramen and its bony canal. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 21:581–586
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank Assistant Technologist Mr. Goh Matsubara of the Department of Anatomy-1, Tsurumi University School of Dental Medicine for supporting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuakami, K., Shiozaki, K., Mishima, A. et al. Detection of buccal perimandibular neurovascularisation associated with accessory foramina using limited cone-beam computed tomography and gross anatomy. Surg Radiol Anat 33, 141–146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0719-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0719-0