Abstract
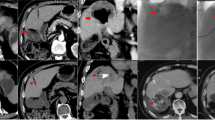
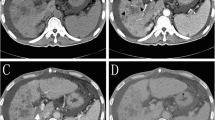
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the added role of a chemotherapeutic in transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The issue is of major importance since, as suggested by recent evidence, hypoxia or incomplete devascularization of the tumor is a potent stimulator of angiogenesis, and there are not many papers supplying level one evidence confirming the value of a chemotherapeutic. The hypothesis was that since drug-eluting bead (DEB)-TACE is standardized and reproducible, a comparison with bland TACE can readily reveal the potential value of the chemotherapeutic. Two groups were randomized in this prospective study: group A (n = 41) was treated with doxorubicin DEB-TACE, and group B (n = 43) with bland embolization. Patients were randomized for tumor diameter. Patients were embolized at set time intervals (2 months), with a maximum of three embolizations. Tumor response was evaluated using the EASL criteria and α-fetoprotein levels. At 6 months a complete response was seen in 11 patients (26.8%) in the DEB-TACE group and in 6 patients (14%) in the bland embolization group; a partial response was achieved in 19 patients (46.3%) and 18 (41.9%) patients in the DEB-TACE and bland embolization groups, respectively. Recurrences at 9 and 12 months were higher for bland embolization (78.3% vs. 45.7%) at 12 months. Time to progression (TTP) was longer for the DEB-TACE group (42.4 ± 9.5 and 36.2 ± 9.0 weeks), at a statistically significant level (p = 0.008). In conclusion, DEB-TACE presents a better local response, fewer recurrences, and a longer TTP than bland embolization with BeadBlock. However, survival benefit and bland embolization with smaller particles must be addressed in future papers to better assess the clinical value.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sergio A, Cristofori C, Cardin R et al (2008) Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): the role of angiogenesis and invasiveness. Am J Gastroenterol 103(4):914–921
Mamori S, Asakura T, Ohkawa K et al (2007) Survivin expression in early hepatocellular carcinoma and post-treatment with anti-cancer drug under hypoxic culture condition. World J Gastroenterol 13(40):5306–5311
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST et al (2008) Survivin: key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res 14(16):5000–5005
Bruix J, Llovet JM, Castells A et al (1998) Transarterial embolization versus symptomatic treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a randomized, controlled trial in a single institution. Hepatology 27:1578–1583
Covey AM, Maluccio MA, Schubert J et al (2006) Particle embolization of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Cancer 106(10):2181–2189
Maluccio MA, Covey AM, Ben Porat L et al (2008) Transcatheter arterial embolization with only particles for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19(6):862–869
Maluccio M, Covey AM, Gandhi R et al (2005) Comparison of survival rates after bland arterial embolization and ablation versus surgical resection for treating solitary hepatocellular carcinoma up to 7 cm. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:955–961
Brown KT, Nevins AB, Getrajdman GI et al (1998) Particle embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 9:822–828
Gamma C, Schepis F, Orlando A et al (2002) Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Radiology 224:47–54
Chang JM, Tzeng WS, Pan HB et al (1994) Transcatheter arterial embolization with or without cisplatin treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. A randomized controlled study. Cancer 74:2449–2453
Kawai S, Okamura J, Ogawa M (1992) Prospective and randomized clinical trial for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. A comparison of lipiodol-transcatheter arterial embolization with and without adiamycin (first cooperative study). The Cooperative Study Group for Liver Cancer Treatment of Japan. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 31(Suppl):S1–S6
Llovet JM, Real MI, Montana X et al (2002) Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 359:1734–1739
Llovet JM, Bruix J (2003) Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 37:429–442
Gerschwind JF, Ramsey DE, Choti MA et al (2003) Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clini Oncol 26(4):344–349
Brown DB, Geschwind JF, Soulen MC et al (2006) Society of interventional radiology position statement on chemoembolization of hepatic malignancies. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:217–230
Brown DB, Gould JG, Gervais DA et al (2007) Transcatheter therapy for hepatic malignancy: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18:1469–1478
Varela M, Real MI, Burrel M et al (2007) Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with drug eluting beads: efficacy and doxorubicin pharmacokinetics. J Hepatol 46(3):474–481
Poon R, Kuen Tso W, Roberta W et al (2007) A Phase I/II trial of chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma using a novel intra-arterial drug-eluting bead. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:1100–1108
Malagari K, Alexopoulou E, Chatzimichail K et al (2008) Transcatheter chemoembolization in the treatment of HCC in patients not eligible for curative treatments: midterm results of doxorubicin-loaded DC bead. Abdom Imaging 33(5):512–519
Kettenbach J, Stadler A, Katxler IV et al (2008) Drug-loaded microspheres for the treatment of liver cancer: review of current results. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 31:468–476
Lencioni R, Malagari K, Vogl T et al (2009) Prospective randomised study of doxorubicin in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma by drug-eluting bead embolisation—results of the PRECISION V study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol (in press)
Lewis AL, Gonzalez MV, Lloyd AW et al (2006) DC bead: in vitro characterization of a drug-delivery device for transarterial chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:335–342
Hong K, Khwaja A, Liapi E et al (2006) New intra-arterial drug delivery system for the treatment of liver cancer: preclinical assessment in a rabbit model of liver cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:2563–2567
Lewis AL, Taylor RR, Hall B et al (2006) Pharmacokinetic and safety study of doxorubicin-eluting Beads in a porcine model of hepatic arterial embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17(8):1335–1343
Forner A, Ayuso C, Varela M et al (2009) Evaluation of tumor response after locoregional therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: Are response evaluation criteria in solid tumors reliable? Cancer 115(3):616–623
Kalayci C, Johnson PJ, Raby N et al (1990) Intraarterial adriamycin and lipiodol for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparison with intravenous adriamycin. J Hepatol 11:349–353
Arora AS, deGroen PC, Croall DE et al (1996) Hepatocellular carcinoma cells during anoxia by preventing phospholipase-mediated activation. J Cell Physiol 167:434–442
Wang XW, Jia L, Sun Z (1997) Interactive effects of p53 tumor suppressor gene and hepatitis B virus in hepatocellular carcinoma. In: Arroyo V, Bosch J, Bruguera M, Rodés J et al (eds) Therapy in liver diseases. The pathophysiological basis of therapy. Masson, Barcelona, pp 471–478
Osuga K, Khankan AA, Hori S et al (2002) Transarterial embolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma with use of superabsorbent polymer microspheres: initial experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13:929–934
Osuga K, Hori S, Hiraishi K et al (2008) Bland embolization using superabsorbent polymer microspheres. CarcioVasc Interv Radiol 31:1108–1116
Kobayashi N, Ishii M, Ueno Y et al (1999) Coexpression of Bcl-2 protein and vascular endothelial growth factor in hepatocellular carcinomas treated by chemoembolization. Liver 19:25–31
Gupta S, Kobayashi S, Phongkitkarun S et al (2006) Effect of transcatheter hepatic arterial embolization on angiogenesis in an animal model. Invest Radiol 41:516–521
Virmani S, Rhee TK, Ryu RK et al (2008) Comparison of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression before and after transcatheter arterial embolization in rabbit VX2 liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19(10):1483–1489
Rhee TK, Young JY, Larson AC et al (2007) Effect of transcatheter arterial embolization on levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in rabbit VX2 liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18(5):639–645
Liao XF, Yi JL, Li XR et al (2004) Angiogenesis in rabbit hepatic tumor after transcatheter arterial embolization. World J Gastroenterol 10(13):1885–1889
Li X, Feng GS, Zheng CS et al (2003) Influence of transarterial chemoembolization on angiogenesis and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in rat with Walker-256 transplanted hepatoma: an experimental study. World J Gastroenterol 9(11):2445–2449
Rand T, Loewe Ch, Schoder M et al (2006) Arterial embolization of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with use of microspheres, lipiodol and cyanoacrulate. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 28:313–318
Lee KH, Liapi E, Vossen JA et al (2008) Distribution of iron oxide-containing Embosphere particles after transcatheter arterial embolization in an animal model of liver cancer: evaluation with MR imaging and implication for therapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19(10):1490
Brown K (2004) Fatal pulmonary complications after arterial embolization with 40–120 μm tris-acryl gelatin microspheres. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15:197–200
Ngan H, Peh WCG (1997) Arteriovenous shunting in hepatocellular carcinoma: its prevalence and clinical significance. Clin Radiol 52:36–40
Kobayashi S, Nakanuma Y, Terada T et al (1993) Postmortem survey of bile duct necrosis and biloma in hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization therapy: relevance to microvascular damages of peribiliary capillary plexus. Am J Gastroenterol 88(9):1410–1415
Malagari K, Chatzimichael K, Alexopoulou E et al (2008) Transarterial chemoembolization of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with drug eluting beads: results of an open-label study of 62 patients. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 31(2):269–280
Amesur NB, Zajko AB, Carr BI (2008) Chemo-embolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with different sizes of embolization particles. Dig Dis Sci 53(5):1400–1404
Brown DB, Pilgram TK, Darcy MD et al (2005) Hepatic arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of survival rates with different embolic agents. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:1661–1666
Kirschhoff TD, Rudolph KL, Layer G et al (2006) Chemooclusion vs. chemoperfusion for treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized trial. EJSO 32:201–207
Zhou Z-H, Liu SL, Chen W-W et al (2007) Combined therapy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Radiol 80:194–201
Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S et al (2006) Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcimona. J Clin Oncol 24(26/10):4293–4300
Uka K, Aikata H, Takaki S, Miki D et al (2007) Pretreatment predictor of response, time to progression, and survival to intraarterial 5-fluorouracil/interferon combination therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 42(10):845–853
Kanai T, Hirohaxhi S, Upton M et al (1987) Pathology of small hepatocellular carcinoma: a proposal for a new classification. Cancer 60:810–819
Yuki K, Hirohashi S, Sakamoto M et al (1990) Growth and spread of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review of 240consecutive autopsy cases. Cancer 66:2174–2179
Ngan H, Lai C, Fan S et al (1996) Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: four year follow-up. J Vasc Interv Radiol 7:419–425
Tezuka M, Hayashi K, Okada Y et al (2009) Therapeutic results of computed tomography guided transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for local recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after initial transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; the results of 85 recurrent tumors in 35 patients. Dig Dis Sci 54:661–669
Hayashi K, Tezuka M, Irie T et al (2007) Local therapeutic results of computed tomography-guided transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: the results for 265 tumors in 79 patients. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 30:1144–1155
Murakami T, Ishimaru H, Sakamoto I et al (2007) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: rate and risk factors for local recurrence. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 30(4):696–704
Komorizono Y, Oketani M, Sako K et al (2003) Risk factors for local recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma tumors after a single session, single application of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Cancer 97(5):1253–1262
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L et al (2005) Early stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: long term results of percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology 234:961–967
Llovet JM, Di Biscerglie AM, Bruix J et al (2008) For the panel of experts in HCC-Design Clinical Trials Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(10):698–711
Llovet JM, Di Bisceglie AM, Bruiz J et al (2008) Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(10):698–711
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malagari, K., Pomoni, M., Kelekis, A. et al. Prospective Randomized Comparison of Chemoembolization with Doxorubicin-Eluting Beads and Bland Embolization with BeadBlock for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33, 541–551 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9750-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9750-0