Abstract
Background
Breast and chest wall disfiguration attributable to a funnel chest is an aesthetically and sometimes functionally debilitating deformity requiring surgical correction. Whereas extensive and combined deformities of the ventral chest wall are classically corrected using a so-called minimally invasive repair of the pectus excavatum, a modified Ravitch repair, or the minimized Erlangen repair, plastic surgeons are mostly challenged with alloplastic implant corrections of mild funnel chests. The authors have introduced an endoscopic method for placement of customized implants to restore the visible and nonfunctionally disturbing deformation of mild funnel chests when only the sternal plate is involved. This study compared these different plastic surgical and thoracic surgical approaches in a multicenter experience to develop a clinical algorithm and to identify those patients not requiring bony correction but rather alloplastic endoscopic implant correction alone.
Methods
Patients with deformed rib cages and sternal plates were treated with the Erlangen minimally invasive procedure or a modified Ravitch procedure. For deformities involving the sternal bones only, endoscopically assisted minimally invasive implantation of silastic implants was performed.
Results
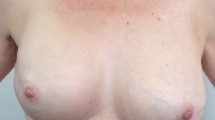
Between 1987 and 2003, 599 patients with a pectus excavatum deformity were treated surgically by the authors’ group. Between 1999 and 2003, 515 patients underwent surgery using the Erlangen minimally invasive repair technique at Friedrich–Alexander University–Erlangen. In addition, 84 patients underwent surgery at the Freiburg University Medical Center. In the current series, 79 patients underwent surgery using the modified Ravitch method. The mean patient age was 20.5 years (range, 3–54 years), and the rate of postoperative relapses was 5%. The findings showed that 73% of the patients judged the aesthetic result as excellent to good, and 20% were satisfied. In contrast, only five patients were suitable for soft tissue augmentation only. Two of these patients in the initial period received custom implants presternally via classical transverse skin incisions, whereas three patients were treated with endoscopic customized implant tissue augmentation.
Conclusion
Whereas with combined deformity of the sternal plate and the rib cage, a modified Ravitch repair yields good results, the endoscopic soft tissue correction with customized implants helps to avoid unsightly scars, allows for safe hemostasis in the dissection pocket, and leads to enhanced patient satisfaction. In the case of major chest wall deformity with orthopedic and functional relevance, a combination of the minimally invasive procedures (e.g., endoscopic correction and Erlangen repair) seems to show both optimized cosmetic results and maximized functionality.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baroudi R: Discussion: Minibrachioplasty: Minimizing scars while maximizing results. Plast Reconstr Surg 114:1635–1637, 2004
Bentz ML, Rowe MI, Wiener ES: Improved sternal fixation in the correction of pediatric pectus excavatum. Ann Plast Surg 32:638–641, 1994
Biemer E: Breast reconstruction only by implant of a silicone gel prosthesis, possibly following tissue stretching by an expander. Chirurg 60:611–613, 1989
Biggs TM: Augmentation mammaplasty: A comparative analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:1761–1762, 1999 discussion 1763–1765
Biggs TM: Limited incision for breast surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:691, 2003 author reply 692
Biggs TM: Transposing a chest wall flap to the breast. Plast Reconstr Surg 112: 691, 2003
Borowitz D, Cerny F, Zallen G, Sharp J, Burke M, Gross K, Glick PL: Pulmonary function and exercise response in patients with pectus excavatum after Nuss repair. J Pediatr Surg 38:544–547, 2003
Coln D, Gunning T, Ramsay M, Swygert T, Vera R: Early experience with the Nuss minimally invasive correction of pectus excavatum in adults. World J Surg 26:1217–1221, 2002
Croitoru DP, Kelly RE Jr, Goretsky MJ, Lawson ML, Swoveland B, Nuss D: Experience and modification update for the minimally invasive Nuss technique for pectus excavatum repair in 303 patients. J Pediatr Surg 37:437–445, 2002
Erbella J Jr, Behmand R, Cederna PS: Endoscopically assisted pectus excavatum repair. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 11:213–216, 2001
Fonkalsrud EW, Beanes S: Surgical management of pectus carinatum: 30 years’ experience. World J Surg 25:898–903, 2001
Fonkalsrud EW, Beanes S, Hebra A, Adamson W, Tagge E: Comparison of minimally invasive and modified Ravitch pectus excavatum repair. J Pediatr Surg 37:413–417, 2002
Haller JA Jr, Scherer LR, Turner CS, Colombani PM: Evolving management of pectus excavatum based on a single institutional experience of 664 patients. Ann Surg 209:578–582, 1989 discussion 582–583
Hebra A, Swoveland B, Egbert M, Tagge EP, Georgeson K, Othersen HB Jr, Nuss D: Outcome analysis of minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum: Review of 251 cases. J Pediatr Surg 35:252–257, 2000 discussion 257–258
Hodgkinson DJ: Chest wall implants: Their use for pectus excavatum, pectoralis muscle tears, Poland’s syndrome, and muscular insufficiency. Aesthetic Plast Surg 21:7–15, 1997
Horch RE, Springer O: Minimally-invasive endoscopic correction of funnel chest deformity via an umbilical incision. Aesth Plast Surg 26:295–298, 2002
Hougaard G, Svensson H, Holmqvist KG: Casting the implant for reconstruction of pectus excavatum. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 29:227–231, 1995
Johnson PE: Refining silicone implant correction of pectus excavatum through computed tomography. Plast Reconstr Surg 97:445–449, 1996
Kneser U, Jaeger K, Bach AD, Polykandriotis E, Ohnolz J, Kopp J, Horch RE: Breast-reduction surgery: A long-term survey of indications and outcomes. MMW Fortschr Med 146:36–38, 40, 2004
Lacquet LK, Morshuis WJ, Folgering HT: Long-term results after correction of anterior chest wall deformities. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 39:683–688, 1998
Lavey E, Apfelberg DB, Lash H, Maser MR, Laub DR, Gosain A: Customized silicone implants of the breast and chest. Plast Reconstr Surg 69:646–651, 1982
Marks MW, Argenta LC, Lee DC: Silicone implant correction of pectus excavatum: Indications and refinement in technique. Plast Reconstr Surg 74:52–58, 1984
Marks MW, Iacobucci J: Reconstruction of congenital chest wall deformities using solid silicone onlay prostheses. Chest Surg Clin North Am 10:341–355, 2000 vii
Mendelson B, Masson JK: Silicone implants for contour deformities of the trunk. Plast Reconstr Surg 59:538–544, 1977
Miller KA, Ostlie DJ, Wade K, Chaignaud B, Gittes GK, Andrews WM, Ashcraft KW, Sharp RJ, Snyder CL, Holcomb III GW: Minimally invasive bar repair for “redo” correction of pectus excavatum. J Pediatr Surg 37:1090–1092, 2002
Miller KA, Woods RK, Sharp RJ, Gittes GK, Wade K, Ashcraft KW, Snyder CL, Andrews WM, Murphy JP, Holcomb III GW: Minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum: A single institution’s experience. Surgery 130:652–657, 2001 discussion 657–659
Morshuis WJ, Mulder H, Wapperom G, Folgering HT, Assman M, Cox AL, van Lier HJ, Vincent JG, Lacquet LK: Pectus excavatum: A clinical study with long-term postoperative follow-up. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 6:318–28, 1992 discussion 328–329
Nuss D, Croitoru DP, Kelly RE Jr, Goretsky MJ, Nuss KJ, Gustin TS: Review and discussion of the complications of minimally invasive pectus excavatum repair. Eur J Pediatr Surg 12:230–234, 2002
Onishi K, Maruyama Y: Correction of pectus excavatum using a sternal elevator: Preliminary report. Br J Plast Surg 54:117–124, 2001
Paolini A, Ruggieri M, Leone Sossi FL, Paolini G, Dal Pra G, Scuderi N: Pectus excavatum in adults: Destructive surgery or simple correction of an aesthetic defect? Riv Eur Sci Med Farmacol 18:11–17, 1996
Ravitch MM: Repair of pectus excavatum in children under 3 years of age: A twelve-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg 23:301, 1977
Ravitch MM: Technical problems in the operative correction of pectus excavatum. Ann Surg 162:29–33, 1965
Shamberger RC, Welch KJ: Surgical repair of pectus excavatum. J Pediatr Surg 23:615–622, 1988
Sorensen JL: Subcutaneous silicone implants in pectus excavatum. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 22:173–176, 1988
Uemura S, Nakagawa Y, Yoshida A, Choda Y: Experience in 100 cases with the Nuss procedure using a technique for stabilization of the pectus bar. Pediatr Surg Int 19:186–189, 2003
Wu PC, Knauer EM, McGowan GE, Hight DW: Repair of pectus excavatum deformities in children: A new perspective of treatment using minimal access surgical technique. Arch Surg 136:419–424, 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horch, R.E., Stoelben, E., Carbon, R. et al. Pectus Excavatum Breast and Chest Deformity: Indications for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery Versus Thoracic Surgery in a Multicenter Experience. Aesth Plast Surg 30, 403–411 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-004-0138-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-004-0138-x