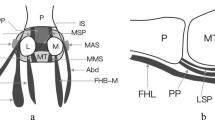
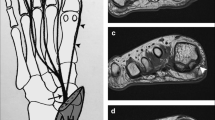
Abstract
Objective
Abnormalities of the plantar aponeurosis are commonly encountered in patients with subcalcaneal heel pain. Understanding normal anatomy is required to accurately diagnose some disorders of the foot. The purpose of our study was to describe the normal anatomy of the plantar aponeurosis, using ultrasonography and MRI with close anatomic correlation in cadavers.
Materials and methods
After MRI and ultrasonography of 10 cadaveric foot specimens, the thickness of the central and lateral portions of the plantar aponeurosis displayed by imaging studies was measured by three radiologists. One specimen was sectioned in the transverse plane, one in the coronal plane, one in the sagittal plane, and two in a sagittal oblique plane. Normal anatomy was identified and similar measurements of the plantar aponeurosis were also made. An average value was determined and a statistical analysis was accomplished.
Results
The calcaneal insertions of the plantar aponeurosis were better visualized than its distal portions with both MRI and ultrasonography. The measurements of the plantar aponeurosis made by three different radiologists were different, but without statistical significance. The average measurements for the central and lateral portions of the plantar aponeurosis with both imaging methods were different from each other because of differences in the morphology of these structures. The values obtained with ultrasonography and MRI, were also different from each other for both the central and lateral portions of the plantar aponeurosis, but with no statistical significance.
Conclusions
We have described the detailed anatomy of the plantar aponeurosis with emphasis on the more distal structures that can be visualized with MRI. There was no statistically significant difference between the accuracy of ultrasonography and MRI regarding the measurements of the thickness of the central and lateral portions of the plantar aponeurosis. Knowledge of the normal anatomy of these structures enables the radiologist to identify early alterations, providing timely diagnosis and treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarrafian S. Plantar aponeurosis. In: Sarrafian S, editor. Anatomy of the foot and ankle: descriptive, topographic, and functional. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott; 1993. p. 137–149.
Warwick R, Williams P, editors. Gray’s anatomy of the human body. 35th British ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1973. p. 579–580.
Bojsen-Møller F, Flagstad K. Plantar aponeurosis and internal architecture of the ball of the foot. J Anat 1976; 121: 599–611.
Resnick D. Abnormalities of the plantar soft tissues. In: Resnick D, editor. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1995. p. 3204–3208.
Resnick D, Kang H, Pretterklieber M. Internal derangements of joints, vol 1. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2007. p. 129–152.
Resnick D, Kang H, Pretterklieber M. Internal derangements of joints, vol 2. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2007. p. 1218–1419.
Hicks J. The mechanics of the foot: the plantar aponeurosis and the arch. J Anat 1954; 88: 25–31.
Berkowitz JF, Kier R, Rudicel S. Plantar fasciitis: MR imaging. Radiology 1991; 179: 665–667.
Cardinal E, Chem R, Beauregard G, et al. Plantar fasciitis: sonographic evaluation. Radiology 1996; 201: 257–259.
Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, et al. Disorders of the plantar aponeurosis: a spectrum of MR imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001; 176: 97–104.
Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Kakitsubata Y, et al. Plantar fasciitis and fascial rupture: MR imaging findings in 26 patients supplemented with anatomic data in cadavers. Radiographics 2000; 20: S181–S197.
Gibbon W, Long G. Ultrasound of the plantar aponeurosis (fascia). Skeletal Radiol 1999; 28: 21–26.
Balint PV, Kane D, Wilson H, McInnes IB, Sturrock RD. Ultrasonography of entheseal insertions in the lower limb in spondyloarthropathy. Ann Rheum Dis 2002; 61: 905–910.
Griffith JF, Wong TY, et al. Sonography of plantar fibromatosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002; 179: 1167–1172.
Brushoj C, Henriksen BM, Albrecht-Beste E, Hölmich P, Larsen K, Nielsen MB. Reproducibility of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging measurements of tendon size. Acta Radiol 2006; 47 9: 954–959.
Muhle C, Frank LR, Rand T, et al. Collateral ligaments of the ankle: high-resolution MR imaging with a local gradient coil and anatomic correlation in cadavers. Radiographics 1999; 19: 673–683.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Paul Clopton for the statistical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moraes do Carmo, C.C., Fonseca de Almeida Melão, L.I., Valle de Lemos Weber, M.F. et al. Anatomical features of plantar aponeurosis: cadaveric study using ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging. Skeletal Radiol 37, 929–935 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-008-0497-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-008-0497-5