Abstract
Introduction
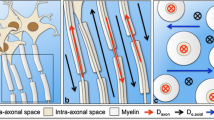
Our aim was to determine diffusion abnormalities in the uncinate fasciculus (UF) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by diffusion tensor tractography (DTT) using a new method for measuring the core of the tract.
Methods
We studied 19 patients with AD and 19 age-matched control subjects who underwent MRI using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). DTT of the UF was generated. The mean diffusivity (MD) and fractional anisotropy (FA) of the core of the tract were measured after voxelized tract shape processing. Student’s t-test was used to compare results between patients with AD and controls. Intraobserver correlation tests were also performed.
Results
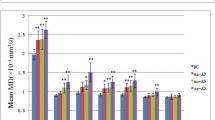
FA was significantly lower (P < 0.0001) in the UF of patients with AD than of controls. There was no significant difference in MD along the UF between the two groups. Intraobserver reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient) for the first and second measurement was r > 0.93 for measured FA and r > 0.92 for measured MD.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that FA reflects progression of AD-related histopathological changes in the UF of the white matter and may represent a useful biological index in monitoring AD. Diffusion tensor tract-specific analysis with voxelized tract shape processing to measure the core of the tract may be a sensitive tool for evaluation of diffusion abnormalities of white matter tracts in AD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brun A, Englund E (1986) A white matter disorder in dementia of the Alzheimer type: a pathoanatomical study. Ann Neurol 9(3):253–262
Bozzali M, Franceschi M, Falini A et al (2001) Quantification of tissue damage in AD using diffusion tensor and magnetization transfer MRI. Neurology 57(6):1135–1157
Hanyu H, Sakurai H, Iwamoto T et al (1998) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the hippocampus and temporal white matter in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 156(2):195–200
Kantarci K, Jack CR Jr, Xu YC et al (2000) Regional metabolic patterns in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: A 1H MRS study. Neurology 55(2):210–217
Rose SE, Chen F, Chalk JB et al (2000) Loss of connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease: an evaluation of white matter tract integrity with colour coded MR diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69(4):528–530
Sandson TA, Felician O, Edelman RR et al (1999) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 10:166–171
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B 103:247–254
Le Bihan D, van Zijl P (2002) From the diffusion coefficient to the diffusion tensor. NMR Biomed 15:431–434
Bozzali M, Falini A, Franceschi M et al (2002) White matter damage in Alzheimer’s disease assessed in vivo using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72(6):742–746
Choi SJ, Lim KO, Monteiro I et al (2005) Diffusion tensor imaging of frontal white matter microstructure in early Alzheimer’s disease: a preliminary study. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 18(1):12–19
Fellgiebel A, Muller MJ, Wille P et al (2005) Color-coded diffusion-tensor-imaging of posterior cingulate fiber tracts in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 26(8):1193–1198
Fellgiebel A, Wille P, Muller MJ et al (2004) Ultrastructural hippocampal and white matter alterations in mild cognitive impairment: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 18(1):101–108
Head D, Buckner RL, Shimony JS et al (2004) Differential vulnerability of anterior white matter in nondemented aging with minimal acceleration in dementia of the Alzheimer type: evidence from diffusion tensor imaging. Cereb Cortex 14(4):410–423
Medina D, DeToledo-Morrell L, Urresta F (2006) White matter changes in mild cognitive impairment and AD: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neurobiol Aging 27(5):663–672
Muller MJ, Greverus D, Dellani PR et al (2005) Functional implications of hippocampal volume and diffusivity in mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 28(4):1033–1042
Sugihara S, Kinoshita T, Matsusue E et al (2004) Usefulness of diffusion tensor imaging of white matter in Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. Acta Radiol 45(6):658–663
Takahashi S, Yonezawa H, Takahashi J et al (2002) Selective reduction of diffusion anisotropy in white matter of Alzheimer disease brains measured by 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosci Lett 332(1):45–48
Yoshiura T, Mihara F, Ogomori K et al (2002) Diffusion tensor in posterior cingulate gyrus: correlation with cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 13(17):2299–2302
Mori S, Frederiksen K, van Zijl PC et al (2002) Brain white matter anatomy of tumor patients evaluated with diffusion tensor imaging. Ann Neurol 51(3):377–380
Beaulieu C, Allen PS (1994) Determinants of anisotropic water diffusion in nerves. Magn Reson Med 31:394–400
Henkelman R, Stanisz G, Kim J et al (1994) Anisotropy of NMR properties of tissues. Magn Reson Med 32:592–601
Taoka T, Iwasaki S, Sakamoto M et al (2006) Diffusion anisotropy and diffusivity of white matter tracts within the temporal stem in Alzheimer disease: evaluation of the “tract of interest” by diffusion tensor tractography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(5):1040–1045
Aoki S, Iwata NK, Masutani Y et al (2005) Quantitative evaluation of the pyramidal tract segmented by diffusion tensor tractography: feasibility study in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Radiat Med 23(3):195–199
Kunimatsu A, Aoki S, Masutani Y et al (2004) The optimal trackability threshold of fractional anisotropy for diffusion tensor tractography of the corticospinal tract. Magn Reson Med Sci 3(1):11–17
Ebeling U, von Cramon D (1992) Topography of the uncinate fascicle and adjacent temporal fiber tracts. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 115:143–148
Kier EL, Staib LH, Davis LM et al (2004) MR imaging of the temporal stem: anatomic dissection tractography of the uncinate fasciculus, inferior occipitofrontal fasciculus, and Meyer’s loop of the optic radiation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:677–691
Catani M, Howard RJ, Pajevic S et al (2002) Virtual in vivo interactive dissection of white matter fasciculi in the human brain. Neuroimage 17(1):77–94
Gaffan D, Easton A, Parker A (2002) Interaction of inferior temporal cortex with frontal cortex and basal forebrain: double dissociation in strategy implementation and associative learning. J Neurosci 22(16):7288–7296
Levine B, Black SE, Cabeza R et al (1998) Episodic memory and the self in a case of isolated retrograde amnesia. Brain 121(10):1951–1973
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M et al (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34(7):939–944
Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A et al (1987) MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 149(2):351–356
Masutani Y, Aoki S, Abe O, Hayashi N et al (2003) MR diffusion tensor imaging: recent advance and new techniques for diffusion tensor visualization. Eur J Radiol 46(1):53–66
Pajevic S, Pierpaoli C (1999) Color schemes to represent the orientation of anisotropic tissues from diffusion tensor data: application to white matter fiber tract mapping in the human brain. Magn Reson Med 42:526–540. Erratum in: Magn Reson Med 2000; 43(6):921
Makris N, Worth AJ, Sorensen AG et al (1997) Morphometry of in vivo human white matter association pathways with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 42(6):951–962
Kunimatsu A, Aoki S, Masutani Y et al (2003) Three-dimensional white matter tractography by diffusion tensor imaging in ischaemic stroke involving the corticospinal tract. Neuroradiology 45(8):532–535
Lohmann G (1998) Volumetric image analysis. Wiley-Teubner, Chichester, pp 96–99
Kantarci K, Jack CR Jr, Xu YC et al (2001) Mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease: regional diffusivity of water. Radiology 219(1):101–107
Schneider RC, Crosby EC, Bacchi BK et al (1961) Temporal or occipital hallucinations triggered from frontal lobe lesions. Neurology 11:172–179
Schneider RC, Crosby EC, Farhat SM (1965) Extratemporal lesions triggering the temporal-lobe syndrome. J Neurosurg 22:246–253
Schneider RC, Crosby EC, Calhoun HD (1982) Surgery of convulsive seizures and allied disorders. In: Schneider RC, Kahn EA, Crosby EC, Taren JA (eds) Correlative neurosurgery, vol. 1. Thomas, Springfield, pp 576–580
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasmin, H., Nakata, Y., Aoki, S. et al. Diffusion abnormalities of the uncinate fasciculus in Alzheimer’s disease: diffusion tensor tract-specific analysis using a new method to measure the core of the tract. Neuroradiology 50, 293–299 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0353-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0353-7