Abstract
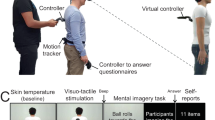
It is well known that our body works as a fundamental reference when we perform visuo-perceptual judgements in spatial surroundings, and that body illusions can modify our perception of size and distance of objects in space. To date, however, few studies have evaluated whether or not a body illusion could have a significant impact on the way individuals perceive to move within the environment. Here, we used a full-body illusion paradigm to verify the hypothesis that an altered representation of the legs of the individuals influences their time-to-walk estimation while imaging to reach objects in a virtual environment. To do so, we asked a group of young healthy volunteers to perform a task in which they were required to imagine walking towards a previously seen target location in a virtual environment, soon after receiving the body illusion; we required participants to use a response button to time their imagined walk from start to end. We found that participants imagined walking faster following the illusion elicited by the vision of longer legs presented from an anatomical perspective, as compared to when experiencing standard legs in the same position.This difference in imagined walking distance decreased when the object to reach was displayed farther, suggesting a fading effect. Furthermore, taking into consideration the baseline error in walking time estimation in VR, we noticed a specific influence of the long anatomical legs in reducing the perceived time needed to reach an object and a general increase in the percentage of error when the same legs are presented in a non-anatomical orientation. These findings provide evidence that body illusions could influence the way individuals perceive their locomotion in the spatial surrounding.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annett J (1995) Motor imagery: perception or action? Neuropsychologia 33(11):1395–1417. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3932(95)00072-B
Banakou D, Grotenac R, Slater M (2013) Illusory ownership of a virtual child body causes overestimation of object sizes and implicit attitude changes. PNAS 110(31):12846–12851. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas
Cumming G (2014) The new statistics: Why and how. Psychol Sci 25(1):7–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613504966
De Vignemont F (2010) Body schema and body image–pros and cons. Neuropsychologia 48(3):669–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.09.022
De Vignemont F, Tsakiris M, Haggard P(2006) Body mereology. Human body perception from the inside out 147–170
Decety J, Jeannerod M, Prablanc C (1989) The timing of mentally represented actions. Behav Brain Res 34(1–2):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(89)80088-9
Ehrsson, H. H. (2007). The experimental induction of out-of-body experiences. Science (New York, N.Y.), 317(5841), 1048. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1142175
Fini C, Brass M, Committeri G (2015) Social scaling of extrapersonal space: Target objects are judged as closer when the reference frame is a human agent with available movement potentialities. Cognition 134:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2014.08.014
Finke RA (1985) Theories relating mental imagery to perception. Psychol Bull 98(2):236. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.98.2.236
Flor H, Nikolajsen L, Jensen TS (2006) Phantom limb pain: a case of maladaptive CNS plasticity ? Nat Rev Neurosci 7(11):873–881. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1991
Gandevia SC, Phegan CML (1999) Perceptual distortions of the human body image produced by local anaesthesia, pain and cutaneous stimulation. J Physiol 514(2):609–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.609ae.x
Holmes NP, Spence C (2004) The body schema and multisensory representation (s) of peripersonal space. Cogn Process 5(2):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-004-0013-3.The
Keizer A, Van Elburg A, Helms R, Dijkerman HC (2016) A virtual reality full body illusion improves body image disturbance in anorexia nervosa. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163921
Kelly JW, Donaldson LS, Sjolund LA, Freiberg JB (2013) More than just perception-action recalibration: Walking through a virtual environment causes rescaling of perceived space. Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics 75(7):1473–1485. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-013-0503-4
Kilteni K, Normand JM, Sanchez-Vives MV, Slater M (2012) Extending body space in immersive virtual reality: A very long arm illusion. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0040867
Klein, E., Swan, J. E., Schmidt, G. S., Livingston, M. A., & Staadt, O. G. (2009) Measurement protocols for medium-field distance perception in large-screen immersive displays In 2009 IEEE Virtual Reality Conference (pp. 107–113). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/VR.2009.4811007
Kokkinara E, Kilteni K, Blom KJ, Slater M (2016) First person perspective of seated participants over a walking virtual body leads to illusory agency over the walking. Sci Rep 6:28879. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28879
Linkenauger SA, Ramenzoni V, Proffitt DR (2010) Illusory shrinkage and growth: Body-based rescaling affects the perception of size. Psychol Sci 21(9):1318–1325. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797610380700
Longo MR, Azañón E, Haggard P (2010) More than skin deep: body representation beyond primary somatosensory cortex. Neuropsychologia 48(3):655–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.08.022
Longo MR, Lourenco. (2006) On the nature of near space: effects of tool use and the transition to far space. Neuropsychologia 48:977–981
Longo MR, Schüür F, Kammers MPM, Tsakiris M, Haggard P (2008) What is embodiment? A psychometric approach. Cognition 107(3):978–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2007.12.004
Loomis JM, Knapp JM (2003) Visual perception of egocentric distance in real and virtual environments. Virtual Adap Environm 11:21–46. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420003864.ch18
Mancini F, Longo MRR, Kammers MPMPM, Haggard P (2011) Visual distortion of body size modulates pain perception. Psychol Sci 22(3):325–330. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797611398496
Marino BFM, Stucchi N, Nava E, Haggard P, Maravita A (2010) Distorting the visual size of the hand affects hand pre-shaping during grasping. Exp Brain Res 202(2):499–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-2143-4
Maselli A, Slater M (2014) Sliding perspectives: dissociating ownership from self-location during full body illusions in virtual reality. Front Human Neurosci 8:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00693
Merleau-Ponty M (1945) Phenomenology of perception. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10031-9
Nanay B (2010) Perception and imagination: amodal perception as mental imagery. Philos Stud 150(2):239–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11098-009-9407-5
Nori R, Iachini T, Giusberti F (2004) Object localisation and frames of reference. Cogn Process 5(1):45–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-004-0008-0
Oculus R (2018) Facebook Technologies, LLC
Paivio A (1990) Mental representations: A dual coding approach (Vol. 9). Oxford University Press
Pavani F, Spence C, Driver J (2000) Visual capture of touch: Out-of-the-Body Experiences With Rubber Gloves. Psychol Sci 11(5):353–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9280.00270
Petkova VI, Ehrsson HH (2008) If I were you: Perceptual illusion of body swapping. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003832
Plumert JM, Kearney JK, Cremer JF, Recker K (2005) Distance perception in real and virtual environments. ACM Trans Appl Percep 2(3):216–233. https://doi.org/10.1145/1077399.1077402
Proffitt DR, Bhalla M, Gossweiler R, Midgett J (1995) Perceiving geographical slant. Psychod Bull Rev 2(4):409–428
Proffitt DR, Stefanucci J, Banton T, Epstein W (2003) The role of effort in perceiving distance. Psychol Sci 14(2):106–112. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TRAG.0000005082.29212.cf
Rizzolatti G, Fadiga L, Fogassi L, Gallese V (1997) The space around us. Science 277(5323):190–191. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5323.190
Romano D, Caffa E, Hernandez-Arieta A, Brugger P, Maravita A (2015) The robot hand illusion: Inducing proprioceptive drift through visuo-motor congruency. Neuropsychologia 70:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.10.033
Romano D, Llobera J, Blanke O (2016) Size and Viewpoint of an Embodied Virtual Body Affect Processing of Painful Stimuli. J Pain 17(3):350–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2015.11.005
Romano D, Pfeiffer C, Maravita A, Blanke O (2014) Illusory self-identification with an avatar reduces arousal responses to painful stimuli. Behav Brain Res 261:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.12.049
Sanchez-Vives MV, Spanlang B, Frisoli A, Bergamasco M, Slater M (2010) Virtual hand illusion induced by visuomotor correlations. PLoS ONE 5(4):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010381
Schwoebel J, Coslett HB (2005) Evidence for multiple, distinct representations of the human body. J Cogn Neurosci 17(4):543–553. https://doi.org/10.1162/0898929053467587
Sposito AV, Bolognini N, Vallar G, Maravita A (2012) Extension of perceived arm length following tool-use: Clues to plasticity of body metrics. Neuropsychologia 50(9):2187–2194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.05.022
Stefanucci JK, Geuss MN (2009) Big people, little world: The body influences size perception. Perception 38(12):1782–1795. https://doi.org/10.1068/p6437
Swan JE, Jones A, Kolstad E, Livingston MA, Smallman HS (2007) Egocentric depth judgments in optical, see-through augmented reality. IEEE Trans Visual Comput Graphics 13(3):429–442. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2007.1035
Taylor-Clarke M, Jacobsen P, Haggard P (2004) Keeping the world a constant size: object constancy in human touch. Nat Neurosci 7(3):219–220. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1199
Tieri G, Tidoni E, Pavone EF, Aglioti SM (2015) Mere observation of body discontinuity affects perceived ownership and vicarious agency over a virtual hand. Exp Brain Res 233(4):1247–1259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4202-3
Tosi G, Romano D, Maravita A (2018) Mirror Box Training in Hemiplegic Stroke Patients Affects Body Representation. Front Human Neurosci 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00617
van der Hoort B, Guterstam A, Ehrsson HH (2011) Being barbie: The size of one’s own body determines the perceived size of the world. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020195
Warren WH, Whang S (1987) Visual guidance of walking through. J Experime Psychol Human Percep Performance 13(3):371–383. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.13.3.371
Witt JK, Proffitt DR (2008) Action-specific influences on distance perception: a role for motor simulation. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 34(6):1479. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0010781
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (University of Calgary Conjoint Faculties Research Ethics Board—CFREB18-1494) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Communicated by Carlo Alberto Marzi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tosi, G., Parmar, J., Dhillon, I. et al. Body illusion and affordances: the influence of body representation on a walking imagery task in virtual reality. Exp Brain Res 238, 2125–2136 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05874-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05874-z