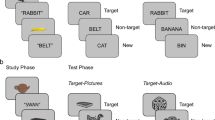
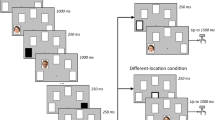
Abstract
Episodic memory (EM) is defined as a long-term memory system that stores information that can be retrieved along with details of the context of the original events (binding). Several studies have shown that manipulation of attention during encoding can impact subsequent memory performance. An influential model of attention distinguishes between three partially independent attentional networks: the alerting, the orienting and the executive or conflict resolution component. To date, the impact of the engagement of these sub-systems during encoding on item and relational context binding has not been investigated. Here, we developed a new task combining the Attentional Network Test and an incidental episodic memory encoding task to study this issue. We reported that when the alerting network was not solicited, resolving conflict hindered item encoding. Moreover, resolving conflict, independently of the cueing condition, had a negative impact on context binding. These novel findings could have a potential impact in the understanding EM formation, and memory disorders in different populations, including healthy elderly people.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams NC, Jarrold C (2012) Inhibition in autism: children with autism have difficulty inhibiting irrelevant distractors but not prepotent responses. J Autism Dev Disord 42(6):1052–1063
Anderson ND, Iidaka T, Cabeza R, Kapur S, McIntosh AR, Craik FI (2000) The effects of divided attention on encoding-and retrieval-related brain activity: a PET study of younger and older adults. J Cogn Neurosci 12(5):775–792
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S, Christensen RHB, Singmann H, Dai B (2014) lme4: linear mixed-effects models using Eigen and S4 (version 1.1-7). http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lme4/index.html
Casey BJ, Thomas KM, Welsh TF, Badgaiyan RD, Eccard CH, Jennings JR, Crone EA (2000) Dissociation of response conflict, attentional selection, and expectancy with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(15):8728–8733
Chajut E, Schupak A, Algom D (2009) Are spatial and dimensional attention separate? Evidence from Posner, Stroop, and Eriksen tasks. Mem Cognit 37(6):924–934
Chiu YC, Egner T (2015a) Inhibition-induced forgetting when more control leads to less memory. Psychol Sci 26(1):27–38
Chiu YC, Egner T (2015b) Inhibition-induced forgetting results from resource competition between response inhibition and memory encoding processes. J Neurosci 35(34):11936–11945
Craik FI, Lockhart RS (1972) Levels of processing: a framework for memory research. J Verbal Learn Verbal Behav 11(6):671–684
Davachi L (2006) Item, context and relational episodic encoding in humans. Curr Opin Neurobiol 16(6):693–700
Dulas MR, Duarte A (2014) Aging affects the interaction between attentional control and source memory: an fMRI study. J Cognit Neurosci 26(12):2653–2669
Fan J, McCandliss BD, Sommer T, Raz A, Posner MI (2002) Testing the efficiency and independence of attentional networks. J Cognit Neurosci 14(3):340–347
Fan J, McCandliss BD, Fossella J, Flombaum JI, Posner MI (2005) The activation of attentional networks. Neuroimage 26(2):471–479
Fan J, Gu X, Guise KG, Liu X, Fossella J, Wang H, Posner MI (2009) Testing the behavioral interaction and integration of attentional networks. Brain Cogn 70(2):209–220
Gazzaley A, D’Esposito MARK (2007) Top–down modulation and normal aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1097(1):67–83
Janowsky JS, Shimamura AP, Squire LR (1989) Source memory impairment in patients with frontal lobe lesions. Neuropsychologia 27(8):1043–1056
Kilb A, Naveh-Benjamin M (2007) Paying attention to binding: further studies assessing the role of reduced attentional resources in the associative deficit of older adults. Mem Cognit 35(5):1162–1174
Krebs RM, Boehler CN, De Belder M, Egner T (2013) Neural conflict–control mechanisms improve memory for target stimuli. Cereb Cortex 25(3):833–843
Meiser T, Sattler C, Weißer K (2008) Binding of multidimensional context information as a distinctive characteristic of remember judgments. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn 34(1):32
Naveh-Benjamin M, Guez J, Marom M (2003) The effects of divided attention at encoding on item and associative memory. Mem Cogn 31(7):1021–1035
Nee DE, Wager TD, Jonides J (2007) Interference resolution: insights from a meta-analysis of neuroimaging tasks. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 7(1):1–17
Pallier C (2002) Computing discriminability and bias with the R software. http://www.pallier.org/ressources/aprime/aprime. Accessed 12 June 2015
Park H, Leal F, Abellanoza C, Schaeffer JD (2014) The formation of source memory under distraction. Behav Brain Funct 10(1):40
Peirce JW (2007) Psychopy–psychophysics software in Python. J Neurosci Methods 162(1):8–13
Posner MI (2008) Measuring alertness. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1129(1):193–199
Posner MI, Petersen SE (1990) The attention system of the human brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 13:25–42
Ranganath C (2010) Binding items and contexts the cognitive neuroscience of episodic memory. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 19(3):131–137
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Manual. Vienna, Austria. http://www.r-project.org
Rosner TM, D’Angelo MC, MacLellan E, Milliken B (2015) Selective attention and recognition: effects of congruency on episodic learning. Psychol Res 79(3):411–424
Sanderson C, Allen ML (2013) The specificity of inhibitory impairments in autism and their relation to ADHD-type symptoms. J Autism Dev Disord 43(5):1065–1079
Sperduti M, Makowski D, Piolino P (2016) The protective role of long-term meditation on the decline of the executive component of attention in aging: a preliminary cross-sectional study. Aging Neuropsychol Cogn 23(6):691–702
Stanislaw H, Todorov N (1999) Calculation of signal detection theory measures. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 31(1):137–149
Staresina BP, Davachi L (2008) Selective and shared contributions of the hippocampus and perirhinal cortex to episodic item and associative encoding. J Cogn Neurosci 20(8):1478–1489
Staresina BP, Gray JC, Davachi L (2009) Event congruency enhances episodic memory encoding through semantic elaboration and relational binding. Cereb Cortex 19(5):1198–1207
Stark SM, Yassa MA, Lacy JW, Stark CE (2013) A task to assess behavioral pattern separation (BPS) in humans: data from healthy aging and mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychologia 51(12):2442–2449
Summerfield C, Mangels JA (2006) Dissociable neural mechanisms for encoding predictable and unpredictable events. J Cogn Neurosci 18(7):1120–1132
Summerfield C, Greene M, Wager T, Egner T, Hirsch J, Mangels J (2006) Neocortical connectivity during episodic memory formation. PLoS Biol 4(5):e128
Troyer AK, Winocur G, Craik FI, Moscovitch M (1999) Source memory and divided attention: reciprocal costs to primary and secondary tasks. Neuropsychology 13(4):467
Tulving E (2002) Episodic memory: from mind to brain. Annu Rev Psychol 53(1):1–25
Turk-Browne NB, Golomb JD, Chun MM (2013) Complementary attentional components of successful memory encoding. NeuroImage 66:553–562
Uncapher M, Rugg M (2008) Fractionation of the component processes underlying successful episodic encoding: a combined fMRI and divided-attention study. J Cogn Neurosci 20(2):240–254
Uncapher MR, Hutchinson JB, Wagner AD (2011) Dissociable effects of top–down and bottom–up attention during episodic encoding. J Neurosci 31(35):12613–12628
van den Honert RN, McCarthy G, Johnson MK (2017) Holistic versus feature-based binding in the medial temporal lobe. Cortex 91:56–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sperduti, M., Armougum, A., Makowski, D. et al. Interaction between attentional systems and episodic memory encoding: the impact of conflict on binding of information. Exp Brain Res 235, 3553–3560 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-017-5081-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-017-5081-6