Abstract
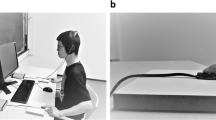
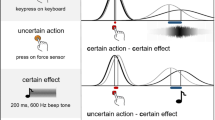
Sense of agency is the way in which we understand the causal relationships between our actions and sensory events. Agency is implicitly measured using intentional binding paradigms, where voluntary self-made actions and consequential sensory events are perceived as shifted closer together in time. However, a crucial question remains as to how we understand the relationship between others’ actions and sensory events. Do we use similar binding processes as for our own actions? Previous attempts to investigate this phenomenon in others’ have reached no clear consensus. Therefore, in an attempt to understand how we attribute the causal relationships between others’ actions and sensory events, we investigated intentional binding in others’ actions using an interval estimation paradigm. In a first experiment participants were required to make a button-press response to indicate the perceived interval between a self-made action and a tone, between a closely matched observed action and tone, and between two tones. For both self-made and observed actions, we found a significant perceived shortening of the interval between the actions and tones as compared with the interval between two tones, thus intentional binding was found for both self-made and observed actions. In a second experiment we validated the findings of the first by contrasting the perceived intervals between an observed action and tone with a matched visual–auditory stimulus and a tone. We again found a significant perceived shortening of the interval for observed action compared with the closely matched visual–auditory control stimulus. The occurrence of intentional binding when observing an action suggests we use similar processes to make causal attributions between our own actions, others’ actions, and sensory events.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blakemore SJ, Frith CD, Wolpert DM (2001) The cerebellum is involved in predicting the sensory consequences of action. NeuroReport 12(9):1879–1884
Blakemore SJ, Wolpert DM, Frith CD (2002) Abnormalities in the awareness of action. Trends Cogn Sci 6(6):237–242
Buehner MJ, Humphreys GR (2009) Causal binding of actions to their effects. Psychol Sci 20(10):1221–1228
Chambon V, Domenech P, Pacherie E, Koechlin E, Baraduc P, Farrer C (2011) What are they up to? The role of sensory evidence and prior knowledge in action understanding. Plos One 6(2). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017133
Ebert JP, Wegner DM (2010) Time warp: authorship shapes the perceived timing of actions and events. Conscious Cogn 19(1):481–489. doi:10.1016/j.concog.2009.10.002
Engbert K, Wohlschlager A (2007) Intentions and expectations in temporal binding. Conscious Cogn 16(2):255–264. doi:10.1016/J.Concog.2006.09.010
Engbert K, Wohlschlager A, Haggard P (2008) Who is causing what? The sense of agency is relational and efferent-triggered. Cognition 107(2):693–704. doi:10.1016/J.Cognition.2007.07.021
Fadiga L, Fogassi L, Pavesi G, Rizzolatti G (1995) Motor facilitation during action observation—a magnetic stimulation study. J Neurophysiol 73(6):2608–2611
Gallagher II (2000) Philosophical conceptions of the self: implications for cognitive science. Trends Cogn Sci 4(1):14–21
Haggard P, Clark S (2003) Intentional action: conscious experience and neural prediction. Conscious Cogn 12(4):695–707. doi:10.1016/S1053-8100(03)00052-7
Haggard P, Clark S, Kalogeras J (2002) Voluntary action and conscious awareness. Nat Neurosci 5(4):382–385. doi:10.1038/Nn827
Humphreys GR, Buehner MJ (2010) Temporal binding of action and effect in interval reproduction. Exp Brain Res 203(2):465–470. doi:10.1007/S00221-010-2199-1
Kilner JM, Friston KJ, Frith CD (2007) Predictive coding: an account of the mirror neuron system. Cogn Process 8(3):159–166. doi:10.1007/s10339-007-0170-2
Libet B (1985) Unconscious cerebral initiative and the role of conscious will in voluntary action. Behav Brain Sci 8(4):529–566
Libet B, Gleason CA, Wright EW, Pearl DK (1983) Time of conscious intention to act in relation to onset of cerebral-activity (readiness-potential)—the unconscious initiation of a freely voluntary act. Brain 106:623–642
Moore J, Haggard P (2008) Awareness of action: inference and prediction. Conscious Cogn 17(1):136–144. doi:10.1016/J.Concog.2006.12.004
Moore JW, Obhi SS (2012) Intentional binding and the sense of agency: a review. Conscious Cogn 21(1):546–561. doi:10.1016/J.Concog.2011.12.002
Moore J, Lagnado D, Deal DC, Haggard P (2009) Feelings of control: contingency determines experience of action. Cognition 110(2):279–283. doi:10.1016/J.Cognition.2008.11.006
Obhi S, Hall P (2011a) Sense of agency and intentional binding in joint action. Exp Brain Res 211(3–4):655–662. doi:10.1007/S00221-011-2675-2
Obhi S, Hall P (2011b) Sense of agency in joint action: influence of human and computer co-actors. Exp Brain Res 211(3–4):663–670. doi:10.1007/S00221-011-2662-7
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9(1):97–113
Rizzolatti G, Fabbri-Destro M (2010) Mirror neurons: from discovery to autism. Exp Brain Res 200(3–4):223–237. doi:10.1007/s00221-009-2002-3
Strother L, House KA, Obhi SS (2010) Subjective agency and awareness of shared actions. Conscious Cogn 19(1):12–20. doi:10.1016/J.Concog.2009.12.007
Voss M, Moore J, Hauser M, Gallinat J, Heinz A, Haggard P (2010) Altered awareness of action in schizophrenia: a specific deficit in predicting action consequences. Brain 133:3104–3112. doi:10.1093/brain/awq152
Wohlschlager A, Engbert K, Haggard P (2003a) Intentionality as a constituting condition for the own self-and other selves. Conscious Cogn 12(4):708–716. doi:10.1016/S1053-8100(03)00083-7
Wohlschlager A, Haggard P, Gesierich B, Prinz W (2003b) The perceived onset time of self- and other-generated actions. Psychol Sci 14(6):586–591
Wolpert DM, Ghahramani Z (2000) Computational principles of movement neuroscience. Nat Neurosci 3(Suppl):1212–1217. doi:10.1038/81497
Wolpert DM, Ghahramani Z, Jordan MI (1995) An internal model for sensorimotor integration. Science 269(5232):1880–1882
Acknowledgments
Ross Cunnington is funded by an Australian Research Council Future Fellowship. Thank you to Jessica McFadyen who collected data for experiment two.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poonian, S.K., Cunnington, R. Intentional binding in self-made and observed actions. Exp Brain Res 229, 419–427 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3505-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3505-5