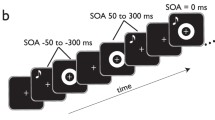
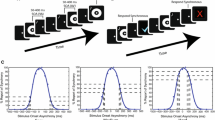
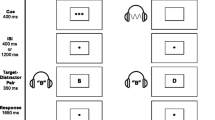
Abstract
The importance of multisensory integration for human behavior and perception is well documented, as is the impact that temporal synchrony has on driving such integration. Thus, the more temporally coincident two sensory inputs from different modalities are, the more likely they will be perceptually bound. This temporal integration process is captured by the construct of the temporal binding window—the range of temporal offsets within which an individual is able to perceptually bind inputs across sensory modalities. Recent work has shown that this window is malleable and can be narrowed via a multisensory perceptual feedback training process. In the current study, we seek to extend this by examining the malleability of the multisensory temporal binding window through changes in unisensory experience. Specifically, we measured the ability of visual perceptual feedback training to induce changes in the multisensory temporal binding window. Visual perceptual training with feedback successfully improved temporal visual processing, and more importantly, this visual training increased the temporal precision across modalities, which manifested as a narrowing of the multisensory temporal binding window. These results are the first to establish the ability of unisensory temporal training to modulate multisensory temporal processes, findings that can provide mechanistic insights into multisensory integration and which may have a host of practical applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adini Y, Sagi D, Tsodyks M (2002) Context-enabled learning in the human visual system. Nature 415:790–793
Alais D, Cass J (2010) Multisensory perceptual learning of temporal order: audiovisual learning transfers to vision but not audition. PLoS ONE 5:e11283
Andersen TS, Tiippana K, Sams M (2004) Factors influencing audiovisual fission and fusion illusions. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 21:301–308
Bastien-Toniazzo M, Stroumza A, Cavé C (2009) Audio-visual perception and integration in developmental dyslexia: An exploratory study using the McGurk effect. Current Psychol Lett 25
Boddaert N, Chabane N, Gervais H, Good CD, Bourgeois M, Plumet MH, Barthelemy C, Mouren MC, Artiges E, Samson Y, Brunelle F, Frackowiak RS, Zilbovicius M (2004) Superior temporal sulcus anatomical abnormalities in childhood autism: a voxel-based morphometry MRI study. Neuroimage 23:364–369
Brainard DH (1997) The psychophysics toolbox. Spat Vis 10:433–436
Colonius H, Diederich A (2004) Multisensory interaction in saccadic reaction time: a time-window-of-integration model. J Cogn Neurosci 16:1000–1009
Conrey BL, Pisoni DB (2004) Detection of auditory-visual asynchrony in speech and nonspeech signals. In: Pisoni DB (ed) Research on spoken language processing, vol 26. Indiana University, Bloomington, pp 71–94
Conrey B, Pisoni DB (2006) Auditory-visual speech perception and synchrony detection for speech and nonspeech signals. J Acoust Soc Am 119:4065–4073
Diederich A, Colonius H (2004) Bimodal and trimodal multisensory enhancement: effects of stimulus onset and intensity on reaction time. Percept Psychophys 66:1388–1404
Dixon NF, Spitz L (1980) The detection of auditory visual desynchrony. Perception 9:719–721
Foss-Feig JH, Kwakye LD, Cascio CJ, Burnette CP, Kadivar H, Stone WL, Wallace MT (2010) An extended multisensory temporal binding window in autism spectrum disorders. Exp Brain Res 203:381–389
Foucher JR, Lacambre M, Pham BT, Giersch A, Elliott MA (2007) Low time resolution in schizophrenia Lengthened windows of simultaneity for visual, auditory and bimodal stimuli. Schizophr Res 97:118–127
Fujisaki W, Shimojo S, Kashino M, Nishida S (2004) Recalibration of audiovisual simultaneity. Nat Neurosci 7:773–778
Gervais H, Belin P, Boddaert N, Leboyer M, Coez A, Sfaello I, Barthelemy C, Brunelle F, Samson Y, Zilbovicius M (2004) Abnormal cortical voice processing in autism. Nat Neurosci 7:801–802
Gibbon J (1977) Scalar expectancy theory and Weber’s law in animal timing. Psychol Rev 84:179–325
Gibbon J, Church RM, Meck WH (1984) Scalar timing in memory. Ann N Y Acad Sci 423:52–77
Hairston WD, Burdette JH, Flowers DL, Wood FB, Wallace MT (2005) Altered temporal profile of visual-auditory multisensory interactions in dyslexia. Exp Brain Res 166:474–480
Hershenson M (1962) Reaction time as a measure of intersensory facilitation. J Exp Psychol 63:289–293
Hillock AR, Powers AR, Wallace MT (2011) Binding of sights and sounds: age-related changes in multisensory temporal processing. Neuropsychologia 49:461–467
James TW, Stevenson RA, Kim S (2012) Inverse effectiveness in multisensory processing. In: Stein BE (ed) The new handbook of multisensory processes. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Keetels M, Vroomen J (2005) The role of spatial disparity and hemifields in audio-visual temporal order judgments. Exp Brain Res 167:635–640
Kim RS, Seitz AR, Shams L (2008) Benefits of stimulus congruency for multisensory facilitation of visual learning. PLoS ONE 3:e1532
Kwakye LD, Foss-Feig JH, Cascio CJ, Stone WL, Wallace MT (2011) Altered auditory and multisensory temporal processing in autism spectrum disorders. Front Integr Neurosci 4:129
Levitt JG, Blanton RE, Smalley S, Thompson PM, Guthrie D, McCracken JT, Sadoun T, Heinichen L, Toga AW (2003) Cortical sulcal maps in autism. Cereb Cortex 13:728–735
Lovelace CT, Stein BE, Wallace MT (2003) An irrelevant light enhances auditory detection in humans: a psychophysical analysis of multisensory integration in stimulus detection. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 17:447–453
Macaluso E, George N, Dolan R, Spence C, Driver J (2004) Spatial and temporal factors during processing of audiovisual speech: a PET study. Neuroimage 21:725–732
McGurk H, MacDonald J (1976) Hearing lips and seeing voices. Nature 264:746–748
Meredith MA, Stein BE (1986a) Spatial factors determine the activity of multisensory neurons in cat superior colliculus. Brain Res 365:350–354
Meredith MA, Stein BE (1986b) Visual, auditory, and somatosensory convergence on cells in superior colliculus results in multisensory integration. J Neurophysiol 56:640–662
Meredith MA, Nemitz JW, Stein BE (1987) Determinants of multisensory integration in superior colliculus neurons. I. Temporal factors. J Neurosci 7:3215–3229
Miller LM, D’Esposito M (2005) Perceptual fusion and stimulus coincidence in the cross-modal integration of speech. J Neurosci 25:5884–5893
Navarra J, Vatakis A, Zampini M, Soto-Faraco S, Humphreys W, Spence C (2005) Exposure to asynchronous audiovisual speech extends the temporal window for audiovisual integration. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 25:499–507
Nelson WT, Hettinger LJ, Cunningham JA, Brickman BJ, Haas MW, McKinley RL (1998) Effects of localized auditory information on visual target detection performance using a helmet-mounted display. Hum Factors 40:452–460
Pekkola J, Laasonen M, Ojanen V, Autti T, Jaaskelainen IP, Kujala T, Sams M (2006) Perception of matching and conflicting audiovisual speech in dyslexic and fluent readers: an fMRI study at 3 T. Neuroimage 29:797–807
Pelli DG (1997) The VideoToolbox software for visual psychophysics: transforming numbers into movies. Spat Vis 10:437–442
Pelphrey KA, Carter EJ (2008a) Brain mechanisms for social perception: lessons from autism and typical development. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1145:283–299
Pelphrey KA, Carter EJ (2008b) Charting the typical and atypical development of the social brain. Dev Psychopathol 20:1081–1102
Pöppel E, Schill K, von Steinbüchel N (1990) Sensory integration within temporally neutral systems states: a hypothesis. Naturwissenschaften 77:89–91
Powers AR 3rd, Hillock AR, Wallace MT (2009) Perceptual training narrows the temporal window of multisensory binding. J Neurosci 29:12265–12274
Powers AR 3rd, Hevey MA, Wallace MT (2012) Neural correlates of multisensory perceptual learning. J Neurosci 32:6263–6274
Richards T, Stevenson J, Crouch J, Johnson LC, Maravilla K, Stock P, Abbott R, Berninger V (2008) Tract-based spatial statistics of diffusion tensor imaging in adults with dyslexia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1134–1139
Roach NW, Heron J, Whitaker D, McGraw PV (2011) Asynchrony adaption reveals neural population code for audio-visual timing. Proc R Soc 278:9
Royal DW, Carriere BN, Wallace MT (2009) Spatiotemporal architecture of cortical receptive fields and its impact on multisensory interactions. Exp Brain Res 198:127–136
Schall S, Quigley C, Onat S, Konig P (2009) Visual stimulus locking of EEG is modulated by temporal congruency of auditory stimuli. Exp Brain Res 198:137–151
Seitz AR, Nanez JE Sr, Holloway SR, Watanabe T (2006) Perceptual learning of motion leads to faster flicker perception. PLoS ONE 1:e28
Senkowski D, Talsma D, Grigutsch M, Herrmann CS, Woldorff MG (2007) Good times for multisensory integration: effects of the precision of temporal synchrony as revealed by gamma-band oscillations. Neuropsychologia 45:561–571
Shams L, Kamitani Y, Shimojo S (2000) Illusions. What you see is what you hear. Nature 408:788
Shenton ME, Dickey CC, Frumin M, McCarley RW (2001) A review of MRI findings in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 49:1–52
Spence C (2007) Audiovisual multisensory integration. Acoustics Sci Technol 28:61–70
Stein B, Meredith MA (1993) The merging of the senses. MIT Press, Boston, MA
Stein BE, Wallace MT (1996) Comparisons of cross-modality integration in midbrain and cortex. Prog Brain Res 112:289–299
Stevenson RA, James TW (2009) Audiovisual integration in human superior temporal sulcus: inverse effectiveness and the neural processing of speech and object recognition. Neuroimage 44:1210–1223
Stevenson RA, Wallace MW (under review) Multisensory temporal integration: task and stimulus dependencies Exp Brain Res
Stevenson RA, Altieri NA, Kim S, Pisoni DB, James TW (2010) Neural processing of asynchronous audiovisual speech perception. Neuroimage 49:3308–3318
Stevenson RA, VanDerKlok RM, Pisoni DB, James TW (2011) Discrete neural substrates underlie complementary audiovisual speech integration processes. Neuroimage 55:1339–1345
Stevenson RA, Zemtsov RK, Wallace MT (2012) Individual differences in the multisensory temporal binding window predict susceptibility to audiovisual illusions. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 38:1517–1529
Talsma D, Senkowski D, Woldorff MG (2009) Intermodal attention affects the processing of the temporal alignment of audiovisual stimuli. Exp Brain Res 198:313–328
van Atteveldt NM, Formisano E, Blomert L, Goebel R (2007) The effect of temporal asynchrony on the multisensory integration of letters and speech sounds. Cereb Cortex 17:962–974
van Eijk RL, Kohlrausch A, Juola JF, van de Par S (2008) Audiovisual synchrony and temporal order judgments: effects of experimental method and stimulus type. Percept Psychophys 70:955–968
van Wassenhove V, Grant KW, Poeppel D (2007) Temporal window of integration in auditory-visual speech perception. Neuropsychologia 45:598–607
Vatakis A, Spence C (2006) Audiovisual synchrony perception for music, speech, and object actions. Brain Res 1111:134–142
Vatakis A, Spence C (2007) Crossmodal binding: evaluating the “unity assumption” using audiovisual speech stimuli. Percept Psychophys 69:744–756
Vatakis A, Navarra J, Soto-Faraco S, Spence C (2007) Temporal recalibration during asynchronous audiovisual speech perception. Exp Brain Res 181:173–181
Vatakis A, Ghazanfar AA, Spence C (2008) Facilitation of multisensory integration by the “unity effect” reveals that speech is special. J Vis 8(14):1–11
Vroomen J, Baart M (2009) Phonetic recalibration only occurs in speech mode. Cognition 110:254–259
Vroomen J, Keetels M, de Gelder B, Bertelson P (2004) Recalibration of temporal order perception by exposure to audio-visual asynchrony. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 22:32–35
Wallace MT, Roberson GE, Hairston WD, Stein BE, Vaughan JW, Schirillo JA (2004) Unifying multisensory signals across time and space. Exp Brain Res 158:252–258
Wearden JH, Edwards H, Fakhri M, Percival A (1998) Why “sounds are judged longer than lights”: application of a model of the internal clock in humans. Q J Exp Psychol B 51:97–120
Wilkinson LK, Meredith MA, Stein BE (1996) The role of anterior ectosylvian cortex in cross-modality orientation and approach behavior. Exp Brain Res 112:1–10
Zampini M, Guest S, Shore DI, Spence C (2005) Audio-visual simultaneity judgments. Percept Psychophys 67:531–544
Acknowledgments
Authors RAS and MMW contributed equally to this publication. Funding for this work was provided by National Institutes of Health F32 DC011993, Multisensory Integration and Temporal Processing in ASD, National Institutes of Health R34 DC010927, Evaluation of Sensory Integration Treatment in ASD, the Vanderbilt Brain Institute, and the Vanderbilt Kennedy Center. We also acknowledge the help of Zachary Barnett for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ryan A. Stevenson, Magdalena M. Wilson contributed equally to this publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevenson, R.A., Wilson, M.M., Powers, A.R. et al. The effects of visual training on multisensory temporal processing. Exp Brain Res 225, 479–489 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3387-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3387-y