Abstract
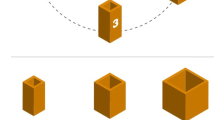
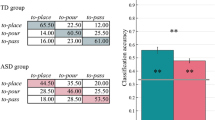
Eighteen- and 25-month-old human toddlers’ ability to manually solve a puzzle and their ability to anticipate the goal during observation of similar actions were investigated. Results demonstrate that goal anticipation during action observation is dependent on manual ability, both on a group level (only 25-month-olds solved the manual task and anticipated the goal during observation) and individually within the older age group (r xy = 0.53). These findings suggests a connection between manual ability and the ability to anticipate the goal of others’ actions in toddlers, in accordance with the direct matching hypothesis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calvo-Merino B, Glaser DE, Grèzes J, Passingham RE, Haggard P (2005) Action observation and acquired motor skills: an fMRI study with expert dancers. Cereb Cortex 15:1243–1249
Csibra G, Gergely G, Bíró S, Koós O, Brockbank M (1999) Goal attribution without agency cues: the perception of ‘pure reason’ in infancy. Cognition 72:237–267
Csibra G, Bíró S, Koós O, Gergely G (2003) One-year-old infants use teleological representations of action productivity. Cogn Sci 27:111–133
Eshuis R, Coventry KR, Vulchanova M (2009) Predictive eye movements are driven by goals, not by the mirror neuron system. Psychol Sci 20:438–440
Falck-Ytter T, Gredebäck G, von Hofsten C (2006) Infants predict other people’s action goals. Nat Neurosci 9:878–879
Flanagan JR, Johansson RS (2003) Action plans used in action observation. Nature 14:769–771
Gergely G, Csibra G (2003) Teleological reasoning in infancy: the naive theory of rational action. Trends Cogn Sci 7:287–292
Gredebäck G, Melinder A (2009) Infants’ understanding of everyday social interactions: a dual process account. Cognition (in press)
Gredeback G, Stasiewicz D, Falck-Ytter T, Rosander K, von Hofsten C (2009) Action type and goal type modulate goal-directed gaze shifts in 14-month-old infants. Dev Psychol 45:1190–1194
Jarvelainen J, Schurmann M, Hari R (2004) Activation of the human primary motor cortex during observation of tool use. Neuroimage 23:187–192
Johansson RS, Westling G, Bäckström A, Flanagan JR (2001) Eye–hand coordination in object manipulation. J Neurosci 21:6917–6932
Kamewari K, Kato M, Kanda T, Ishiguro H, Hiraki K (2005) Six-and-a-half-month-old children positively attribute goals to human action and to humanoid-robot motion. Cogn Dev 20:303–320
Lee DN, Young DS, Reddish PE, Lough S, Clayton TM (1983) Visual timing in hitting an accelerating ball. Q J Exp Psychol A 35:333–336
Nyström P (2008) The infant mirror neuron system studied with high density EEG. Soc Neurosci 3:334–347
Örnkloo H, von Hofsten C (2007) Fitting objects into holes: on the development of spatial cognition skills. Dev Psychol 43:404–416
Saffran JR, Aslin RN, Newport EL (1996) Statistical learning by 8-month-old infants. Science 274:1926–1928
Sommerville J, Woodward A, Needham A (2005) Action experience alters 3-month-old infants’ perception of others’ actions. Cognition 96:B1–B11
van Elk M, van Schie HT, Hunnis S, Vesper C, Bekkering H (2008) You’ll never crawl alone: neurophysiological evidence for experience-dependent motor resonance in infancy. Neuroimage 43:808–814
von Hofsten C (2004) An action perspective on motor development. Trends Cogn Sci 8:266–272
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Swedish Research Council (VR 421-2006-1794).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gredebäck, G., Kochukhova, O. Goal anticipation during action observation is influenced by synonymous action capabilities, a puzzling developmental study. Exp Brain Res 202, 493–497 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-2138-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-2138-1