Abstract
Introduction
The hypo-glutamatergic hypothesis of schizophrenia is based on clinical similarities between schizophrenia and phencyclidine (PCP)-induced psychosis in mentally healthy humans. Sensorimotor gating, as measured by prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response (ASR), is impaired in schizophrenic patients. In animals, noncompetitive N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists such as PCP disrupt PPI in a way that resembles the defect seen in schizophrenia. In a previous study with inbred mouse strains, low PPI levels have been demonstrated in CPB-K mice possessing low levels of hippocampal NMDA receptor densities. The present study was performed to test whether the low magnitude of PPI in CPB-K mice can be reversed by the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine (CLZ).
Results
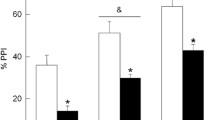
Before any treatment, CPB-K mice displayed a significant (p < 0.001) lower level in PPI and a significant (p < 0.001) higher ASR when compared to BALB/cJ mice known to have high hippocampal NMDA receptor densities. Acute and subchronic effects of a 2-week treatment with CLZ at daily doses of 5 and 10 mg/kg intraperitoneally, respectively, did not reveal any significant alteration of PPI levels in CPB-K mice. Nevertheless, the examination of motor behavior during nonstimulus trials provided a positive control for the drug’s effectiveness.
Conclusion
In summary, (1) this study confirmed our working hypothesis: Lower levels of hippocampal glutamatergic receptor densities correspond to lower sensorimotor gating in CPB-K mice, and (2) acute or subchronic treatment with CLZ did not elevate low PPI levels in CPB-K mice. Thus, further experiments will concentrate on other antipsychotic drugs to prove the predictive validity of this animal model.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMPA:
-
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-proprionic acid
- ASR:
-
acoustic startle response to startle stimulus alone
- CLZ:
-
clozapine
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartate
- NOSTIM:
-
nonstimulus
- NMDA-R1:
-
NMDA receptor subunit R1
- PCP:
-
phencyclidine
- PPI:
-
prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex
- PREPULSE:
-
prepulse only
- PREPULSE + PULSE:
-
prepulse followed by the startle stimulus
- PULSE-ALONE:
-
startle stimulus alone
- 5-HT:
-
serotonin
References
Angst MJ, Macedo CE, Guiberteau T, Sandner G (2007) Alteration of conditioned emotional response and conditioned taste aversion after neonatal ventral hippocampus lesions in rats. Brain Res 1143:183–192
Bakshi VP, Geyer MA (1998) Multiple limbic regions mediate the disruption of prepulse inhibition produced in rats by the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist dizocilpine. J Neurosci 18:8394–8401
Bast T, Feldon J (2003) Hippocampal modulation of sensorimotor processes. Prog Neurobiol 70:319–345
Bast T, Zhang W, Feldon J, White IM (2000) Effects of MK801 and neuroleptics on prepulse inhibition: re-examination in two strains of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:647–658
Bast T, Zhang WN, Heidbreder C, Feldon J (2001) Hyperactivity and disruption of prepulse inhibition induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate stimulation of the ventral hippocampus and the effects of pretreatment with haloperidol and clozapine. Neuroscience 103:325–335
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia. Human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:181–188
Braff DL, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR (2001) Human studies of prepulse inhibition of startle: normal subjects, patient groups, and pharmacological studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 156:234–258
Brody SA, Geyer MA, Large CH (2003) Lamotrigine prevents ketamine but not amphetamine-induced deficits in prepulse inhibition in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 169:240–246
Carlsson A, Waters N, Holm-Waters S, Tedroff J, Nilsson M, Carlsson ML (2001) Interactions between monoamines, glutamate, and GABA in schizophrenia: new evidence. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:237–260
Duncan GE, Moy SS, Perez A, Eddy DM, Zinzow WM, Lieberman JA, Snouwaert JN, Koller BH (2004) Deficits in sensorimotor gating and tests of social behavior in a genetic model of reduced NMDA receptor function. Behav Brain Res 153:507–519
Duncan GE, Moy SS, Lieberman JA, Koller BH (2006) Effects of haloperidol, clozapine, and quetiapine on sensorimotor gating in a genetic model of reduced NMDA receptor function. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 184:190–200
Erhardt S, Schwieler L, Emanuelsson C, Geyer M (2004) Endogenous kynurenic acid disrupts prepulse inhibition. Biol Psychiatry 56:255–260
Fradley RL, O'Meara GF, Newman RJ, Andrieux A, Job D, Reynolds DS (2005) STOP knockout and NMDA NR1 hypomorphic mice exhibit deficits in sensorimotor gating. Behav Brain Res 163:257–264
Geyer MA (2006) The family of sensorimotor gating disorders: comorbidities or diagnostic overlaps? Neurotox Res 10:211–220
Geyer MA, Braff DL (1982) Habituation of the Blink reflex in normals and schizophrenic patients. Psychophysiology 19:1–6
Geyer MA, Braff DL (1987) Startle habituation and sensorimotor gating in schizophrenia and related animal models. Schizophr Bull 13:643–668
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 156:117–154
Goff DC, Henderson DC, Evins AE, Amico E (1999a) A placebo-controlled crossover trial of D-cycloserine added to clozapine in patients with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 45:512–514
Goff DC, Tsai G, Levitt J, Amico E, Manoach D, Schoenfeld DA, Hayden DL, McCarley R, Coyle JT (1999b) A placebo-controlled trial of D-cycloserine added to conventional neuroleptics in patients with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56:21–27
Heresco-Levy U, Javitt DC, Ermilov M, Mordel C, Horowitz A, Kelly D (1996) Double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of glycine adjuvant therapy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 169:610–617
Inada K, Ishigooka J, Anzai T, Suzuki E, Miyaoka H, Saji M (2003) Antisense hippocampal knockdown of NMDA-NR1 by HVJ-liposome vector induces deficit of prepulse inhibition but not of spatial memory. Neurosci Res 45:473–481
Javitt DC, Zukin SR (1991) Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 148:1301–1308
Kumari V, Sharma T (2002) Effects of typical and atypical antipsychotics on prepulse inhibition in schizophrenia: a critical evaluation of current evidence and directions for future research. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 162:97–101
Kumari V, Soni W, Sharma T (1999) Normalization of information processing deficits in schizophrenia with clozapine. Am J Psychiatry 156:1046–1051
Kumari V, Das M, Hodgins S, Zachariah E, Barkataki I, Howlett M, Sharma T (2005) Association between violent behaviour and impaired prepulse inhibition of the startle response in antisocial personality disorder and schizophrenia. Behav Brain Res 158:159–166
Kusljic S, van den Buuse M (2006) Differential involvement of 5-HT projections within the amygdala in prepulse inhibition but not in psychotomimetic drug-induced hyperlocomotion. Behav Brain Res 168:74–82
Law AJ, Deakin JF (2001) Asymmetrical reductions of hippocampal NMDAR1 glutamate receptor mRNA in the psychoses. NeuroReport 12:2971–2974
Linn GS, Negi SS, Gerum SV, Javitt DC (2003) Reversal of phencyclidine-induced prepulse inhibition deficits by clozapine in monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 169:234–239
Lipina T, Labrie V, Weiner I, Roder J (2005) Modulators of the glycine site on NMDA receptors, D-serine and ALX 5407, display similar beneficial effects to clozapine in mouse models of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:54–67
Lipska BK, Weinberger DR (2000) To model a psychiatric disorder in animals: schizophrenia as a reality test. Neuropsychopharmacology 23:223–239
Long LE, Malone DT, Taylor DA (2006) Cannabidiol reverses MK-801-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:795–803
Ludewig K, Geyer MA, Etzensberger M, Vollenweider FX (2002) Stability of the acoustic startle reflex, prepulse inhibition, and habituation in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 55:129–137
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1989) Effects of phencyclidine and phencyclidine biologs on sensorimotor gating in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2:299–308
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1991) Parametric determinants in pre-stimulus modification of acoustic startle: interaction with ketamine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 105:162–168
Meincke U, Morth D, Voss T, Thelen B, Geyer MA, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E (2004) Prepulse inhibition of the acoustically evoked startle reflex in patients with an acute schizophrenic psychosis—a longitudinal study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 254:415–421
Meltzer HY, Stahl SM (1976) The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: a review. Schizophr Bull 2:19–76
Moy SS, Perez A, Koller BH, Duncan GE (2006) Amphetamine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition in mice with reduced NMDA receptor function. Brain Res 1089:186–194
Olney JW, Farber NB (1995) Glutamate receptor dysfunction and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:998–1007
Olney JW, Newcomer JW, Farber NB (1999) NMDA receptor hypofunction model of schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 33:523–533
Ossowska K, Pietraszek M, Wardas J, Nowak G, Zajaczkowski W, Wolfarth S, Pilc A (2000) The role of glutamate receptors in antipsychotic drug action. Amino Acids 19:87–94
Parwani A, Duncan EJ, Bartlett E, Madonick SH, Efferen TR, Rajan R, Sanfilipo M, Chappell PB, Chakravorty S, Gonzenbach S, Ko GN, Rotrosen JP (2000) Impaired prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 47:662–669
Sawa A, Snyder SH (2002) Schizophrenia: diverse approaches to a complex disease. Science 296:692–695
Schwabe K, Brosda J, Wegener N, Koch M (2005) Clozapine enhances disruption of prepulse inhibition after sub-chronic dizocilpine- or phencyclidine-treatment in Wistar rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80:213–219
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1998) Using an animal model of deficient sensorimotor gating to study the pathophysiology and new treatments of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 24:285–301
Swerdlow NR, Bakshi V, Geyer MA (1996) Seroquel restores sensorimotor gating in phencyclidine-treated rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 279:1290–1299
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1999) Cross-species studies of sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex. Ann NY Acad Sci 877:202–216
Swerdlow NR, Hanlon FM, Henning L, Kim YK, Gaudet I, Halim ND (2001) Regulation of sensorimotor gating in rats by hippocampal NMDA: anatomical localization. Brain Res 898:195–203
Swerdlow NR, Krupin AS, Bongiovanni MJ, Shoemaker JM, Goins JC, Hammer RP Jr (2006a) Heritable differences in the dopaminergic regulation of behavior in rats: relationship to D2-like receptor G-protein function. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:721–729
Swerdlow NR, Light GA, Cadenhead KS, Sprock J, Hsieh MH, Braff DL (2006b) Startle gating deficits in a large cohort of patients with schizophrenia: relationship to medications, symptoms, neurocognition, and level of function. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:1325–1335
Tsai G, Yang P, Chung LC, Lange N, Coyle JT (1998) D-serine added to antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 44:1081–1089
Varty GB, Walters N, Cohen-Williams M, Carey GJ (2001) Comparison of apomorphine, amphetamine and dizocilpine disruptions of prepulse inhibition in inbred and outbred mice strains. Eur J Pharmacol 424:27–36
Weike AI, Bauer U, Hamm AO (2000) Effective neuroleptic medication removes prepulse inhibition deficits in schizophrenia patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:61–70
Wiley JL (1994) Clozapine’s effects on phencyclidine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 49:1025–1028
Wiley JL, Kennedy KL (2002) Evaluation of the efficacy of antipsychotic attenuation of phencyclidine-disrupted prepulse inhibition in rats. J Neural Transm 109:523–535
Wolf R, Dobrowolny H, Matzke K, Paelchen K, Bogerts B, Schwegler H (2006) Prepulse inhibition is different in two inbred mouse strains (CPB-K and BALB/cJ) with different hippocampal NMDA receptor densities. Behav Brain Res 166:78–84
Yilmazer-Hanke DM, Roskoden T, Zilles K, Schwegler H (2003) Anxiety-related behavior and densities of glutamate, GABAA, acetylcholine and serotonin receptors in the amygdala of seven inbred mouse strains. Behav Brain Res 145:145–159
Zhang WN, Bast T, Feldon J (2000) Microinfusion of the non-competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist MK-801 (dizocilpine) into the dorsal hippocampus of wistar rats does not affect latent inhibition and prepulse inhibition, but increases startle reaction and locomotor activity. Neuroscience 101:589–599
Zilles K, Wu J, Crusio WE, Schwegler H (2000) Water maze and radial maze learning and the density of binding sites of glutamate, GABA, and serotonin receptors in the hippocampus of inbred mouse strains. Hippocampus 10:213–225
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research of Germany (BMBF, FKZ 01ZZ0407).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolf, R., Paelchen, K., Matzke, K. et al. Acute or subchronic clozapine treatment does not ameliorate prepulse inhibition (PPI) deficits in CPB-K mice with low levels of hippocampal NMDA receptor density. Psychopharmacology 194, 93–102 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0824-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0824-x