Abstract
Purpose
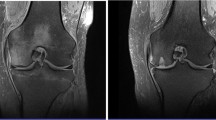
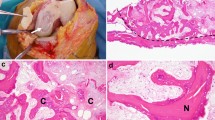
Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SONK/Morbus Ahlback) mainly affects the medial condyle of elderly women. It is assumed that localized vascular insufficiency leads to necrosis of the subchondral bone with subsequent disruption of the nutrition supply to the cartilage above. The aetiology remains unclear in detail. Operative treatment procedures compete against non-operative strategies, whereas the outcome is unpredictable in many cases.
Method
A consecutive case series of five patients suffering from SONK was analysed. All patients underwent a clinical examination, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan, as well as laboratory analyses and visual analogue scale (VAS) evaluation. Our treatment regime is based on high-dose vitamin D administered orally and intravenous application of 3 mg ibandronate two times within 8 weeks. Another 8 weeks later, all patients were followed up including a follow-up MRI.
Results
Within 4 weeks, all patients were free of symptoms. The MRI follow-up showed remission of the bone marrow oedema in every case studied. VAS decreased significantly from 7.4 ± 1.0 pre-interventional to 0.8 ± 1.0 post-interventional. No allergic reactions or other side effects were documented.
Conclusion
We showed that our treatment regime not only eliminated the pathological findings in the MRI of all cases studied, but also decreased the pain level and functional limitations within a short-time period.
Level of evidence
IV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwala S, Shah S, Joshi VR (2009) The use of alendronate in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head: follow-up to eight years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91:1013–1018
Ahlback S, Bauer GC, Bohne WH (1968) Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 11:705–733
al-Kaar M, Garcia J, Fritschy D, Bonvin JC (1997) Aseptic osteonecrosis of the femoral condyle after meniscectomy by the arthroscopic approach. J Radiol 78:283–288
Astrand J, Aspenberg P (2002) Systemic alendronate prevents resorption of necrotic bone during revascularization. A bone chamber study in rats. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 3:19
Bonutti PM, Seyler TM, Delanois RE, McMahon M, McCarthy JC, Mont MA (2006) Osteonecrosis of the knee after laser or radiofrequency-assisted arthroscopy: treatment with minimally invasive knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(Suppl 3):69–75
Brahme SK, Fox JM, Ferkel RD, Friedman MJ, Flannigan BD, Resnick DL (1991) Osteonecrosis of the knee after arthroscopic surgery: diagnosis with MR imaging. Radiology 178:851–853
DeFalco RA, Ricci AR, Balduini FC (2003) Osteonecrosis of the knee after arthroscopic meniscectomy and chondroplasty: a case report and literature review. Am J Sports Med 31:1013–1016
DVO (2011) Guideline 2009 for prevention, diagnosis and therapy of osteoporosis in adults. Osteologie 20:55–74
Faletti C, Robba T, de Petro P (2002) Postmeniscectomy osteonecrosis. Arthroscopy 18:91–94
Heyse TJ, Khefacha A, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, Cartier P (2011) UKA after spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee: a retrospective analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131:613–617
Johnson TC, Evans JA, Gilley JA, DeLee JC (2000) Osteonecrosis of the knee after arthroscopic surgery for meniscal tears and chondral lesions. Arthroscopy 16:254–261
Khosla S et al (2007) Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 22:1479–1491
Kim HK, Randall TS, Bian H, Jenkins J, Garces A, Bauss F (2005) Ibandronate for prevention of femoral head deformity after ischemic necrosis of the capital femoral epiphysis in immature pigs. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:550–557
Koshino T (1982) The treatment of spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee by high tibial osteotomy with and without bone-grafting or drilling of the lesion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 64:47–58
Kraenzlin ME, Graf C, Meier C, Kraenzlin C, Friedrich NF (2010) Possible beneficial effect of bisphosphonates in osteonecrosis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:1638–1644
Lai KA, Shen WJ, Yang CY, Shao CJ, Hsu JT, Lin RM (2005) The use of alendronate to prevent early collapse of the femoral head in patients with nontraumatic osteonecrosis. A randomized clinical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:2155–2159
Little DG, Peat RA, Mcevoy A, Williams PR, Smith EJ, Baldock PA (2003) Zoledronic acid treatment results in retention of femoral head structure after traumatic osteonecrosis in young Wistar rats. J Bone Miner Res 18:2016–2022
MacDessi SJ, Brophy RH, Bullough PG, Windsor RE, Sculco TP (2008) Subchondral fracture following arthroscopic knee surgery. A series of eight cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90:1007–1012
Miltner O, Niedhart C, Piroth W, Weber M, Siebert CH (2003) Transient osteoporosis of the navicular bone in a runner. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 123:505–508
Mont MA, Baumgarten KM, Rifai A, Bluemke DA, Jones LC, Hungerford DS (2000) Atraumatic osteonecrosis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:1279–1290
Muscolo DL, Costa-Paz M, Makino A, Ayerza MA (1996) Osteonecrosis of the knee following arthroscopic meniscectomy in patients over 50-years old. Arthroscopy 12:273–279
Narvaez J, Narvaez JA, Rodriguez-Moreno J, Roig-Escofet D (2000) Osteonecrosis of the knee: differences among idiopathic and secondary types. Rheumatology (Oxford) 39:982–989
Pape D, Filardo G, Kon E, van Dijk CN, Madry H (2010) Disease-specific clinical problems associated with the subchondral bone. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:448–462
Patel DV, Breazeale NM, Behr CT, Warren RF, Wickiewicz TL, O’Brien SJ (1998) Osteonecrosis of the knee: current clinical concepts. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 6:2–11
Ramachandran M, Ward K, Brown RR, Munns CF, Cowell CT, Little DG (2007) Intravenous bisphosphonate therapy for traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:1727–1734
Ringe JD, Dorst A, Faber H (2005) Effective and rapid treatment of painful localized transient osteoporosis (bone marrow edema) with intravenous ibandronate. Osteoporos Int 16:2063–2068
Takeda M, Higuchi H, Kimura M, Kobayashi Y, Terauchi M, Takagishi K (2008) Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee: histopathological differences between early and progressive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:324–329
Takeuchi R, Aratake M, Bito H, Saito I, Kumagai K, Hayashi R, Sasaki Y, Akamatsu Y, Ishikawa H, Amakado E, Aota Y, Saito T (2009) Clinical results and radiographical evaluation of opening wedge high tibial osteotomy for spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 17:361–368
Varenna M, Zucchi F, Binelli L, Failoni S, Gallazzi M, Sinigaglia L (2002) Intravenous pamidronate in the treatment of transient osteoporosis of the hip. Bone 31:96–101
Yates PJ, Calder JD, Stranks GJ, Conn KS, Peppercorn D, Thomas NP (2007) Early MRI diagnosis and non-surgical management of spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Knee 14:112–116
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. Breer and R. Oheim contributed equally to this work and, therefore, share first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breer, S., Oheim, R., Krause, M. et al. Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SONK). Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21, 340–345 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2017-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2017-3