Abstract
Purpose
Traumatic events in adolescence rarely occur in isolation. Multiple traumatic experiences are prevalent, diverse and a well-established risk factor for mental health disorders. The aim of this study was to explore and explain the heterogeneity in trauma profiles in a nationally representative sample of US adolescents.
Method
Using latent class analysis, data on 10,123 adolescents aged between 13 and 18 from the National Comorbidity Survey Adolescent Supplement were examined. In addition, the relationships between the emergent classes and demographic and clinical variables were explored.
Results
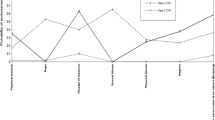
A four-class solution was the best fit of adolescent trauma patterns, with classes labelled as low risk, sexual assault risk, non-sexual risk and high risk. When compared to the low risk class, those in the other classes were significantly more likely not to live with either biological parent, display symptoms indicative of mood and anxiety disorders, and to have higher rates of disorder comorbidity.
Conclusions
This provides evidence of four distinct groups of adolescents who have experienced a variety of traumas. Evidence demonstrates the increased risk of adolescents with a history of trauma meeting the diagnostic criteria for not only individual disorders but also comorbidity across disorder categories.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shevlin M, Elklit A (2008) A latent class analysis of adolescent adverse life events based on a Danish national youth probability sample. Nord J Psychiatry 62:218–224
Elklit A, Petersen T (2008) Exposure to traumatic events among adolescents in four nations. Torture 18(1):2–11
Petersen T, Elklit A, Olesen JG (2010) Victimization and PTSD in a Faroese youth total-population sample. Scand J Psychol 51(1):56–62
Macdonald A, Danielson CK, Resnick HS, Saunders BE, Kilpatrick DG (2010) PTSD and comorbid disorders in a representative sample of adolescents: the risk associated with multiple exposures to potentially traumatic events. Child Abuse Negl 34:773–783
Breslau N, Wilcox HC, Storr CL, Lucia VC, Anthony JC (2004) Trauma exposure and posttraumatic stress disorder: a study of youths in urban America. J Urban Health 81:530–544
Houston JE, Shevlin M, Adamson G, Murphy J (2011) A person-centred approach to modelling population experiences of trauma and mental illness. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 46:149–157
Nooner KB, Linares LO, Batinjane J, Kramer RA, Silva R, Cloitre M (2012) Factors related to posttraumatic stress disorder in adolescence. Trauma Violence Abuse 13(3):153–166
Mullen PE, Walton VA, Romans-Clarkson SE, Herbison P (1988) Impact of sexual and physical abuse on women’s mental health. Lancet 331(8590):841–845
Gibb BE, Chelminski I, Zimmerman M (2007) Childhood emotional, physical and sexual abuse, and diagnoses of depressive and anxiety disorders in adult psychiatric outpatients. Depress Anxiety 24(4):256–263
Carr S, Francis A (2009) Childhood maltreatment and adult personality disorder symptoms in a non-clinical sample. Aust Psychol 44(3):146–155
Green JG, McLaughlin KA, Berglund PA, Gruber MJ, Sampson NA, Zaslavsky AM et al (2010) Childhood adversities and adult psychopathology in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R) I: associations with first onset of DSM-IV disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67(2):113–133
Guadiano BA, Zimmerman M (2010) The relationship between childhood trauma history and the psychotic subtype of major depression. Acta Psychiatr Scand 121(6):462–470
Horwitz AV, Widom CS, McLaughlin J, White HR (2001) The impact of childhood abuse and neglect on adult mental health: a prospective study. J Health Soc Behav 42(4):184–201
Cutajar MC, Mullen PE, Ogloff JRP, Thomas SD, Wells DL, Spataro J (2010) Psychopathology in a large cohort of sexually abused children followed up to 43 years. Child Abuse Neglect 34:813–822
Perez-Fuentes G, Olfson M, Villegas L, Morcillo C, Wang S, Blanco C (2013) Prevalence and correlates of child sexual abuse: a national study. Compr Psychiat 54:16–27
Edwards VJ, Holden GW, Felitti VJ, Anda RF (2003) Relationship between multiple forms of childhood maltreatment and adult mental health in community respondents: results from the adverse childhood experiences study. Am J Psychiatry 160:1453–1460
Green BL, Goodman LA, Krupnick JL, Corcoran CB, Petty RM, Stockton P et al (2000) Outcomes of single versus multiple trauma exposure in a screening sample. J Trauma Stress 13(2):271–286
Finkelhor D, Ormrod RK, Turner HA (2007) Poly-victimization: a neglected component in child victimization. Child Abuse Negl 31:7–26
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders DSM-IV-TR, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
McLaughlin KA, Grief Green J, Gruber MJ, Sampson NA, Zaslavsky AM, Kessler RC (2012) Childhood adversities and first onset of psychiatric disorders in a national sample of US adolescents. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69(11):1151–1160
McLaughlin KA, Koenen KC, Hill ED, Petukhova M, Sampson NA, Zaslavsky AM, Kessler RC (2013) Trauma exposure and posttraumatic stress disorder in a national sample of adolescents. J Am Acad Child Psy 52(8):815–830
Merikangas KR, Avenevoli S, Costello EJ, Koretz D, Kessler RC (2009) The National Comorbidity Survey Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A): I. Background and measures. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 48(4):367–369
Grob GN (2005) Public policy and mental illnesses: Jimmy Carter’s presidential commission on mental health. Milbank Q 83(3):425–456
Kessler RC (2011) The National Comorbidity Survey (NCS) and its extensions. In: Tsuang MT, Tohen M, Jones P (eds) Textbook of psychiatric epidemiology, 3rd edn, 14th chap. John Wiley, Chichester
Kessler RC, Merikangas KR (2004) The National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R): background and aims. Int J Meth Psych Res 13:60–68
Kessler RC, Avenevoli E, Costello EJ, Green JG, Gruber MJ, Heeringa S et al (2009) Design and field procedures in the US National Comorbidity Survey Replication Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A). Int J Meth Psych Res 18(2):69–83
Kessler RC, Avenevoli S, Costello EJ, Green JG, Gruber MJ, Heeringa S et al (2009) National Comorbidity Survey Replication Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A): II. Overview and design. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 48:380–385
Kessler RC, Ustun TB (2004) The World Mental Health (WMH) survey initiative version of the World Health Organization (WHO) Composite International Diagnostic Interview (CIDI). Int J Meth Psych Res 13(2):93–121
Hovens JG, Wiersma JE, Giltay EJ, Van Oppen P, Spinhoven P, Penninx BW et al (2010) Childhood life events and childhood trauma in adult patients with depressive anxiety and comorbid disorders vs controls. Acta Psychiatr Scand 122:66–74
Kessler RC, Avenevoli S, Green JG, Gruber MJ, Guyer M, He Y et al (2009) National Comorbidity Survey Replication Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A): III. Concordance of DSM-IV/CIDI diagnoses with clinical reassessments. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 48:386–399
Muthen LK, Muthen BO (2012) Mplus user’s guide (7th edn). Muthen & Muthen, Los Angeles, CA. http://www.StatModel.com
Akaike H (1987) Factor-analysis and Aic. Psychometrika 52:317–332
Scwartz G (1978) Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6:461–464
Sclove SL (1987) Application of model-selection criteria to some problems in multivariate-analysis. Psychometrika 52:333–343
Yang C-C (2006) Evaluating latent class analysis models in qualitative phenotype identification. Comput Stat Data Anal 50:1090–1104
Lo Y, Mendell NR, Rubin DB (2001) Testing the number of components in a normal mixture. Biometrika 88(3):767–778
Celeux G, Soromenho G (1996) An entropy criterion for assessing the number of clusters in a mixture model. J Classif 13:195–212
Wang J, Wang X (2012) Structural equation modeling: applications using Mplus. John Wiley, Chichester, UK
Roberts AL, Gilman SE, Breslau J, Breslau N, Koenen KC (2011) Race/ethnic differences in exposure to traumatic events, development of post-traumatic stress disorder, and treatment-seeking for post-traumatic stress disorder in the United States. Psyhcol Med 41(1):71–83
Manning WD, Lamb KA (2004) Adolescent well-being in cohabiting, married, and single-parent families. J Marriage Fam 65(4):876–893
Elklit A (2002) Victimization and PTSD in a Danish National Youth Probability Sample. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41(2):174–181
Stein MB, Walker JR, Anderson G, Hazen AL, Ross CA, Eldridge G et al (1996) Childhood physical and sexual abuse in patients with anxiety disorders and in a community sample. Am J Psychiatry 153(2):275–277
Cougle JR, Timpano KR, Sachs-Ericsson N, Keough ME, Riccardi CJ (2010) Examining the unique relationships between anxiety disorders and childhood physical and sexual abuse in the National Comorbidity Survey-Replication. Psychiatry Res 177:150–155
Lochner C, Seedat S, Allgulander C, Kidd M, Stein D, Gerdner A (2010) Childhood trauma in adults with social anxiety disorder and panic disorder: a cross-national study. Afr J Psychiatry 13(5):376–381
Safren SA, Gershuny BS, Marzol P, Otto MW, Pollack MH (2002) History of childhood abuse in panic disorder, social phobia, and generalized anziety disorder. J Nerv Ment Dis 190(7):453–456
Hasin DS, Stinson FS, Ogburn E, Grant BF (2007) Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: results From the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64(7):830–842
Compton WM, Thomas YF, Stinson FS, Grant BF (2007) Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV drug abuse and dependence in the United States: results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:566–576
Kilpatrick DG, Saunders BE, Smith DW (2003) Youth victimization: prevalence and implications. National Institute of Justice, US Department of Justice. Office of Justice Programs, Washington
Funk RR, Mcdermeit M, Godley SH, Adams L (2003) Maltreatment issues by level of adolescent substance abuse treatment: the extent of the problem at intake and relationship to early outcomes. Child Maltreat 8(1):36–45
Giaconia RM, Reinherz HZ, Hauf AC, Paradis AD, Wasserman MS, Langhammer DM (2000) Comorbidity of substance use and post-traumatic stress disorders in a community sample of adolescents. Am J Orthopsychiatry 70(2):253–262
Everett B, Gallop R (2001) The link between childhood trauma and mental illness: effective interventions for mental health professionals. Sage Publications Inc, California
Suliman S, Mkabile SG, Fincham DS, Ahmed R, Stein DJ, Seedat S (2009) Cumulative effect of multiple trauma on symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, anxiety and depression in adolescents. Compr Psychiatry 50:121–127
Merikangas KR, He J-P, Brody D, Fisher PW, Bourdon K, Koretz DS (2010) Prevalence and treatment of mental disorders among US children in the 2001–2004 NHANES. Pediatrics 125(1):75–81
Meltzer H, Bebbington P, Brugha T, Farrell M, Jenkins R, Lewis G (2000) The reluctance to seek treatment for neurotic disorders. J Mental Health 9(3):319–327
Tishelman AC, Geffner R (2011) Child and adolescent trauma across the spectrum of experience: research and clinical interventions. J Child Adolesc Trauma 4:1–7
Jonsson U, Bohman H, von Knorring L, Olsson G, Paaren A, von Knorring A-L (2011) Mental health outcome of long term and episodic adolescent depression: 15-year follow-up of a community sample. J Affect Disord 130(3):395–404
Williams LM, Siegel JA, Pomeroy JJ (2000) Validity of women’s self-reports of documented child abuse. In: Stone S, Turkkan JS (eds) The science of self-report: implications for research and practice. Erlbaum, Malwah
Molnar BE, Buka SL, Kessler RC (2001) Child sexual abuse and subsequent psychopathology. Results from the national comorbidity survey. Am J Public Health 91:753–760
Lee S, Tsang A, von Korff M, de Graaf R, Benjet C, Haro JM, Angermeyer M, Demyttenaere K, de Girolamo G, Gasquet I, Merikangas K, Posada-Villa J, Takeshima T, Kessler RC (2009) Association of headache with childhood adversity and mental disorder: cross-national study. BJP 194:111–116
Acknowledgments
This study was funded as part of a PhD studentship through a Department of Education and Learning (DEL) Northern Ireland award to the corresponding author. DEL had no further role in study design; data analysis; report writing or in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McChesney, G.C., Adamson, G. & Shevlin, M. A latent class analysis of trauma based on a nationally representative sample of US adolescents. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 50, 1207–1217 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-015-1075-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-015-1075-5