Abstract
Purpose
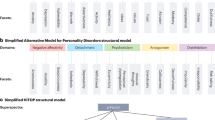
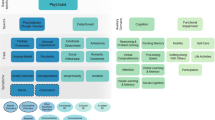
Classification is the cornerstone of clinical diagnostic practice and research. However, the extant psychiatric classification systems are not well supported by research evidence. In particular, extensive comorbidity among putatively distinct disorders flags an urgent need for fundamental changes in how we conceptualize psychopathology. Over the past decade, research has coalesced on an empirically based model that suggests many common mental disorders are structured according to two correlated latent dimensions: internalizing and externalizing.
Methods
We review and discuss the development of a dimensional-spectrum model which organizes mental disorders in an empirically based manner. We also touch upon changes in the DSM-5 and put forward recommendations for future research endeavors.
Results
Our review highlights substantial empirical support for the empirically based internalizing–externalizing model of psychopathology, which provides a parsimonious means of addressing comorbidity.
Conclusions
As future research goals, we suggest that the field would benefit from: expanding the meta-structure of psychopathology to include additional disorders, development of empirically based thresholds, inclusion of a developmental perspective, and intertwining genomic and neuroscience dimensions with the empirical structure of psychopathology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blashfield RK, Keeley JW, Flanagan EH, Miles SR (2014) The cycle of classification: DSM-I through DSM-5. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 10:25–51
Stahl SM (2013) The last Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM): replacing our symptom-based diagnoses with a brain circuit-based classification of mental illnesses. CNS Spectr 18:65–68
Eaton NR, Rodriguez-Seijas C, Carragher N, Krueger RF (2015) Transdiagnostic factors of psychopathology and substance use disorders: a review. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. doi:10.1007/s00127-014-1001-2
Slade T, Watson D (2006) The structure of common DSM-IV and ICD-10 mental disorders in the Australian general population. Psychol Med 36:1593–1600
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5), 5th edn. American Psychiatric Publishing, Washington DC
Hickie IB, Scott J, McGorry PD (2013) Clinical staging for mental disorders: a new development in diagnostic practice in mental health. Med J Aust 198:461–462
Krueger R, Bezdjian S (2009) Enhancing research and treatment of mental disorders with dimensional concepts: toward DSM-V and ICD-11. World Psychiatry 8:3–6
Carragher N, Adamson G, Bunting B, McCann S (2009) Subtypes of depression in a nationally representative sample. J Affect Disord 113:88–99
Roberts MC, Reed GM, Medina-Mora ME, Keeley JW, Sharan P, Johnson DK et al (2012) A global clinicians’ map of mental disorders to improve ICD-11: analysing meta-structure to enhance clinical utility. Int Rev Psychiatry 24:578–590
Verheul R, Widiger TA (2004) A meta-analysis of the prevalence and usage of the personality disorder not otherwise specified (PDNOS) diagnosis. J Pers Disord 18:309–319
Verheul R, Bartak A, Widiger T (2007) Prevalence and construct validity of Personality Disorder Not Otherwise Specified (PDNOS). J Pers Disord 21:359–370
Szodoray P, Nakken B, Barath S, Gaal J, Aleksza M, Zeher M et al (2008) Progressive divergent shifts in natural and induced T-regulatory cells signify the transition from undifferentiated to definitive connective tissue disease. Int Immunol 20:971–979
Kraemer HC (2007) DSM categories and dimensions in clinical and research contexts. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 16:S8–S15
Kamphuis JH, Noordhof A (2009) On categorical diagnoses in DSM-V: cutting dimensions at useful points? Psychol Assess 21:294–301
Krueger RF (1999) The structure of common mental disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56:921–926
Krueger RF, Chentsova-Dutton YE, Markon KE, Goldberg DP, Ormel J (2003) A cross-cultural study of the structure of comorbidity among common psychopathological syndromes in the general health care setting. J Abnorm Psychol 112:437–447
Kessler RC, Ormel J, Petukhova M, McLaughlin KA, Green JG, Russo LJ et al (2011) Development of lifetime comorbidity in the World Health Organization world mental health surveys. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:90–100
Krueger RF, Caspi A, Moffitt TE, Silva PA (1998) The structure and stability of common mental disorders (DSM-III-R): a longitudinal-epidemiological study. J Abnorm Psychol 107:216–227
Eaton NR, Krueger RF, Keyes KM, Skodol AE, Markon KE, Grant BF et al (2011) Borderline personality disorder co-morbidity: relationship to the internalizing–externalizing structure of common mental disorders. Psychol Med 41:1041–1050
Krueger RF, Markon KE (2006) Reinterpreting comorbidity: a model-based approach to understanding and classifying psychopathology. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 2:111–133
Eaton NR, South SC, Krueger RF (2010) The meaning of comorbidity among common mental disorders. In: Millon T, Krueger RF, Simonsen E (eds) Contemporary directions in psychopathology: scientific foundations of the DSM-V and ICD-11, 2nd edn. Guilford Publications, New York, pp 223–241
Blanco C, Krueger RF, Hasin DS, Liu SM, Wang S, Kerridge BT et al (2013) Mapping common psychiatric disorders: structure and predictive validity in the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. JAMA Psychiatry 70:199–208
Achenbach TM, Edelbrock CS (1978) The classification of child psychopathology: a review and analysis of empirical efforts. Psychol Bull 85:1275–1301
Achenbach TM, Edelbrock CS (1984) Psychopathology of childhood. Annu Rev Psychol 35:227–256
Wolf AWSD, Patterson MB, Grande TP, Brocco KJ, Pendleton L (1988) Associations among major psychiatric diagnoses. J Consult Clin Psychol 56:292–294
Vollebergh WA, Iedema J, Bijl RV, de Graaf R, Smit F, Ormel J (2001) The structure and stability of common mental disorders: the NEMESIS study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58:597–603
Røysamb E, Kendler KS, Tambs K, Ørstavik RE, Neale MC, Aggen SH et al (2011) The joint structure of DSM-IV axis I and axis II disorders. J Abnorm Psychol 120:198–209
Eaton NR, Keyes KM, Krueger RF, Balsis S, Skodol AE, Markon KE et al (2012) An invariant dimensional liability model of gender differences in mental disorder prevalence: evidence from a national sample. J Abnorm Psychol 121:282–288
Eaton NR, Keyes KM, Krueger RF, Noordhof A, Skodol AE, Markon KE et al (2013) Ethnicity and psychiatric comorbidity in a national sample: evidence for latent comorbidity factor invariance and connections with disorder prevalence. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 48:701–710
Eaton NR, Krueger RF, Oltmanns TF (2011) Aging and the structure and long-term stability of the internalizing spectrum of personality and psychopathology. Psychol Aging 26:987–993
Eaton NR (2014) Transdiagnostic psychopathology factors and sexual minority mental health: evidence of disparities and associations with minority stressors. Psychol Sex Orientat Gend Divers 1:244–254
Measelle JR, Stice E, Hogansen JM (2006) Developmental trajectories of co-occurring depressive, eating, antisocial, and substance abuse problems in female adolescents. J Abnorm Psychol 115:524–538
South SC, Krueger RF, Iacono WG (2011) Understanding general and specific connections between psychopathology and marital distress: a model based approach. J Abnorm Psychol 120:935–947
South SC, Miller ML (2014) Measuring momentary stress, affect, and cognition: relationships with the internalizing and externalizing spectra. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 36:9–104
Conway C, Hammen C, Brennan PA (2012) Expanding stress generation theory: test of a transdiagnostic model. J Abnorm Psychol 121:754–766
Kendler KS, Myers J (2014) The boundaries of the internalizing and externalizing genetic spectra in men and women. Psychol Med 44:647–665
Kendler KS, Aggen SH, Knudsen GP, Røysamb E, Neale MC, Reichborn-Kjennerud T (2011) The structure of genetic and environmental risk factors for syndromal and subsyndromal common DSM-IV axis I and all axis II disorders. Am J Psychiatry 168:29–39
Kendler KS, Prescott CA, Myers JM, Neale MC (2003) The structure of genetic and environmental risk factors for common psychiatric and substance use disorders in men and women. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:929–937
Lahey BB, van Hulle C, Singh AL, Waldman ID, Rathouz PJ (2011) Higher-order genetic and environmental structure of prevalent forms of child and adolescent psychopathology. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:181–189
Lahey BB, Zald DH, Hakes JK, Krueger RF, Rathouz PJ (2014) Patterns of heterotypic continuity associated with the cross-sectional correlational structure of prevalent mental disorders in adults. JAMA Psychiatry 71:989–996
Wittchen HU, Beesdo-Baum K, Gloster AT, Höfler M, Klotsche J, Lieb R et al (2009) The structure of mental disorders re-examined: is it developmentally stable and robust against additions? Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 18:189–203
Seeley JR, Kosty DB, Farmer RF, Lewinsohn PM (2011) The modeling of internalizing disorders on the basis of patterns of lifetime comorbidity: associations with psychosocial functioning and psychiatric disorders among first-degree relatives. J Abnorm Psychol 120:308–321
Kendler KS, Neale MC, Kessler RC, Heath AC, Eaves LJ (1992) Major depression and generalized anxiety disorder. Same genes, (partly) different environments? Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:716–722
Kendler KS (1996) Major depression and generalised anxiety disorder. Same genes, (partly) different environments—revisited. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 168:68–75
Starr L, Conway CC, Hammen CL, Brennan PA (2014) Transdiagnostic and disorder-specific models of intergenerational transmission of internalizing pathology. Psychol Med 44:161–172
Krueger RF, South SC (2009) Externalizing disorders: cluster 5 of the proposed meta-structure for DSM-V and ICD-11. Psychol Med 39:2061–2070
Tackett JL, Lahey BB, van Hulle C, Waldman I, Krueger RF, Rathouz PJ (2013) Common genetic influences on negative emotionality and a general psychopathology factor in childhood and adolescence. J Abnorm Psychol 122:1142–1153
Lahey BB, Applegate B, Hakes JK, Zald DH, Hariri AR, Rathouz PJ (2012) Is there a general factor of prevalent psychopathology during adulthood? J Abnorm Psychol 121:971–977
Caspi A, Houts RM, Belsky DW, Goldman-Mellor S, Harrington HL, Israel S et al (2014) The p factor: one general psychopathology factor in the structure of psychiatric disorders? Clin Psychol Sci 2:119–137
Helzer JE, Kraemer HC, Krueger RF (2006) The feasibility and need for dimensional psychiatric diagnoses. Psychol Med 36:1671–1680
First MB (2005) Clinical utility: a prerequisite for the adoption of a dimensional approach in DSM. J Abnorm Psychol 114:560–564
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ, Boden JM (2006) Structure of internalising symptoms in early adulthood. Br J Psychiatry 189:540–546
Ferdinand RR, de Nija PF, van Lier P, Verhulst FC (2005) Latent class analysis of anxiety and depressive symptoms in referred adolescents. J Affect Disord 88:299–306
Vaidyanathan Patrick CJ, Iacono WG (2011) Patterns of comorbidity among mental disorders: a person-centered approach. Compr Psychiatry 52:527–535
Eaton N, Krueger RF, Markon KE, Keyes KM, Skodol AE, Wall M et al (2013) The structure and predictive validity of the internalizing disorders. J Abnorm Psychol 122:86–92
Wright AG, Krueger RF, Hobbs MJ, Markon KE, Eaton NR, Slade T (2013) The structure of psychopathology: toward an expanded quantitative empirical model. J Abnorm Psychol 122:281–294
Carragher N, Krueger RF, Eaton NR, Markon KE, Keyes KM, Blanco C et al (2014) ADHD and the externalizing spectrum: direct comparison of categorical, continuous, and hybrid models of liability in a nationally representative sample. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 49:1307–1317
Witkiewitz K, King K, McMahon RJ, Wu J, Luk J, Bierman KL (2013) Evidence for a multi-dimensional latent structural model of externalizing disorders. J Abnorm Child Psychol 41:223–237
Walton K, Ormel J, Krueger RF (2011) The dimensional nature of externalizing behaviors in adolescence: evidence from a direct comparison of categorical, dimensional, and hybrid models. J Abnorm Child Psychol 39:553–561
Muthén B (2006) Should substance use disorders be considered as categorical or dimensional? Addiction 101:6–16
Markon KE (2010) Modeling psychopathology structure: a symptom-level analysis of axis I and II disorders. Psychol Med 40:273–288
Lubke GH, Miller PJ (2014) Does nature have joints worth carving? A discussion of taxometrics, model-based clustering and latent variable mixture modeling. Psychol Med (in press)
Borsboom D, Cramer AO (2013) Network analysis: an integrative approach to the structure of psychopathology. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 9:91–121
Cramer AO, Waldorp LJ, van der Maas HL, Borsboom D (2010) Comorbidity: a network perspective. Behav Brain Sci 33:137–193
Stein DJ, Craske MG, Friedman MJ, Phillips KA (2011) Meta-structure issues for the DSM-5: how do anxiety disorders, obsessive–compulsive and related disorders, post-traumatic disorders, and dissociative disorders fit together? Curr Psychiatry Rep 1:248–250
Keyes KM, Eaton NR, Krueger RF, Skodol AE, Wall MM, Grant B et al (2013) Thought disorder in the meta-structure of psychopathology. Psychol Med 43:1673–1683
Kotov R, Chang SW, Fochtmann LJ, Mojtabai R, Carlson GA, Sedler MA et al (2011) Schizophrenia in the internalizing–externalizing framework: a third dimension? Schizophr Bull 37:1168–1178
Kotov R, Ruggero CJ, Krueger RF, Watson D, Yuan Q, Zimmerman M (2011) New dimensions in the quantitative classification of mental illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:1003–1011
Noordhof A, Krueger RF, Ormel J, Oldehinkel AJ, Hartman CA (2014) Integrating autism-related symptoms into the dimensional internalizing and externalizing model of psychopathology. The TRAILS Study. J Abnorm Child Psychol 8:8
Forbush K, Watson D (2013) The structure of common and uncommon mental disorders. Psychol Med 43:97–108
Oleski J, Cox BJ, Clara I, Hills A (2011) Pathological gambling and the structure of common mental disorders. J Nerv Ment Dis 199:956–960
Forbes M, Schniering CA (2013) Are sexual problems a form of internalizing psychopathology? A structural equation modeling analysis. Arch Sex Behav 42:23–34
Cox BJ, Clara IP, Enns MW (2002) Posttraumatic stress disorder and the structure of common mental disorders. Depress Anxiety 15:168–171
Wolf EJ, Miller MW, Krueger RF, Lyons MJ, Tsuang MT, Koenen KC (2010) Posttraumatic stress disorder and the genetic structure of comorbidity. J Abnorm Psychol 119:320–330
James LM, Taylor J (2008) Revisiting the structure of mental disorders: borderline personality disorder and the internalizing/externalizing spectra. Br J Clin Psychol 47:361–380
Sharp C, Elhai J, Kalpacki A, Michonski J, Pavlidis I (2014) Locating adolescent BPD within the internalizing–externalizing spectrum in adolescents. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the National Association for the Study of Personality Disorder, Boston
Hudson J, Zanarini MC, Mitchell KS, Choi-Kain LW, Gunderson JG (2014) The contribution of familial internalizing and externalizing liability factors to borderline personality disorder. Psychol Med (in press)
Forbush KT, South SC, Krueger RF, Iacono WG, Clark LA, Keel PK (2010) Locating eating pathology within an empirical diagnostic taxonomy: evidence from a community-based sample. J Abnorm Psychol 119:282–292
Mitchell KS, Wolf EJ, Reardon AF, Miller MW (2014) Association of eating disorder symptoms with internalizing and externalizing dimensions of psychopathology among men and women. Int J Eat Disord 47:860–869
Cox BJ, Clara IP, Hills AL, Sareen J (2010) Obsessive–compulsive disorder and the underlying structure of anxiety disorders in a nationally representative sample: confirmatory factor analytic findings from the German Health Survey. J Anxiety Disord 24:30–33
Simms LJ, Prisciandaro JJ, Krueger RF, Goldberg DP (2012) The structure of depression, anxiety and somatic symptoms in primary care. Psychol Med 42:15–28
Tackett JL, Daoud SL, De Bolle M, Burt SA (2013) Is relational aggression part of the externalizing spectrum? A bifactor model of youth antisocial behavior. Aggress Behav 39:149–159
Ofrat S, Krueger RF, Eaton NR, Keyes KM, Skodol AE, Grant BF et al (2014) Nonmedical prescription drug use comorbidity: developing a cohesive risk model. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 36:371–379
Krueger RF, Derringer J, Markon KE, Watson D, Skodol AE (2012) Initial construction of a maladaptive personality trait model and inventory for DSM-5. Psychol Med 42:1879–1890
Zimmermann J, Altenstein D, Krieger T, Holtforth MG, Pretsch J, Alexopoulos J et al (2014) The structure and correlates of self-reported DSM-5 maladaptive personality traits: findings from two German-speaking samples. J Pers Disord 28:518–540
Morey LC, Krueger RF, Skodol AE (2013) The hierarchical structure of clinician ratings of proposed DSM-5 pathological personality traits. J Abnorm Psychol 122:836–841
Krueger RF, Markon KE (2014) The role of the DSM-5 personality trait model in moving toward a quantitative and empirically based approach to classifying personality and psychopathology. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 10:477–501
Mullins-Sweatt SN, Widiger TA (2009) Clinical utility and DSM-V. Psychol Assess 21:302–312
Berghuis H, Kamphuis JH, Verheul R, Larstone R, Livesley J (2013) The General Assessment of Personality Disorder (GAPD) as an instrument for assessing the core features of personality disorders. Clin Psychol Psychother 20:544–557
Beesdo-Baum K, Höfler M, Gloster AT, Klotsche J, Lieb R, Beauducel A (2009) The structure of common mental disorders: a replication study in a community sample of adolescents and young adults. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 18:204–220
Knäuper B, Wittchen HU (1994) Diagnosing major depression in the elderly: evidence for response bias in standardized diagnostic interviews? J Psychiatr Res 28:147–164
Verona E, Javdani S, Sprague J (2011) Comparing factor structures of adolescent psychopathology. Psychol Assess 23:545–551
Cosgrove VE, Rhee SH, Gelhorn HL, Boeldt D, Corley RC, Ehringer MA et al (2011) Structure and etiology of co-occurring internalizing and externalizing disorders in adolescents. J Abnorm Child Psychol 39:109–123
Kessler RC, Avenevoli S, McLaughlin KA, Green JG, Lakoma MD, Petukhova M et al (2012) Lifetime co-morbidity of DSM-IV disorders in the US National Comorbidity Survey Replication Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A). Psychol Med 42:1997–2010
Lahey BB, Applegate B, Waldman ID, Loft JD, Hankin BL, Rick J (2004) The structure of child and adolescent psychopathology: generating new hypotheses. J Abnorm Psychol 113:358–385
Lahey BB, Rathouz PJ, van Hulle C, Urbano RC, Krueger RF, Applegate B (2008) Testing structural models of DSM-IV symptoms of common forms of child and adolescent psychopathology. J Abnorm Child Psychol 36:187–206
Verona E, Sachs-Ericsson N, Joiner TE (2004) Suicide attempts associated with externalizing psychopathology in an epidemiological sample. Am J Psychiatry 161:444–451
Yoder KA, Longley SL, Whitbeck LB, Hoyt DR (2008) A dimensional model of psychopathology among homeless adolescents: suicidality, internalizing, and externalizing disorders. J Abnorm Child Psychol 36:95–104
Wittchen HU, Höfler M, Gloster AT, Craske MG, Beesdo K (2011) Options and dilemmas of dimensional measures for DSM-5: which types of measures fare best in predicting course and outcome. In: Regier DA, Narrow WE, Kuhl EA, Kupfer DJ (eds) Options and dilemmas of dimensional measures for DSM-5: which types of measures fare best in predicting course and outcome. American Psychiatric Publishing, Arlington, pp 119–146
Regier DA, Narrow WE, First MB, Marshall T (2002) The APA classification of mental disorders: future perspectives. Psychopathology 35:166–170
Walker EF, Sabuwalla Z, Huot R (2004) Pubertal neuromaturation, stress sensitivity, and psychopathology. Dev Psychopathol 16:807–834
Paus T, Keshavan M, Giedd JN (2008) Why do many psychiatric disorders emerge during adolescence? Nat Rev Neurosci 9:947–957
Merikangas KR, He JP, Burstein M, Swanson SA, Avenevoli S, Cui L et al (2010) Lifetime prevalence of mental disorders in U.S. adolescents: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication—Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A). J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49:980–989
Kim-Cohen J, Caspi A, Moffitt TE, Harrington H, Milne BJ, Poulton R (2003) Prior juvenile diagnoses in adults with mental disorder: developmental follow-back of a prospective-longitudinal cohort. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:709–717
Hudziak JJ, Achenbach TM, Althoff RR, Pine DS (2007) A dimensional approach to developmental psychopathology. In J Methods Psychiatr Res 16:S16–S23
Kendler KS, Gardner CO, Lichtenstein P (2008) A developmental twin study of symptoms of anxiety and depression: evidence for genetic innovation and attenuation. Psychol Med 38:1567–1575
Balsis S, Gleason ME, Woods CM, Oltmanns TF (2007) An item response theory analysis of DSM-IV personality disorder criteria across younger and older age groups. Psychol Aging 22:171–185
Eaton NR, Krueger RF, South SC, Gruenewald TL, Seeman TE, Roberts BW (2012) Genes, environments, personality, and successful aging: toward a comprehensive developmental model in later life. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 67:480–488
Phillips ML, Vieta E (2007) Identifying functional neuroimaging biomarkers of bipolar disorder: toward DSM-V. Schizophr Bull 33:893–904
Kupfer D (2014) DSM-5: new opportunities and challenges for teaching and training. Acad Psychiatry 38:58–60
Sanislow CA, Pine DS, Quinn KJ, Kozak MJ, Garvey MA, Heinssen RK et al (2010) Developing constructs for psychopathology research: research domain criteria. J Abnorm Psychol 119:631–639
Cuthbert BN, Kozak MJ (2013) Constructing constructs for psychopathology: the NIMH research domain criteria. J Abnorm Psychol 122:928–937
Ofrat S, Krueger RF (2012) How research on the meta-structure of psychopathology aids in understanding biological correlates of mood and anxiety disorders. Biol Mood Anxiety Disord 2:13
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carragher, N., Krueger, R.F., Eaton, N.R. et al. Disorders without borders: current and future directions in the meta-structure of mental disorders. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 50, 339–350 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-014-1004-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-014-1004-z