Abstract
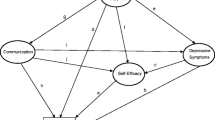
This study employed multivariate analyses and structural modeling procedures to examine a model for the determinants of adherence to medical regimens. Fifty adult hypertensive patients at a health maintenance organization completed questionnaires and participated in home interviews over a 10-week period. Knowledge of medical regimens, information communication between the patient and the medical professionals, satisfaction with health-care providers, health locus of control, social support, and treatment disruption to life-style were assessed. Adherence was assessed through self-report and behavioral (i.e., pill-count ratio, percentage of kept medical appointments) indices. Finally, repeated blood-pressure measurements were obtained. Structural modeling procedures revealed that greater expectancy for internal control over health and hypertension, greater knowledge of the treatment regimen, and stronger social support were significant determinants of adherence; in turn, higher levels of adherence facilitated blood-pressure reduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker, M. H. (1979). Understanding patient compliance: The contributions of attitudes and other psychosocial factors. In Cohen, S. J. (ed.),New Directions in Patient Compliance, D. C. Heath, Lexington, Mass., pp. 1–32.
Becker, M. H., and Maiman, L. A. (1975). Sociobehavioral determinants of compliance with health and medical care regimens.Med. Care 13: 10–24.
Becker, M. H., and Maiman, L. A. (1980). Strategies for enhancing patient compliance.J. Commun. Health 6: 113–135.
Bender, P. M., and Bonett, D. G. (1980). Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures.Psychol. Bull. 88: 588–606.
Caplan, R. D., Robinson, E. A. R., French, J. R. P., Caldwell, J. R., and Shinn, M. (1976).Adhering to Medical Regimens: Pilot Experiments in Patient Education and Social Support, Institute for Social Research, Ann Arbor, Mich.
Caplan, R. D., Harrison, R. V., Wellons, R. V., and French, J. R. P. (1980).Social Support and Patient Adherence: Experimental and Survey Findings, Institute for Social Research, Ann Arbor, Mich.
Cromwell, R. L., Butterfield, E. C., Brayfield, F. M., and Curry, J. L. (1977).Acute Myocardial Infarction: Reaction and Recovery, Mosby, St. Louis, Mo.
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests.Psychometrika 16: 297–334.
Davis, M. S. (1966). Variations in patients' compliance with doctors' orders: Analysis of congruence between survey responses and results of empirical investigations.J. Med. Educ. 41: 1037–1048.
Epstein, L. H., and Cluss, P. A. (1982). A behavioral medicine perspective on adherence to long-term medical regimens.J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 50: 950–971.
Garrity, T. F. (1981). Medical compliance and the clinician-patient relationship: A review.Soc. Sci. Med. 15E: 215–222.
Haynes, R. B. (1976). A critical review of the “determinants” of patient compliance with therapeutic regimens. In Sackett, D. L. and Haynes, R. B. (eds.),Compliance with Therapeutic Regimens, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Md., pp. 26–39.
Haynes, R. B. (1979). Strategies to improve compliance with referrals, appointments, and prescribed medical regimens. In Haynes, R. B., Taylor, D. W., and Sackett, D. L. (eds.),Compliance in Health Care, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Md., pp. 121–143.
Haynes, R. B., Taylor, D. W., and Sackett, D. L. (eds.) (1979).Compliance in Health Care, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Md.
Howe, G. W. (1981).Evaluating a Medical Consumer Assertion Training Program: Effects on Patient-Physician Interaction and Compliance with Therapeutic Regimen, Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Connecticut, Storrs.
Hulka, B. S. (1979). Patient-clinician interactions and compliance. In Haynes, R. B., Taylor, D. W., and Sackett, D. L. (eds.),Compliance in Health Care, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Md., pp. 63–77.
Janz, N. K., and Becker, M. H. (1984). The health belief model: A decade later.Health Educ. Q. 11: 1–47.
Jöreskog, K. G., and Sörbom, D. (1983).LISREL V and VI-Analysis of Linear Structural Relationships by Maximum Likelihood and Least Squares Methods, International Educational Services, Chicago.
Kirscht, J. P., and Rosenstock, I. M. (1979). Patients' problems in following recommendations of health care experts. In Stone, G. C., Cohen, F., and Adler, N. E. (eds.),Health Psychology, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, pp. 189–215.
Laughlin, K. D., Sherrard, D. J., and Fisher, L. (1980). Comparison of clinic and home blood pressure levels in essential hypertension and variables associated with clinic-home differences.J. Chron. Dis. 33: 197–206.
Leventhal, H., Zimmerman, R., and Gutmann, M. (1984). Compliance: A self-regulation perspective. In Gentry, W. D. (ed.),Handbook of Behavioral Medicine, Guilford Press, New York, pp. 369–436.
Ley, P. (1977). Psychological studies of doctor-patient communication. In Rachman, S. (ed.),Contributions to Medical Psychology, Pergamon Press, New York, pp. 9–42.
Masur, F. T. (1981). Adherence to health care regimens. In Prokop, C. K., and Bradley, L. A. (eds.),Medical Psychology: Contributions to Behavioral Medicine, Academic Press, New York, pp. 441–470.
Sackett, D. L., and Snow, J. C. (1979). The magnitude of compliance and noncompliance. In Haynes, R. B., Taylor, D. W., and Sackett, D. L. (eds.),Compliance in Health Care, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Md., pp. 11–22.
Sackett, D. L., Haynes, R. B., Gibson, E. S., and Johnson, A. (1976). The problem of compliance with antihypertensive therapy.Pract. Cardiol. 2: 35–39.
Seeman, M., and Evans, J. W. (1962). Alienation and learning in a hospital setting.Am. Social. Rev. 27: 772–783.
Strahan, R., and Gerbasi, K. (1972). Short, homogeneous version of the Marlowe-Crowne social desirability scale.J. Clin. Psychol. 28: 191–193.
U. S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (1979).Healthy People: The Surgeon General's Report on Health Promotion and Disease Prevention, DHEW (PHS) Publ. No. 79-55071, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
Wallston, K. A., Wallston, B. S., and DeVellis, R. (1978). Development of the multidimensional health locus of control (MHLC) scales.Health Educ. Monogr. 6: 160–170.
Ware, J. E., Kane, R. L., and Davies-Avery, A. (1978). Effects of differences in quality of care on patient satisfaction and other variables: An experimental simulation. Paper presented at the 17th Annual Conference on Research in Medical Education, New Orleans, October.
Weinstein, M. C., and Stason, W. B. (1976).Hypertension: A Policy Perspective, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass.
Witenberg, S. H., Blanchard, E. B., Suls, J., Tennen, H., McCoy, G., and McGoldrick, M. D. (1983). Perceptions of control and causality as predictors of compliance and coping in hemodialysis.Basic Appl. Soc. Psychol. 4: 319–336.
Wolf, M. H., Putnam, S. M., James, S. A., and Stiles, W. B. (1978). The medical interview satisfaction scale: Development of a scale to measure patient perceptions of physician behavior.J. Behav. Med. 1: 391–401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article is based on the author's doctoral dissertation completed at the University of Connecticut and was supported in part by that institutions's Research Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanton, A.L. Determinants of adherence to medical regimens by hypertensive patients. J Behav Med 10, 377–394 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00846477
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00846477