Abstract
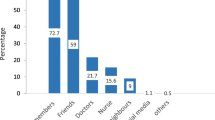
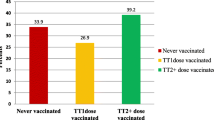
Objective : To study the awareness among general public and health care providers about tetanus immunization in relation to injuries, and their knowledge about tetanus immunization schedules in children, pregnant females and adults.Methods : It was a cross-sectional study done at a perfect health mela and all the government allopathic health agencies in Delhi.Results : The knowledge of tetanus immunization was poor among general public as well as health care providers. A substantial proportion of them indicated tetanus injection after every injury, which was unwarranted. The knowledge of tetanus immunization schedule for adults was poor among all categories of respondents, though it was comparatively better for pregnant females, but only 75% of doctors and 51.1 % of nursing personnel correctly knew the immunization schedule against tetanus in children.Conclusion : There is a need to upgrade the level of knowledge among health care providers so as to ensure that schedules of tetanus are followed properly and unnecessary repeated immunizations are avoided and the same knowledge is passed on to the general public also.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brabek E, Kranke B, Stunzner D, Aberer W. Epidemiologic data for tetanus prophylaxis; assessment of the need for vaccination.Wien Klin Wocheischr 1999 Oct 29; 111(20): 851–854.
Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (CIP), CDC Atlant. Diphtheria, tetanus and pertusis: Recommendations for use and other preventive measures.MMWR Aug 08, 1991; 40 (PR10): 1–28.
Health Facilities in Delhi, 2002. Directorate of Health Services, Government of Delhi.
Ahmed SI, Baig L, Thaver IH, Siddiqui MI, Jafery SI, Javed A. Knowledge attitude and practices of general practitioners in Karachi District Central about tetanus immunization in adults.J Pak Med Assoc 2001 Oct; 51(10): 367–369.
Singh A, Arora AK. Tetanus immunization among adolescent girls in rural Haryana.Indian J Pediatr 2000 Apr; 67(4): 255–258.
Roosihermiatic B, Nidhiyama M, Nakal K. Factors associated with TT immunization among pregnant women in Saparna, Malubu, Indonesia.Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2000 Mar; 21(1): 91–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dabas, P., Agarwal, C.M., Kumar, R. et al. Knowledge of general public and health professionals about tetanus immunization. Indian J Pediatr 72, 1035–1037 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02724406
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02724406