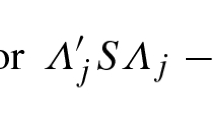Abstract
Structural equation models with latent variables are sometimes estimated using an intuitive three-step approach, here denoted factor score regression. Consider a structural equation model composed of an explanatory latent variable and a response latent variable related by a structural parameter of scientific interest. In this simple example estimation of the structural parameter proceeds as follows: First, common factor models areseparately estimated for each latent variable. Second, factor scores areseparately assigned to each latent variable, based on the estimates. Third, ordinary linear regression analysis is performed among the factor scores producing an estimate for the structural parameter. We investigate the asymptotic and finite sample performance of different factor score regression methods for structural equation models with latent variables. It is demonstrated that the conventional approach to factor score regression performs very badly. Revised factor score regression, using Regression factor scores for the explanatory latent variables and Bartlett scores for the response latent variables, produces consistent estimators for all parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aptech Systems. (1992).GAUSS: System and graphics manual. Maple Valley, WA: Author.
Bartholomew, D.J. (1981). Posterior analysis of the factor model.British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 34, 93–99.
Bartlett, M.S. (1937). The statistical conception of mental factors.British Journal of Psychology, 28, 97–104.
Bartlett, M.S. (1938). Methods of estimating mental factors.Nature, 141, 609–610.
Bollen, K.A. (1989).Structural equations with latent variables. New York, NY: Wiley.
Bollen, K.A., & Lennox, R. (1991). Conventional wisdom on measurement: A structural equation perspective.Psychological Bulletin, 110, 305–314.
Dwyer, P.S. (1937). The determination of the factor loadings of a given test from the known factor loadings of other tests.Psychometrika, 2, 173–178.
Furnam, A. (1994). Explaining health and illness: Lay beliefs on the nature of health.Personality and Individual Differences, 17, 455–466.
Gorsuch, R.L. (1983).Factor analysis. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Hauser, R.M., & Goldberger, A.S. (1971). The treatment of unobservable variables in path analysis. In H.L. Costner (Ed.),Sociological methodology 1971 (pp. 81–117). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Holzinger, K.J., & Swineford, F. (1939).A study in factor analysis: The stability of a bifactor solution (Supplementary Educational Monograph No. 48). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Iwata, S. (1992). Errors-in-variables regression using estimated latent variables.Econometric Reviews, 11, 195–200.
Jöreskog, K.G. (1973). A general method for estimating a linear structural equation system. In A.S. Goldberger & O.D. Duncan (Eds.),Structural equation models in the social sciences (pp. 85–112). New York, NY: Seminar Press.
Jöreskog, K.G. (1977). Structural equation models in the social sciences: Specification, estimation and testing. In P.R. Krishnaiah (Ed.),Applications of Statistics (pp. 265–286). Amsterdam: North-Holland.
Jöreskog, K.G., & Sörbom, D. (1989).LISREL7: A guide to the program and applications. Chicago, IL: SPSS.
Kim, J.-O., & Mueller, C.W. (1978).Factor analysis: Statistical methods and practical issues (Sage university paper series on quantitative applications in the social sciences, No. 07-014). Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Krijnen, W.P., Wansbeek, T.J., & ten Berge, J.M.F. (1996). Best linear predictors for factor scores.Communications in Statistics—Theory and Methods, 25, 3013–3025.
Lastovicka, J.L., & Thamodaran, K. (1991). Common factor score estimates in multiple regression problems.Journal of Marketing Research, 28, 105–112.
Lavik, N.J., Hauff, E., Skrondal, A., & Solberg, O. (1996). Mental disorder among refugees and the impact of persecution and exile: Some findings from an outpatient population.British Journal of Psychiatry, 169, 726–732.
Lawley, D.N., & Maxwell, A.E. (1971).Factor analysis as a statistical method. London: Butterworths.
Mardia, K.V., Kent, J.T., & Bibby, J.M. (1979).Multivariate analysis. New York, NY: Academic.
McDonald, R.P., & Burr, E.J. (1967). A comparison of four methods of constructing factor scores.Psychometrika, 32, 381–401.
Mira, M., Abraham, S., McNeil, D., Vizzard, J., Macaskill, P., Fraser, I., & Llewellyn-Jones, D. (1995). The interrelationship of premenstrual symptoms.Psychological Medicine, 25, 947–955.
Rosen, L.N., Durand, D., Westhuis, D.J., & Teitelbaum, J.M. (1995). Marital adjustment of army spouses one year after Operation Desert Storm.Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 25, 677–692.
Schoenberg, R., & Arminger, G. (1990).LINCS2.0. Kent, WA: RJS Software.
Skrondal, A. (2000). Design and analysis of Monte Carlo experiments: Attacking the conventional wisdom.Multivariate Behavioral Research, 35, 137–167.
ten Berge, J.M.F. (1983). On Green's best linear composites with a specified structure, and oblique estimates of factor scores.Psychometrika, 48, 371–375.
ten Berge, J.M.F., Krijnen, W.P., Wansbeek, T.J., & Shapiro, A. (1999). Some new results on correlation-preserving factor scores prediction methods.Linear Algebra and its Applications, 289, 311–318.
Thomson, G.H. (1934). The meaning of i in the estimate of g.British Journal of Psychology, 25, 92–99.
Thurstone, L.L. (1935).The vectors of mind. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Tucker, L.R. (1971). Relations of factor score estimates to their use.Psychometrika, 36, 427–436.
Zellner, A. (1970). Estimation of regression relationships containing unobservable variables.International Economic Review, 11, 441–454.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skrondal, A., Laake, P. Regression among factor scores. Psychometrika 66, 563–575 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02296196
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02296196