Abstract
Rectal absorption of acetylsalicylic acid and its calcium salt was studied in man and compared with oral absorption.
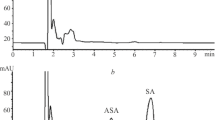
Plasma concentrations of acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid were measured by means ofHplc analysis, after a single dose of acetylsalicylic acid (500 mg) and after single rectal doses of acetylsalicylic acid (500 mg) and calcium acetylsalicylate (640 mg) in a cross-over study in 8 volunteers. The rectal dosage forms included fatty suppositories and aqueous solutions.
Compared with oral administration rectal absorption of acetylsalicylic acid can be equally rapid, if the volume and the pH of the aqueous micro-enema was optimized (20 ml, pH 4.0). Rectal absorption of calcium acetylsalicylate occurred very slowly. If fatty suppositories were used smaller particles favoured the rate of acetylsalicylic acid absorption. Compared with oral administration absorption from the optimized suppository dosage form proceeded significantly (P < 0.05) slower. For all rectal dosage forms, the extent to which acetylsalicylic acid reached the general circulation intact, was smaller than after oral administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bywaters, E. G. L. (1963) Clinical implications of the antiinflammatory effects of salicylate. InSalicylates, an international symposium (A. St. J. Dixon, B. K. Martin, M. J. H. Smith andP. H. W. Wood, eds.), 154–160. Little Brown, Boston.
Cacchillo, A. F., andW. H. Hassler (1954) The influence of suppository bases upon the rectal absorption of acetylsalicylic acid.J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 43, 683–685.
Cid, E. (1974) Absorption rectale de médicaments. Influence de la taille des cristaux d'acide acetylsalicylique.Ann. Pharm. Franc. 32, 273–281.
Coldwell, B. B., G. Solomonray, E. M. Boyd, J. Jantz andA. B. Morrison (1969) The effect of dosage form and route of administration on the absorption and excretion of acetylsalicylic acid in man.Clin. Toxicol. 2, 111–127.
Duthie, J. J. R. (1963) InSalicylates, an international symposium (A. St. J. Dixon, M. J. H. Smith, B. K. Martin andP. H. W. Wood, eds.), 288–292, Little Brown, Boston.
Gibaldi, M., andB. Grundhofer (1975) Bioavailability of aspirin from commercial suppositories.J. Pharm. Sci. 64, 1064–1066.
Ginneken, C. A. M. Van (1976)Pharmacokinetics of antipyretic and anti-inflammatory analgesics. Thesis, Nijmegen.
Houde, R. W., S. L. Wallenstein andW. T. Beaver (1965) Clinical measurement of pain. InAnalgetics (G. De Stevens, ed.), 76–122. Academic Press, New York.
Lasagna, L. (1961) Progress of medical science: Analgesic drugs.Am. J. Med. Sci. (R. A. Kern, T. M. Durant andK. M. Schreck, eds.), Vol. 242, 620–627. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia.
Lester, D., G. Lolli andL. A. Greenberg (1946) The fate of acetylsalicylic acid.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 87, 329–342.
Levy, G., andL. P. Amsel (1966) Kinetics of competitive inhibition of salicylic acid conjugation with glycine in man.Bioch. Pharmacol. 15, 1033–1038.
Lim, R. K. S., D. G. Miller, F. Guzman, D. W. Rodgers, S. K. Wang, P. Y. Chao andT. Y. Shih (1967) Pain and analgesia evaluated by the intraperitoneal bradykininevoked pain method in man.Clin. Pharmacol. Therap. 8, 521–542.
Lowenthal, W., J. F. Borzelleca andC. D. Corder (1970) Drug absorption from the rectum III: Aspirin and some aspirin derivates,J. Pharm. Sci. 59, 1353–1355.
Margolin, S. (1960) Pharmacologic demonstration in man of increased thresholds to tooth pain following carisoprodal and other analgesics.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 105, 531–533.
Moolenaar, F., A. G. G. Stuurman-Bieze, J. Visser andT. Huizinga (1978) Biopharmaceutics of rectal administration of drugs in man, part 1: Introduction of benzoic acid as a test drug.Int. Journ. Pharm. 1, 323–336.
Moolenaar, F., B. Koning and T.Huizinga (1979a), part 7: Absorption rate and bioavailability of phenobarbital and its sodium salt from rectal dosage forms.Int. Journ. Pharm., accepted.
Moolenaar, F., W. J. Greving and T.Huizinga (1979b) part 8: Absorption rate and bioavailability of valproic acid and its sodium salt from different rectal dosage forms.Europ. Journ. Clin. Pharmacol., submitted.
Moolenaar, F., L. Olthof andT. Huizinga (1979c) part 3: Absorption rate and bioavailability of paracetamol from rectal aqueous suspensions,Pharm. Weekblad Sci. Ed. 1, 25–30.
Moolenaar, F., A. J. M. Schoonen, A. Everts andT. Huizinga (1979d) part 4: Absorption rate and bioavailability of paracetamol from fatty suppositories,Pharm. Weekblad Sci. Ed. 1, 89–94.
Neuwald, F., andF. Kunze (1964) Vergleichende Untersuchungen über die Abgabe von Salicylaten aus Suppositorien-fettgrundmassen in vitro und in vivo.Arzneimittel-Forsch. 14, 1162–1167.
Parrot, E. L. (1971) Salicylate absorption from rectal suppositories,J. Pharm. Sci. 60, 867–872.
Parrot, E. L. (1975) Influence of particle size on rectal absorption of aspirin.J. Pharm. Sci. 64, 878–880.
Rowland, M., andS. Riegelman (1968) Pharmacokinetics of acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid after intravenous administration in man.J. Pharm. Sci. 57, 1313–1319.
Rowland, M., S. Riegelman, P. A. Harris andS. D. Sholkoff (1972) Absorption kinetics of aspirin in man following oral administration of an aqueous solution.J. Pharm. Sci. 61, 379–385.
Rowland, M., S. Riegelman, P. A. Harris, S. D. Sholkoff andE. J. Eyring (1967) Kinetics of acetylsalicylic acid disposition in man.Nature 215, 413–414.
Samelius, U., andA. äström (1958) The absorption of an N-methylated barbiturate and acetylsalicylic acid from different suppository masses.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 14, 240–250.
Schoonen, A. J. M., F. Moolenaar, C. Haverschmidt andT. Huizinga (1976) The interphase transport of drugs from fatty suppository bases.Pharm. Weekblad 111, 585–590.
Schoonen, A. J. M., F. Moolenaar and T.Huizinga (1979) Release of drugs from fatty suppository bases in vitro and in vivo.Int. Journ. Pharm., accepted.
Seed, J. C. (1965) A clinical comparison of the antipyretic potency of aspirin and sodium salicylate.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 6, 354–358.
Senior, N. (1974)Advances in pharmaceutical sciences. Academic Press, London.
Smith, M. J. H., andP. K. Smith (1966)The salicylates. Interscience, New York.
Superstine, S. Y., E. Superstine andS. Penchas (1978) Comparison of the bioavailability of aspirin tablets and suppositories.Israel. J. Med. Sci. 14, 292–294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
In honour of ProfessorPolderman on the occasion of his retirement.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moolenaar, F., Oldenhof, N.J.J., Groenewoud, W. et al. Biopharmaceutics of rectal administration of drugs in man. Pharmaceutisch Weekblad Scientific Edition 1, 1459–1469 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02293485
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02293485