Abstract
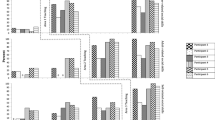
The present case study used a multiple treatment design to assess the effects of two interventions—Peer social initiations and target child initiations— on the social and disruptive behavior of a high-functioning autistic child. Intervention included initiation training and videotaped feedback highlighting successful and unsuccessful initiations. During Interventions 1 and 2, nonhandicapped peers were trained to initiate social interaction with the autistic child, resulting in an increase in social interaction which dramatically decreased in a reversal phase. Social interaction quickly increased again in Intervention 3 when the autistic child was trained to initiate interaction using the same procedures. During Interventions 1 and 2 no decrease in the autistic child's disruptive behaviors was observed; however during Intervention 3 these behaviors decreased to a low rate. Social validation, generalization, and maintenance of these behavior changes are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brady, M. P., McEvoy, M. A., Wehby, J., & Ellis, D. (1987). Using peers as trainers to increase an autistic child's social interaction.Exceptional Child, 54, 213–219.
Brady, M. P., Shores, R. E., McEvoy, Ellis, D., & Fox, J. J. (1987). Increasing social interactions of severely handicapped autistic children.Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 17, 375–390.
Dunlap, G. (1984). The influence of task variation and maintenance on the learning and affect of autistic children.Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 37, 41–64.
Dunlap, G., & Koegel, R. L. (1980). Motivating autistic children through stimulus variation.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 13, 619–627.
Evers, W. L., & Schwartz, J. C. (1973). Modifying social withdrawal in preschoolers: The effect of filmed modeling and teacher praise.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 1, 248–256.
Fox, J. J., Gunter, P., Brady, M. J., Bambara, L. M., Spiegel-McGill, P., & Strain, P. S. (1984). Using multiple peer-exemplars to develop generalized social responding of an autistic girl.Monographs in Behavior Disorders, 7, 17–26.
Gaylord-Ross, R. J., Haring, T. G., Breen, C., & Pitts-Conway, V. (1984). The training and generalization of social interaction skills with autistic youth.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 17, 229–247.
Haring, T. G., & Lovinger, L. (1989). Promoting social interaction through teaching generalized play initiation responses to preschool children with autism.Journal for the Association for Persons with Severe Handicaps, 14, 58–67.
Hecimovic, A., Fox, J. J., Shores, R. E., & Strain, P. S. (1985). An analysis of developmentally integrated and segregated free play settings and the generalization of newly-acquired social behaviors of socially withdrawn preschoolers.Behavioral Assessment, 7, 367–388.
Hendrickson, J. M., Strain, P. S., Tremblay, A., & Shores, R. E. (1982). Interactions of behaviorally handicapped children: Functional effects of peer social initiations.Behavior Modification, 6, 323–353.
Hendrickson, J. M., Tremblay, A., Strain, P. S., & Shores, R. E. (1981). Relationship between toy and material use and the occurrence of social interactive behaviors by normally developing preschool children.Psychology in the Schools, 18, 500–504.
Hunt, P., Alwell, M., & Goetz, L. (1988). Acquisition of conversational skills and the reduction of inappropriate social interaction behaviors.Journal for the Association for Persons with Severe Handicaps, 13, 20–27.
Odom, S. L., Hoyson, M., Jamieson, B., & Strain, P. S. (1985). Increasing handicapped preschoolers peer social interactions: Cross-setting and component analysis.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 18, 3–16.
Odom, S. L., & Strain, P. S. (1986). A comparison of peer-initiation and teacher-antecedent interventions for promoting reciprocal social interaction of autistic preschoolers.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 19, 59–71.
Ragland, E. U., Kerr, M. M., & Strain, P. S. (1978). Behavior of withdrawn autistic children: Effects of peer social initiations.Behavior Modificaiton, 2, 565–578.
Romancyzk, R. G., Diament, C., Goren, E. R., Trunnell, G., & Harris, S. L. (1975). Increasing isolate and social play in severely disturbed children: Intervention and postintervention effectiveness.Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 5, 57–70.
Rutter, M. (1978). Diagnosis and definition of childhood autism.Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 8, 139–161.
Schreibman, L. (1988).Autism. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Schafer, M. S., Egel, A. L., & Neef, N. A. (1984). Training mildly handicapped peers to facilitate changes in the social interaction skills of autistic children.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 17, 461–476.
Strain, P. S. (1977). An experimental analysis of peer social initiations on the behavior of withdrawn preschool children: Some training and generalization effects.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 5, 445–455.
Strain, P.S. (1980). Social behavior programming with severely handicapped and autistic children. In B. Wilcox & A. Thompson (Eds.),Critical issues in educating autistic children and youth (pp. 179–206). NSAC, The National Society for Children and Adults with Autism.
Strain, P. S. (1983). Generalization of autistic children's social behavior change: Effects of developmentally integrated and segregated settings.Analysis and Intervention in Developmental Disabilities, 3, 23–34.
Strain, P. S., & Fox, J. J. (1981a). Peers as behavior change agents for withdrawn classmates. In B. B. Lahey & A. E. Kazdin (Eds.),Advances in Clinical Child Psychology (Vol. 4, pp. 167–198). New York: Plenum Press.
Strain, P. S., & Fox, J. J. (1981b). Peer social initiations and the modification of social withdrawal: A review and future perspective.Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 6, 417–433.
Strain, P. S., Kerr, M. M., & Ragland, E. U. (1979). Effects of peer-mediated social initiations and prompting/reinforcement procedures of the social behavior of autistic children.Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 9, 41–54.
Strain, P. S., Shores, R. E., & Kerr, M. M. (1976). An experimental analysis of “spillover” effects on the social interaction of behaviorally handicapped preschool children.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 9, 31–40.
Strain, P. S., & Timm, M. A. (1974). An experimental analysis of social interaction between a behaviorally disordered preschool child and her classroom peers.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 7, 583–590.
Tremblay, A., Strain, P. S., Hendrickson, J. M., & Shores, R. E. (1981). Social interactions of normal preschool children: Using normative data for subject and target behavior selection.Behavior Modification, 5, 237–253.
Walker, H. M., Greenwood, C. R., Hops, H., & Todd, N. M. (1979). Differential effects of reinforcing topographic components of social interaction: Analysis and direct replication.Behavior Modification, 3, 291–321.
Wing, L. (1976). Diagnosis, clinical description, and prognosis. In L. Wing (Ed.),Early childhood autism (pp. 15–48). Oxford: Pergamon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by U.S. Public Health Service research grants MH 39434 and MH 28210 from the National Institute of Mental Health. The authors are grateful for the participation of the children and the parents. We thank the teachers for their cooperation in the school setting. We also thank Lauren Loos, Kim Litzenberg, and Wendy Kaneko for all their assistance on scoring procedures and data collection and Jamie Reed-Sutton for her assistance collecting social validation data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oke, N.J., Schreibman, L. Training social initiations to a high-functioning autistic child: Assessment of collateral behavior change and generalization in a case study. J Autism Dev Disord 20, 479–497 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02216054
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02216054