Abstract
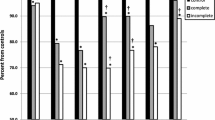
Aerobic capacity of patients with different forms of congenital heart disease was serially evaluated in 79 patients and the evolution was correlated with the lesion and the level of daily activity. The patients were divided into six groups: patients with a small ventricular septal defect (VSD) with mini shunt (n=14), mild pulmonary valve stenosis with gradient <40 mm Hg (PS) (n=12), mild to moderate aortic valve stenosis (gradient 36±17 mm Hg) (AS) (n=12), patients 4.7±2.1 years after repair of tetralogy of Fallot (PO-TF) (n=16), patients 2.2±2.9 years after closure of a high flow/high gradient VSD (PO-VSD) (n=13), and patients 2.6±1.7 years after Fontan repair (Fontan-PO) (n=12). Aerobic capacity was assessed by determination of the ventilatory anaerobic threshold (VAT). VAT reflects the highest aerobic exercise level prior to a disproportionate increase of CO2 and ventilation relative to O2 uptake; it is independent of patient motivation. Data are expressed as percentage of normal O2 uptake at VAT, determined in 234 age/gender matched controls. The habitual level of physical activity was assessed by a standardised questionnaire. Aerobic capacity in all subgroups of patients, even with very mild defects, was at or below the lower limit of normal. Children left unrestricted from physical exercise (VSD, PS, PO-VSD) had no change over the study period. However, aerobic capacity of patients with medically imposed physical restrictions (AS) and significant residual haemodynamic lesions (PO-TF, Fontan) decreased with age. In patients with AS, PO-TF and Fontan-PO the habitual level of physical activity was significantly decreased compared to controls.
Conclusion
Cardiovascular exercise performance in children with medically imposed restriction of intensive physical exercise (AS) or residual haemodynamic lesions (TF and Fontan-PO) declines progressively during medium-term follow up. In the other patient groups (VSD, PS, VSD-PO), exercise performance remains stable.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS :
-
aortic valve stenosis
- Fontan-PO :
-
post Fontan repair
- NYHA :
-
New York Heart Association
- PO-TF :
-
after repair for tetralogy of Fallot
- PS :
-
pulmonary valve stenosis
- VAT :
-
ventilatory anaerobic threshold
- \(\dot VE/\dot VO_2 \) :
-
ventilatory equivalent for carbon dioxide
- \(\dot VE/\dot VO_2 \) :
-
ventilatory equivalent for oxygen
- VSD :
-
ventricular septal defect
References
Alpert BS, Moes DM, Durant RH, Strong WB, Flood NL (1983) Hemodynamic responses to ergometer exercise in children and young adults with left ventricular pressure or volume overload. Am J Cardiol 52:563–567
Balfour IC, Drimmer AM, Nouri S, Pennington DG, Hemkens C, Harvey LL (1991) Pediatric cardiac rehabilitation. Am J Dis Child 145:627–630
Bowyer JJ, Busst CM, Till JA, Lincoln C, Shinebourne EA (1990) Exercise ability after Mustard's operation. Arch Dis Child 65:865–87
Cyran SE, James FW, Daniels S, Mays W, Shukla R, Kaplan S (1988) Comparison of the cardiac output and stroke volume response to upright exercise in children with valvular and subvalvular aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 11:651–658
Dickstein K, Barvik S, Aarsland T, Snappins S, Karlsson JA (1990) Comparison of methodologies in detection of the anaerobic threshold. Circulation 81 [Suppl II]:38–46
Driscoll DJ, Danielson GK, Puga FJ, Schaff HF, Heise CT, Staats BA (1986) Exercise tolerance and cardiorespiratory response to exercise after the Fontan operation for tricuspid atresia or functional single ventricle. J Am Coll Cardiol 7:1087–1094
Driscoll DJ, Wolfe RR, Gersony WM, Haynes CJ, Kean JF, Kidd L, O'Fallon M, Pieroni DR, Weidman WH (1993) Cardiorespiratory responses to exercise of patients with aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis and ventricular septal defect. Circulation 87 [Suppl I]:102–113
Grant GP, Garofany RP, Mansell AL, Leopold MB, Gersong WM (1991) Ventilatory response to exercise after intracardiac repair of tetralogy of Fallot. Am Rev Respir Dis 144:833–836
James FW, Schwartz DC, Kaplan S, Spilkin SP (1982) Exercise electrocardiogram, blood pressure and working capacity in young patients with valvular or discrete subvalvular aortic stenosis. Am J Cardiol 50:769–775
Jones NL (1988) Clinical exercise testing. Saunders, Philadelphia, p 9
Kondoh C, Hiroe M, Nakaniski T, Nakazawa M, Nakoe S, Imai Y, Takao A (1988) Left ventricular characteristics during exercise in patients after Fontan's operation for tricuspid atresia. Heart Vessels 4:34–39
Longmuir PE, Tremblay MS, Goode RC (1990) Postoperative exercise training develops normal levels of physical activity in a group of children following cardiac surgery. Pediatr Cardiol 11:126–130
Perrault H, Drblik SP, Montigny M, Davignon A, Lamarre A, Chartrand C, Stanley P (1989) Comparison of cardiovascular adjustments to exercise in adolescents 8 to 15 years of age after correction of tetralogy of Fallot, ventricular septal defect or atrial septal defect. Am J Cardiol 64:213–217
Reybrouck T, Weymans M, Stijns H, Knops J, Van der Hauwaert LG (1985) Ventilatory anaerobic threshold in healthy children. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:278–284
Reybrouck T, Weymans M, Stijns H, Van der Hauwaert L G (1986) Exercise testing after correction of tetralogy of Fallot: the fallacy of a reduced heart rate response. Am Heart J 112: 998–1003
Reybrouck T, Weymans M, Stijns H, Van der Hauwaert LG (1986) Ventilatory anaerobic threshold for evaluating exercise performance in children with congenital left-to-right intracardiac shunt. Pediatric Cardiol 7:19–24
Reybrouck T, Deroost F, Van der Hauwaert LG (1992) Evaluation of breath-by-breath measurement of respiratory gas exchange in pediatric exercise testing. Chest 102:147–152
Rowe SA, Zakha KG, Manolio TA, Hornheffer PJ, Kidd L (1991) Lung function and pulmonary regurgitation limit exercise capacity in postoperative tetralogy of Fallot. J Am Coll Cardiol 17:461–466
Tomassoni TL, Galioto FM, Vaccaro P (1991) Cardiopulmonary exercise testing in children following surgery for tetralogy of Fallot. Am J Dis Child 145:1290–1293
Snedecor GW, Cochran WC (1972) Statistical methods, 6th Edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames Iowa, p 5
Sullivan MJ, Cobb FR (1990) The anaerobic threshold in chronic heart failure. Relation to blood lactate, ventilatory basis, reproducibility and response to exercise training. Circulation 81 [Suppl II]:47–58
Wasserman K, Hanssen JE, Sue DY, Whipp BJ (1987) Principles of exercise testing and interpretation. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, p 257
Wasserman K, Beaver WL, Whipp BJ (1990) Gas exchange theory and the lactic acidosis (anaerobic threshold). Circulation 18 [Suppl II]:14–30
Wessel HU, Cunningham WJ, Paul MH, Bastanier C, Muster A, Idriss FS (1980) Exercise performance in tetralogy of Fallot after intracardiac repair. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 80:582–593
Weymans M, Reybrouck T (1989) Habitual level of physical activity and cardiorespiratory endurance capacity in children. Eur J Appl Physiol 58:803–807
Zellers TM, Driscroll DJ, Mottram CD, Puga FJ, Schaff HV, Danielson GK (1989) Exercise tolerance and cardiorespiratory response to exercise before and after the Fontan operation. Mayo Clin Proc 64:1489–1497
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Deceased
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reybrouck, T., Rogers, R., Weymans, M. et al. Serial cardiorespiratory exercise testing in patients with congenital heart disease. Eur J Pediatr 154, 801–806 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01959785
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01959785