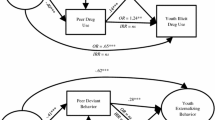
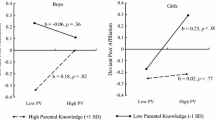
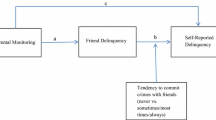
Abstract
The relative influence of peer and parental influence on youths' use of alcohol and other drugs is explored among 446 Anglo and Hispanic youths, ages 9–17. Current users and abstainers are similar in age and gender. Among both groups, parental influence is more profound than that of peers. However, substance users, compared to abstainers, are more influenced by peers. Level of marijuana use by youths' friends is the most reliable predictor of drug use. Youths having viable relationships with parents are less involved with drugs and less influenced by drug-oriented peers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelson, H., Fishburne, P., and Cisin, I. (1977).National Survey on Drug Abuse: 1977 (Volume I)-Main Findings. National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, MD.
Akers, R. L., Krohn, M. D., and Lanza-Kaduce, L. (1979). Social learning and deviant behavior: A specific test of a general theory.Am. Sociol. Rev. 44: 636–655.
Ausubel, D. P., Montemayor, R., and Svajian, P. (1977).Theory and Problems of Development. Grune & Stratton, New York.
Brown, B. B., Clasen, D. R., and Eicher, S. A. (1986). Perceptions of peer pressure, peer conformity dispositions, and self-reported behavior among adolescents.Develop. Psychol. 22: 521–530.
Bry, B. (1983). Predicting drug abuse: Review and reformulations.Int. J. Addict. 18: 223–233
Coombs, R. H. (ed.). (1975).Junkies and Straights: The Camarillo Experience Lexington Books, Lexington, MA.
Coombs, R. H. (ed.). (1988).The Family Context of Adolescent Drug Use. Haworth Press, New York.
Coombs, R. H., and Coombs, K. (1988). Developmental stages in drug use: Changing family involvements. In Coombs, R. H. (ed.),The Family Context of Adolescent Drug Use. Haworth Press, New York.
Coombs, R. H., and Landsverk, J. (1988). Parenting styles and substance use during childhood and adolescence.J. Marriage Family 50: 473–482.
Coombs, R. H., Fry, L. J., and Lewis, P. G. (Eds.). (1976).Socialization in Drug Abuse. Schenkman Publishing Co., Cambridge, MA.
Coombs, R. H., Wellisch, D. K., and Fawzy, F. I. (1985). Drinking patterns and problems among female children and adolescents: A comparison of abstainers, past users, and current users.Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 11: 315–348.
Elliot, D. S., Huizinga, D., and Ageton, S. S. (1982).Explaining Delinquency and Drug Use. Report No. 21, Behavioral Research Institute, Boulder, CO.
Fawzy, F. I., Coombs, R. H., and Gerber, B. (1983). Generational continuity in the use of substances: The impact of parental substance use on adolescent substance use.Addict. Behav. 8: 109–114.
Glynn, T. J. (1981a). From family to peer: A review of transitions of influence among drugusing youth.Youth Adolesc. 10: 363–383.
Glynn, T. J. (1981b).Families and Drugs. DHHS Pub. No. ADM 81-1151, National Institute on Drug Abuse, Research Issues Series No. 29.
Glynn, T. J. (1984). Adolescent drug use and the family environment: A review.J. Drug Issues 14: 271–295.
Glynn, T. J., and Haenlein, M. A. (1988). Family theory and research on adolescent drug use: A review. In Coombs, R. H. (ed.),The Family Context of Adolescent Drug Use. Haworth Press, New York.
Harbin, H., and Maziar, H. (1975). The families of drug abusers: A literature review.Family Process 14: 411–431.
Hawkins, J. D., Lishner, D. M., and Catalano, R. F. (1985). Childhood predictors and the prevention of adolescent substance abuse. In La Rue Jones, C., and Batties, R. J. (eds.),Etiology of Drug Abuse: Implications for Prevention. DHHS ADM 85-1335, 75-126, National Institute on Drug Abuse, Research Monograph Series 56.
Hawkins, J. D., Lishner, D. M., Catalano, R. F., and Howard, M. O. (1985). Childhood predictors of adolescent substance abuse: Toward an empirically grounded theory.J. Children Contemp. Soc. 18: 11–48.
Hays, R. D., and Huba, G. J. (1988). Reliability and validity of drug use items differing in the nature of their response options.J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 56: 470–472.
Hirschi, H. (1969).Causes of Delinquency. University of California Press, Berkeley.
Huba, G. H., Wingard, J. A., and Bentler, P. M. (1979). Beginning adolescent drug use and peer and adult interactions.J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 47: 265–276.
Huba, G. J., and Bentler, P. M. (1980). The role of peer and adult models for drug taking at various stages of adolescence.J. Youth Adolesc. 9: 449–465.
Jessor, R., and Jessor, S. L. (1977).Problem Behavior and Psychosocial Development: A Longitudinal Study of Youth. Academic Press, New York.
Jessor, R., Chase, J. A., and Donovan, J. E. (1980). Psychosocial correlates of marijuana use and problem drinking in a national sample of adolescents.Am. J. Public Health 70: 604–613.
Jurich, A. P., Poison, C. H., Jurich, J. A., and Bates, R. (1985). Family factors in the lives of drug users and abusers.Adolescence 10: 143–159.
Kandel, D. B. (1985). On processes of peer influences in adolescent drug use: A developmental perspective.Adv. Alcohol Substance Abuse 4: 139–163.
Kandel, D. B., and Adler, D. (1982). Socialization into marijuana use among French adolescents: A cross-cultural comparison with the U.S.J. Health Social Behav. 23: 295–309.
Kaplan, H. B., Martin, S. S., and Robbins, C. (1984). Pathways to adolescent drug use: Self-derogation, peer influence, weakening of social controls, and early substance use.J. Health Social Behav. 25: 270–289.
Klagsburn, M., and Davis, D. (1977). Substance abuse and family interaction.Family Process 16: 149–174.
Maddahian, E., Newcomb, M. D., and Bentler, P. M. (1988). Risk factors for substance use: Ethnic differences among adolescents.J. Substance Abuse 1: 11–23.
Marcos, A. C., Bahr, S. J., and Johnson, R. E. (1986). Test of a bonding/association theory of adolescent drug use.Social Forces 65: 135–161.
Needle, R., McCubbin, H., Wilson, M., Reineck, R., Lazar, A., and Mederer, H. (1986). Interpersonal influences in adolescent drug use: The role of older siblings, parents, and peers.Int. J. Addict. 21: 739–766.
Nehemkis, A., Macari, M. A., and Lettieri, D. J. (1976).Drug Abuse Instrument Handbook National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, MD.
Newcomb, M. D., and Bentler, P. M. (1986). Substance use and ethnicity: Differential impact of peer and adult models.J. Psychol. 120: 83–95.
Newcomb, M. D., Maddahian, E., Skager, R., and Bentler, P. (1987). Substance abuse and psychosocial risk factors among teenagers: Associations with sex, age, ethnicity, and type of school.Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 13: 413–433.
Oetting, E. R., and Beauvais, F. (1987). Peer cluster theory, socialization characteristics, and adolescent drug use: Path analysis.J. Counsel. Psychol. 34: 205–213.
Seldin, N. E. (1972). The family of the addict: A review of the literature.Int. J. Addict. 7: 97–107.
Stanton, M. D. (1978). The family and drug misuse: A bibliography.Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 5: 151–170.
Stanton, M. D. (1979).Family Structure and Drug Abuse: A Review. Report prepared for the Office of Program Development and Analysis, National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, MD.
Sutherland, E., and Cressey, D. (1970).Criminology. Lippincott, New York.
Swadi, H., and Zeitlin, H. (1988). Peer influence and adolescent substance abuse: A promising side?Br. J. Addict. 83: 153–157.
Tudor, C. G., Peterson, D. M., and Elifson, K. W. (1980). An examination of the relationship between peer and parental influences and adolescent drug use.Adolescence 15: 783–798.
Welte, J. W., and Barnes, G. M. (1987). Alcohol use among adolescent minority groups.J. Studies Alcohol 48: 329–336.
Wingard, J. A., Huba, G. J., and Bentler, P. M. (1980). A longitudinal analysis of personality structure and adolescent substance use.Personal. Individ. Diff. 1: 259–272.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Funded by a grant (A-003-2) from the California Department of Alcohol and Drug Programs, R. H. Coombs, principal investigator.
Research interests include comparative socialization patterns of adolescents and young adults in substance abuse vs. conventional careers.
Research interests include domestic violence, child abuse, and substance abuse.
Research interests include family interaction patterns, cross-cultural differences, and substance abuse prevention and treatment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coombs, R.H., Paulson, M.J. & Richardson, M.A. Peer vs. parental influence in substance use among hispanic and Anglo children and adolescents. J Youth Adolescence 20, 73–88 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537352
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537352