Abstract
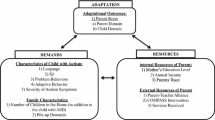
This article reviews the literature on stress in students of grades 1–12. A model to understand stress as the inequality between perceived demands and perceived resources is presented. Student stressors are identified in the family and school environments. Coping with these stressors is conceptualized as problem-focused, emotion-focused, or appraisal-focused strategies that make use of personal, social, and cognitive resources. Physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms of ineffectual coping efforts are then identified. After gender differences in stressors and coping are noted, instruments measuring stressors, coping strategies, and coping resources in children and youth are reviewed. Finally, representative intervention programs developed for school-aged youth are described and evidence of their efficacy is presented. The article concludes that there is a paucity of research on stress in children as compared to research on stress in adults.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altshuler, J. L., and Ruble, D. N. (1989). Developmental changes in children's awareness of strategies for coping with uncontrollable stress.Child Dev. 60(6): 1337–1349.
Antoni, M. A. (1987). Neuroendocrine influences in psychoimmunology and neoplasia: A review.Psychol. Health 1(1): 3–24.
Aptekar, L. (1988). Street children of Columbia.J. Early Adolesc. 8(3): 225–241.
Arent, R. (1985).Stress and Your Child Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall Publishers.
Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavior change.Psychol. Rev. 84: 191–215.
Barker, B. (1987). Helping students cope with stress.Learning 15(5): 45–49.
Basch, C. E., and Kersch, T. B. (1986). Adolescent perceptions of stressful life events.Health Educ. 17: 4–7.
Beck, A. (1976).Cognitive Therapy and the Emotional Disorders NY: International Universities Press.
Bird, G. W., and Kemerait, L. N. (1990). Stress among early adolescents in two-earner families.J. Early Adolesc. 10: 344–365.
Botvin, G., and Eng, A. (1982a).Life Skills Training: Teacher's Manual New York: Smithfield.
Botvin, G., and Eng, A. (1982b). The efficacy of a multi-component approach to the prevention of cigarette smoking.Prev. Med. 11: 199–243.
Boyce, W. T., and Jemerin, J. M. (1990). Psychobiological differences in childhood stress response: I. Patterns of illness and susceptibility.J. Dev. Behav. Pediat. 11(2): 86–94.
Brenner, A. (1984).Helping Children Cope with Stress Lexington: D.C. Heat and Company.
Burts, D. C., Hart, C. H., Charlsworth, R., and Kirk, L. (1990). A comparison of frequencies of stress behaviors observed in kindergarten children in classrooms with developmentally inappropriate instructional practices.Early Childhood Res. Quart. 5(3): 407–423.
Cartledge, G., and Milburn, J. (eds.) (1980).Teaching Social Skills to Children New York: Pergamon Press.
Clark-Lempers, D. S., Lempers, J. D., and Netusil, A. J. (1990). Family financial stress, parental support, and young adolescents' academic achievement and depressive symptoms.J. Early Adolesc. 10: 21–36.
Coddington, R. D. (1972a). The significance of life events as etiologic factors in the diseases of children: A survey of professional workers.J. Psychosomat. Res. 16: 7–18.
Coddington, R. D. (1972b). The significance of life events as etiologic factors in the diseases of children: A study of a normal population.J. Psychosomat. Res. 16: 205–213.
Cohen, L. H., Burt, C. E., and Bjorck, J. P. (1987). Life stress and adjustment: Effects of life events experienced by young adolescents and their parents.Dev. Psychol. 23: 583–592.
Compas, B. E. (1987). Coping with stress during childhood and adolescence.Psychol. Bull. 101(3): 393–403.
Compas, B. E., Malcarne, V. L., and Fondacaro, K. M. (1988). Coping with stressful events in older children and young adolescents.J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 56(3): 405–411.
Compas, B. E., Howell, D. C., Phares, V., Williams, R. A., and Giunta, C. T. (1989). Risk factors for emotional/behavioral problems in young adolescents: A prospective analysis of adolescent and parental stress and symptoms.J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 57: 732–740.
Conners, D. (1983). The school environment: A link to understanding stress.Theory Pract. 22(1): 15–20.
Copple, C., Sigel, I., and Saunders, R. (1979).Educating the Young Thinker New York: D. Van Nostrand Co.
Cox, T. (1978).Stress Baltimore: University Park Press.
Davidson, H. H., and Lang, G. (1960). Children's perceptions of their teachers' feelings toward them related to self-perceptions, school achievement and behavior.J. Exp. Educ. 29: 107–118.
Deal, S. L., and Williams, J. E. (1988). Cognitive distortions as mediators between life stress and depression in adolescents.Adolescence 23(90): 477–490.
Dickey, J. P., and Henderson, P. (1989). What young children say about stress and coping in school.Health Educ. 20(1): 14–17.
Dise-Lewis, J. E. (1988). The life events and coping inventory: An assessment of stress in children.Psychosomat. Med. 50: 484–499.
Donohue, K. C., and Gullotta, T. P. (1983). The coping behavior of adolescents following a move.Adolescence 18(70): 391–401.
Elias, M. (1989). Schools as a source of stress to children: An analysis of causative and ameliorative influences.J. School Psychol. 27: 393–407.
Elias, M. J., and Clabby, J. F. (1989).Social Decision-Making Skills for the Elementary Grades: A Curriculum Guide for Educators and Other School-Based Professionals Rockville, MD: Aspen.
Elias, M. J., Gara, M., Rothbaum, P., Reese, A., and Ubriaco, M. (1987). A multivariate analysis of factors differentiating behaviorally and emotionally dysfunctional children from other groups in school.J. Clin. Child Psychol. 16(4): 307–312.
Elkind, D. (January, 1986). Stress and the middle grader.School Counsel. 196–206.
Farrell, E., Peguero, G., Lindsey, R., and White, R. (1988). Giving voice to high school students: Pressure and boredom, ya know what I'm sayin'?Am. Educ. Res. J. 25: 489–502.
Folkman, S., and Lazarus, R. S. (1980). An analysis of coping in a middle aged community sample.J. Health Soc. Behav. 21: 219–239.
Forman, S., and O'Malley, P. (1984). School stress and anxiety interventions.School Psychol. Rev. 13(2): 162–170.
Francescani, C. (1982). MARC: An affective curriculum for emotionally disturbed adolescents.Teaching Except. Childr. 14: 217–222.
French, J. R. P., Jr., Rodgers, W., and Cobb, S. (1974). Adjustment as person-environment fit. In Coelho, G. V., Hamburg, D. A., and Adams, J. E. (eds.),Coping and Adaptation, New York: Basic Books, pp. 316–333.
Frey, N. (May, 1980). Improving the performance of poor readers through autogenic relaxation training.Reading Teacher 928–932.
Gamble, W. C., and McHale, S. M. (1989). Coping with stress in sibling relationships: A comparison of children with disabled and nondisabled siblings.J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 10(3): 353–373.
Garmezy, N. (1983). Stressors of childhood. In Garmezy, N., and Rutter, M. (eds.),Stress, Coping, and Development in Children New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 43–84.
Green, L. W. (1984). Modifying and developing health behavior.Ann. Rev. Pub. Health 5: 215–237.
Heibert, B., and Eby, W. (January, 1985). The effects of relaxation training for grade 12 students.School Counsel. 205–210.
Helms, B. J., and Gable, R. K. (1989).School Situation Survey Manual Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychology Press.
Helms, B. J., and Gable, R. K. (April, 1990). Assessing and Dealing with School-Related Stress in Grades 3–12 Students. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Boston, MA.
Hill, K. T., and Sarason, S. B. (1966). The relation of test anxiety and defensiveness to test and school performance over the elementary school years.Monogr. Soc. Res. Child Dev. 31(2): 104.
Holmes, T. H., and Rahe, R. H. (1967). The social readjustment rating scale.J. Psychosomat. Res. 11: 213–218.
Honig, A. S. (1986). Stress and coping in children: I.Young Childr. 41(5); 47–59.
Jaret, K. (1987). Stress Intervention Using Cognitive Principles, Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the National Association of School Psychologists, New Orleans, March 4–8, 1987.
Judge Baker Child Guidance Clinic (1982).Adolescent Issue Series Boston, MA: Judge Baker Clinic.
Kanner, A. D., Coyne, J. C., Schaefer, C., and Lazarus, R. S. (1981). Comparison of two models of stress measurement: Daily hassles and uplifts vs. major life events.J. Behav. Med. 4: 1–39.
Kersey, K. (1986).Helping your Child Handle, Stress New York: Acropolis Pub.
Lazarus, R. S. (1966).Psychological Stress and the Coping Process New York: McGraw-Hill.
Lazarus, R. S., and Folkman, S. (1984).Stress, Appraisal, and Coping New York: Springer.
Lazarus, R. S., and Launier, R. (1978). Stress-related transactions between person and environment. In Pervin, L. A. and Lewis, M. (eds.),Perspectives in International Psychology New York: Plenum Press, pp. 287–327.
Lazarus, R. S., Kanner, A. D., and Folkman, S. (1980). Emotions: A cognitive-phenomenological analysis. In Plutchik, R., and Kellerman, H. (eds.),Emotion: Theory, Research, and Experience New York: Academic Press, pp. 189–217.
Love, J. (1981).Improving Self-Worth by Learning to Cope with Distress: A Teaching Module Produced for Mid-Adolescents in the Ann Arbor Public Schools, Ann Arbor, MI: ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED, 232 241.
McCabe, P., and Schneiderman, N. (1985). Psychophysiologic reactions to stress. In Schneiderman, N., and Tapp, J. (eds.),Behavioral Medicine: The Biopsychosocial Approach New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, pp. 24–25.
Maddi, S. (1981). Individual development: Its significance for stress responsivity and stress adaptation. Personality development. In Moore, C. (ed.),Adolescence and Stress (DHHS Publication No. ADM 81-10098), Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, pp. 15–33.
Mason, J. W. (1975). A historical view of the stress field.J. Hum. Stress 1(2): 22–36.
Matheny, K. B., and Cupp, P. (June, 1983). Control, desirability, and anticipation as moderating variables between life change and illness.J. Hum. Stress 14–120.
Matheny, K. B., Aycock, D. W., Pugh, J. L., Curlette, W. L., and Cannella, K. A. (1986).Counsel. Psychol. 14(4): 499–549.
Matheny, K. B., Curlette, W. L., Aycock, D. W., Pugh, J. L., Taylor, H. F., and Cannella, K. S. (1989).The Coping Resources Inventory for Stress in School-Aged Youth Atlanta: Health PRISMS.
Matheny, K. B., Curlette, W. L., Aycock, D. W., Pugh, J. L. Taylor, H. F., and Cannella, K. S. (1990).Manual for the Coping Resources Inventory for Stress in School-Aged Youth, Atlanta, Health PRISMS.
Mathews, B. (1983).Relaxation Training: Its Usefulness in the Middle School Curriculum, Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the National Middle Schools, Chicago, IL (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. 236 150).
Matthews, D., and Justice, C. (1983).Relaxation Training: A Stress Management Model for Schools, Paper presented at the Annual Convention of the American Personnel and Guidance Association, Washington, D.C.: ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED 232 110.
Monaghan, J. H., Robinson, J. O., and Dodge, J. A. (1979). The children's life events inventory.J. Psychosomat. Res. 23: 63–68.
Moos, R. H., and Billings, A. G. (1982). Conceptualizing and measuring coping resources and processes. In Goldberger, L., and Breznitz, S. (eds.),Handbook of Stress New York: Free Press, pp. 212–230.
Moriarty, A., and Toussieng, P. (1976).Adolescent Coping. New York: Grune and Stration.
Omizo, N. M., and Michael, W. B. (1982). Biofeedback-induced relaxation training and impulsivity, attention to task, and locus of control among hyperactive boys.J. Learning Dis. 15(7): 414–416.
Patterson, J. M., and McCubbin, H. I. (1983). The impact of family life events and changes on the health of a chronically ill child.Fam. Relat. 32(2): 255–264.
Patterson, J. M., and McCubbin, H. I. (1987). Adolescent coping style and behaviors: Conceptualization and measurement.J. Adolesc. 10: 163–186.
Penny, J., Gillian, N., and Robinson, J. O. (1986). Psychological resources and cigarette smoking in adolescents.Brit. J. Psychol. 77: 351–357.
Peters, R. (1988). Mental health promotion in children and adolescents: An emerging role for psychology.Can. J. Behav. Sci. 20(4): 389–401.
Phillips, B. N. (1978).School Stress and Anxiety: Theory, Research and Intervention New York: Human Sciences Press.
Price, J. H., Jurs, S. G., Jurs, J., Rhonehouse, M., and Isham, K. A. (1985). An empirical test of a cognitive social learning model for stress moderation with junior high school students.J. School Health 55(6): 217–220.
Prokop, M. S. (April, 1990). Children of divorce: Relearning happiness.Momentum, 72–73.
Pryor-Brown, L., Cowen, E. L., Hightower, A. D., and Lotyczewski, B. S. (1986). Demographic differences among children in judging and experiencing specific stressful life events.J. Spec. Educ. 20(3): 339–346.
Roosa, M. W., Gensheimer, L. K., Short, J. L., Ayers, T. S., and Shell, R. (1989). A preventive intervention for children in alcoholic families: Results of a pilot study.Fam. Relat. 38(3): 295–300.
Rubenzer, R. L. (1987). Helping your children deal with stress. In Dinkmeyer, D., McKay, G. D., Dinkmeyer, D., Jr., Dinkmeyer, J., and McKay, J. L. (eds.),The Effective Parent Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service, p. 84.
Rutter, M. (1979). Protective factors in children's responses to stress and disadvantage. In Kent, M. W. and Rolf, J. E. (eds.),Primary Prevention of Psychopathology: Vol. 3. Social Competence in Children New Hampshire: University Press of New England, pp. 215–222.
Schultz, E. W. (Fall, 1980). Teaching coping skills for stress and anxiety.Teaching Except. Childr. 12–15.
Schultz, E., and Heuchert, C. (1983).Child Stress and the School Experience New York: Human Sciences Press.
Selye, H. (1956).The Stress of Life New York: McGraw-Hill.
Shure, M., and Spivak, G. (1974).The Social Adjustment of Young Children San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Sieman, M. (1978). Mental health in school-aged children.Am. J. Matern. Child Nurs. 3: 211–217.
Sigel, I. E. (1987). Does hothousing rob children of their childhood?Early Childhood Res. Quart. 2(3): 211–225.
Strother, J., and Jacobs, E. (November, 1984). Adolescent stress as it relates to stepfamily living: Implications for school counselors.School Counsel. 97–103.
Thomas, S. P., and Groer, M. W. (1986). Relationship of demographic, life-style, and stress variables to blood pressure in adolescents.Nurs. Res. 35: 169–172.
Weiss, J. R. (1986). Contingency and control beliefs as predictors of psychotherapy outcomes among children and adolescents.J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 54(6): 789–795.
Weiss, J., Weiss, B., Wasserman, A., and Rintoul, B. (1987). Control-related beliefs and depression among clinic-referred children and adolescents.J. Abnorm. Psychol. 96(1): 58–63.
Werner, E. E. (1984). Resilient children.Young Child. 40(1): 68–72.
Werner, E. E. (1986). Resilient off-spring of alcoholics: A longitudinal study from birth to age 18.J. Stud. Alcohol 47(1): 34–40.
Werner, E. E. (1989). High risk children in young adulthood: A longitudinal study from birth to 32 years.Am. J. Orthopsychiat. 59(1): 72–81.
Williams, R. A., and Compas, B. E. (August, 1988). Stress and Psychological Symptoms in Single and Dual Parent Families, Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Psychological Association, Atlanta, Georgia.
Wolf, T. M., Sklov, M. C., Wenzl, P. A., Hunter, S. M., and Berenson, G. (1982). Validation of a measure of type A behavior pattern in children: Bogalusa heart study.Child Dev. 53(1): 126–135.
Yamamoto, K., and Byrnes, D. A. (1984). Classroom social status, ethnicity, and ratings of stressful events.J. Educ. Res. 77: 283–286.
Yamamoto, K., Soliman, A., Parsons, J., and Davies, O. L. (1987). Voices in unison: Stressful events in the lives of children in six countries.J Child Psychol. Psychiat. 28: 855–864.
Youngs, B. B. (1985).Stress in Children Ann Arbor, MI: Arbor House.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matheny, K.B., Aycock, D.W. & McCarthy, C.J. Stress in school-aged children and youth. Educ Psychol Rev 5, 109–134 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01323156
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01323156