Abstract
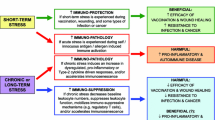
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether subjects who self-report high levels of stress have lower immunity, and whether “low”-immunity subjects under “high” stress could enhance phagocytic activity through biofeedback-assisted relaxation (BAR). During Phase 1, the level of stress and the level of phagocytic immune functioning (nitroblue tetrazolium test) were assessed as “high” or “low.” Significant chi-square analysis (x2=3.8624, df=1, p<.05) showed that subjects with “high” stress had “low” immunity. Sixteen “high”-stress, “low”-immunity subjects were randomly assigned to BAR and control groups during Phase 2. Following treatment, NBT changes showed significant increases (F=11.11, p<.003) for experimental group as compared to control group. White blood cell count and white blood cell differential were unchanged across blood samples for both groups. Experimental subjects reported significant decreases in tension-anxiety and increases in overall coping. BAR was concluded to have improved coping skills and phagocytic capacity. BAR affected the quality, rather than the quantity, of phagocytic neutrophils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achterberg, J., & Lawlis, G. F. (1978).Imagery of cancer. Champaign, Illinois: Institute of Personality and Ability Testing.
Achterberg, J., & Lawlis, G. F. (1979). A canonical relationship between blood chemistries and psychological variables in cancer patients.Multivariate Experimental Research, 4(1).
Achterberg, J., & Lawlis, G. F. (1980). Psychological and blood chemistry factors as predictors of cancer progress.Multivariate Clinical Experimental Research, 3.
Barrett, J. T. (1978).Textbook of immunology St. Louis: C. V. Mosby.
Bartrop, R. W., Lazarus, L., Luckhurst, E., Kiloh, L. G., & Penny, R. (1977). Depressed lymphocyte function after bereavement.Lancet, 1 834–836.
Basmajian, J. V. (Ed.). (1979).Biofeedback — Principles and practice for clinicians. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
Bellanti, J. A. (1978).Immunology II. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders.
Berger, E. M., Bowman, C. M., Harada, R. N., & Repine, J. E. (1982). Neutrophil activity decreases during menses.American Family Physician, 234.
Buhring, M., Bork-Wolwer, L., & Krippner, H. (1978). Peripheral T-lymphocytopenia under exogeneous thermal stress.Cancer, 42 2794–2797.
Fischer, C. L., Gill, G., Daniels, J. C., Cobb, E. K., Berry, C. A., & Ritzmann, S. E. (1972): Effects of the space flight environment on man's immune system: I Serum proteins and immunoglobulins.Aerospace Medicine, 43 856–859.
Fotopoulos, S. S., & Sunderland, Q. P. (1978) Biofeedback in the treatment of psychophysilogic disorders.Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 3 331–358.
Fuller, G. D. (1979).Biofeedback: Methods and procedures in clinical practice. San Francisco: Biofeedback Press.
Homes, T. H., & Rahe, R. H. (1967). The social readjustment rating scale.Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 3 213–218.
Jacobs, M. A., Spilken, A. Z., & Norman, M. (1969). Relationship of life change, maladaptive aggression, and upper respiratory infection in male college students.Psychosomatic Medicine, 31 31–43.
Jacobs, M. A., Spilken, A. Z., Norman, M. M., & Anderson, L. S. (1970). Life stress and respiratory illness.Psychosomatic Medicine, 32 233–242.
Locke, S. E., Hurst, M. W., Heisel, J. S., Krause, L., & Williams, R. M. (1979).The influence of stress and other psychosocial factors on human immunity. Paper presented at the meeting of the American Psychosomatic Society, Boston.
McClelland, D. C., & Jemmott, J. B. (1980). Power motivation, stress, and physical illness.Journal of Human Stress, 6 6–15.
Palmblad, J. (1981). Stress and immunologic competence: Studies in man. In R. Ader (Ed.),Psychoneuro-immunology. New York: Academic Press.
Palmblad, J., Cantell, K., Strander, H., Frogberg, J., Karlsson, C., Levi, L., Granstrom, M., & Under, P. (1975). Stressor exposure and immunological response in man: Interferon-producing capacity and phagocytosis.Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 20 193–199.
Pelletier, K. R. (1977).Mind as healer, mind as slayer. New York: Dell.
Rahe, R. H., & Arthur, R. J. (1968). Life-change patterns surrounding illness experience.Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 11 341–345.
Rahe, R. H., Bennett, L., Romo, M., Siltanen, R., Arthur, R. J. (1979). Subjects' recent life changes and coronary heart disease in Finland.American Journal of Psychiatry, 130 1222–1226.
Rahe, R. H., Meyer, M., Kjaer, G., & Holmes, T. H. (1964). Social stress and illness onset.Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 8 35–44.
Riley, V., Fitsmaurice, M. A., & Spackman, D. H. (1981). Psycho-neuroimmunologic factors in neoplasia: Studies in animals. In R. Ader (Ed.),Psychoneuro-immunology. New York: Academic Press.
Roessler, R., Cato, T. R., Lester, J. W., & Couch, R. B. (1979).Ego strength, life events, and antibody titer. Paper presented at the meeting of the American Psychosomatic Society, Houston.
Ruuskanen, S. P., Soppi, E., Viljanen, M. K., Jarvinen, M., Toivonen, H., & Kovralaninen, K. (1978). Effect of sport stress on lymphocyte transformation and antibody formations.Journal of Experimental Immunology, 32 339–345.
Schwartz, G. E. (1975). Biofeedback, self-regulation, and the pattering of physiological processes.American Scientist, 63 314–323.
Selye, H. (1980).The stress concept today. In I. Kutash, L. B. Schlesinger, & Associates (Eds.), San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Smith, C. W., Schneider, J., Minning, C., & Whitcher, S. (1982).Imagery and neutrophil function studies: A preliminary report. Unpublished manuscript.
Solomon, G. F. (1981). Emotional and personality factors in the onset and course of autoimmune disease, particularly rheumatoid arthritis. In R. Ader (Ed.),Psychoneuro-immunology. New York: Academic Press.
Solomon, G. F., & Amkaraut, A. A. (1972). Emotions, stress and immunity. In J. M. Vaeth (Ed.),Frontiers of radiation therapy and oncology (Vol. 7). Baltimore: University Park Press.
Stein, M., Schleifer, S. J., & Keller, S. E. (1981). Hypothalmic influences on immune responses. In R. Ader (Ed.),Psychoneuro-immunology. New York: Academic Press.
Thompson, E. B., & Lippman, M. E. (1976). Mechanism of action of glucocorticoids.Metabolism, 23 159–203.
Thorn, G. W., Adams, R. D., Braunwald, E., Isselbacher, K. J., & Petersdorf, R. G. (Eds.). (1977).Principles of internal medicine (8th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Wintrobe, M. M., Lee, G. B., Boggs, D. R., Bithell, T. C., Foerster, J., Athens, J. W., & Lukens, J. N. (1981).Clinical hematology (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Lee & Febiger.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peavey, B.S., Lawlis, G.F. & Goven, A. Biofeedback-assisted relaxation: Effects on phagocytic capacity. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation 10, 33–47 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00998676
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00998676