Abstract
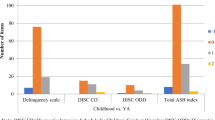
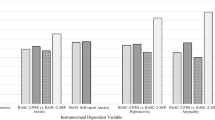
The present study reports on standardized behavioral ratings received by a large sample of hyperactive children meeting research diagnostic criteria (n=108) and a community control sample of normal children (n=61) who were followed prospectively over 8 years into adolescence. On some parentreport measures both groups declined in the severity of their behavior problems across time, while on other measures only the hyperactive group declined, but the hyperactives always remained more deviant than the controls at followup. The hyperactives and controls also differed on most teacher and selfreport ratings at followup. The greatest degree of agreement between raters at adolescence was between parent and youth ratings. These results are consistent with previous research demonstrating more deviant scores for hyperactive children than controls on various rating scales at adolescent followup. They also are consistent with research showing significant longitudinal continuity of both internalizing and externalizing behavioral pathology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991).Manual for the Cross-Informant Program for the CBCLI4-18, YSR, and TRF. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. S. (1981). Behavioral problems and competencies reported by parents of normal and disturbed children aged four through sixteen.Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 46 (Serial No. 188).
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. (1983).Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist and Revised Child Behavior Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. (1986).Manual for the Teacher's Report Form and Teacher Version of the Child Behavior Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. (1987).Manual for the Youth Self-Report and Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M., McConaughy, S. H., & Howell, C. T. (1987). Child/adolescent behavioral and emotional problems: Implications of cross-informant correlations for situational specificity.Psychological Bulletin, 101, 213–232.
Ackerman, P. T., Dykman, R. A., & Peters, J. E. (1977). Teenage status of hyperactive and nonhyperactive learning disabled boys.American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 47, 577–596.
Barkley, R. A. (1981).Hyperactive children. New York: Guilford Press.
Barkley, R. A. (1988a). Child behavior rating scales and checklists. In M. Rutter, H. Tuna, & I. Lann (Eds.),Assessment and diagnosis in child psychopathology (pp. 113–155). New York: Guilford Press.
Barkley, R. A. (1988b). The effects of methylphenidate on the interactions of preschool ADHD children with their mothers.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 27, 336–341.
Barkley, R. A. (1990).Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment. New York: Guilford Press.
Barkley, R. A., & Edelbrock, C. S. (1987). Assessing situational variation in children's behavior problems: The Home and School Situations Questionnaires. In R. Prinz (Ed.),Advances in behavioral assessment of children and families (Vol. 3, pp. 157–176). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Barkley, R. A., Fischer, M., Edelbrock, C. S., & Smallish, L. (1990). The adolescent outcome of hyperactive children diagnosed by research criteria: I. An 8-year prospective follow-up study.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 29, 546–557.
Barkley, R. A., Fischer, M., Edelbrock, C. S., & Smallish, L. (1991). The adolescent outcome of hyperactive children diagnosed by research criteria, III: Mother-child interactions, family conflicts, and maternal psychopathology.Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 32, 233–255.
Barkley, R. A., Karlsson, J., & Pollard, S. (1985). Effects of age on the mother-child interactions of ADD-H and normal boys.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 13, 631–637.
Barkley, R. A., Karlsson, J., Pollard, S., & Murphy, J. V. (1985). Developmental changes in the mother-child interactions of hyperactive boys: Effects of two dose levels of Ritalin.Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 26, 705–715.
Barkley, R. A., Karlsson, J., Strzelecki, E., & Murphy, J. (1984). Effects of age and Ritalin dosage on the mother-child interactions of hyperactive children.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 52, 750–758.
Breen, M., & Barkley, R. A. (1983). The Personality Inventory for Children (PIC): Its clinical utility with hyperactive children.Journal of Pediatrie Psychology, 8, 359–366.
Breen, M., & Barkley, R. A. (1988). Child psychopathology and parenting stress in girls and boys having attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity.Journal of Pediatrie Psychology, 13, 265–280.
Brown, R. T., & Borden, K. A. (1986). Hyperactivity at adolescence: Some misconceptions and new directions.Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 15, 194–209.
Campbell, S. B. (1983). Developmental perspectives in child psychopathology. In T. H. Ollendick & M. Hersen (Eds.),Handbook of child psychopathology (pp. 13–40). New Yurk: Plenum Press.
Cohen, N. J., Weiss, G., & Minde, K. (1972). Cognitive styles in adolescents previously diagnosed hyperactive.Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 13, 203–205.
Dunn, L. M. (1959).Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test (original edition). Circle Pines, MM: American Guidance Service.
Edelbrock, C., Greenbaum, R., & Conover, N. C. (1985). Reliability and concurrent relations between the teacher version of the Child Behavior Profile and the Conners Revised Teacher Rating Scale.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 13, 295–303.
Farrington, D. P., Loeber, R., & Van Kammen, W. B. (1990). Long-term criminal outcomes of hyperactivity-impulsivily-atlention deficit and conduct problems in childhood. In L. N. Robins & M. R. Rutter (Eds.),Straight and devious pathways to adulthood (pp. 62–82). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Fischer, M., Barkley, R. A., Edelbrock, C. S., & Smallish, L. (1990). The adolescent outcome of hyperactive children diagnosed by research criteria: II. Academic, altentional, and neuropsychological status.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 58, 580–588.
Fischer, M., Barkley, R. A., Fletcher, K. E., & Smallish, L. (in press). The adolescent outcome of hyperactive children: Predictors of psychiatric, academic, social, and emotional adjustment.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
Fischer, M., Rolf, J. E., Hasazi, J. E., & Cummings, L. (1984). Follow-up of a preschool epidemiological sample: Cross-age continuities and predictions of later adjustment with internalizing and externalizing dimensions of behavior.Child Development, 55, 137–150.
Gersten, J. C., Langner, T. S., Eisenberg, J. G., Simcha-Fagan, O., & McCarthy, E. D. (1976). Stability and change in types of behavioral disturbance of children and adolescents.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 4, 111–127.
Glow, R. A., Glow, P. H., & Rump, E. E. (1982). The stability of child behavior disorder: A one-year test-retest study of Adelaide Versions of the Conners Teacher and Parent Rating Scales.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 10, 33–60.
Goyette, C. H., Conners, C. K., & Ulrich, R. F. (1978). Normative data for Revised Conners Parent and Teacher Rating Scales.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 6, 221–236.
Hoy, E., Weiss, G., Minde, K., & Cohen, N. (1978). The hyperactive child at adolescence: Cognitive, emotional and social functioning.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 6, 311 -324.
Kellam, S. G., Branch, J. D., Agrawal, K. C., & Ensminger, M. E. (1975).Mental health and going to school. Chicago: University of Chicago.
Kinsbourne, M. (1977). The mechanism of hyperactivity. In M. Blaw, I. Rapin. & M. Kinsbourne (Eds.),Topics in child neurology (pp. 289–306). New York: Spectrum.
Kohlberg, L., LaCrosse, J., & Ricks, D. (1972). The predictability of adult mental health from childhood behavior. In B. B. Wolman (Ed.),Manual of child psychopalhology (pp. 1217–1284). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Kohn, M. (1977).Social competence, symptoms and underachievemeni in childhood: A longitudinal perspective. Washington, DC: Winston.
Kohn, M., & Rosman, B. L. (1972). Relationship of preschool social-emotional functioning to later intellectual achievement.Developmental Psychology, 6, 430–444.
Lerner, J. V., Hertzog, C., Hooker, K. A., Hassibi, M., & Thomas, A. (1988). A longitudinal study of negative emotional states and adjustment from early childhood through adolescence.Child Development, 59, 356–366.
McMahon, R. J., Calvert, S. C., & Tiedemann, G. L. (1988, November).Barkley's Home Situations Questionnaire: Reliability, validity and normative data. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Association for the Advancement of Behavior Therapy, New York.
Milich, R., Loney, J., & Whitten, P. (1983, August).Two year stability and validity of playroom observations of hyperactivity. Paper presented at the annual convention of the American Psychological Association, Anaheim, CA.
Minde, K., Weiss, G., & Mendelson, N. (1972). A 5-year follow-up of 91 hyperactive school children.Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry, 11, 595–610.
Olweus, D. (1979). Stability of aggressive reaction patterns in males: A review.Psychological Bulletin, 86, 852–875.
Patterson, G. R. (1982).Coercive family process. Eugene, OR: Castalia.
Riddle, K. D., & Rappoport, J. L. (1976). A 2 year follow-up of 72 hyperactive boys.Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 162, 126–134.
Robins, L. N. (1966).Deviant children grown up. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
Robins, L. N. (1979). Follow-up studies. In H. C. Quay & J. S. Wcrry (Eds.),Psychopathological disorders of children (2nd ed.) (pp. 483–513). New York: Wiley.
Tarver-Behring, S., Barkley, R., & Karlsson, J. (1985). The mother-child interactions of hyperactive boys and their normal siblings.American Journal of Orlhopsychiatiy, 55, 202–209.
Thorley, G. (1984). Review of follow-up and follow-back studies of childhood hyperactivity.Psychological Bulletin, 96, 116–132.
Trites, R. L., Blouin, A. G., Ferguson, H. B., & Lynch, G. W. (1981). The Conners' Teacher Rating Scale: An epidemiological inter-rater reliability and follow-up investigation. In K. Gadow & J. Loney (Eds.),Psychosocial aspects of drug treatment for hyperactivity. Boulder, CO: Westview.
Ullmann, R. K., Sleator, E. K., & Sprague, R. L. (1985). A change of mind: The Conners Abbreviated Rating Scales reconsidered.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 13, 553–566.
Weiss, G., & Hechtman, L. T. (1986).Hyperactive children grown up. New York: Guilford Press.
Weiss, G., Hechtman, L., Milroy, T., & Perlman, T. (1985). Psychiatric status of hyperactives as adults: A controlled prospective 15-year follow-up of 634 hyperactive children.Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry, 24, 211–221.
Weiss, G., Hechtman, L., & Perlman, T. (1978). Hyperactives as young adults: School, employer, and self-rating scales obtained during ten-year follow-up evaluation.American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 48, 438–445.
Weiss, G., Hechtman, L., Perlman, T., Hopkins, J., & Wener, A. (1979). Hyperaclivcs as young adults: A controlled prospective 10 year follow-up of the psychiatric status of 75 hyperactive children.Archives of General Psychiatry, 36, 675–681.
Weiss, G., Minde, K., Werry, J. S., Douglas, V. I., & Nemeth, E. (1971). Studies on thehyperactive child VIII: Five year follow-up.Archives of General Psychiatry, 24, 409–414.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by NIMH gram 42181. We are grateful to Craig S. Edelbrock, Ph.D., for his assistance with the data entry program, and to Ann Edwards and Gerry Gillespie for their assistance in locating subjects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, M., Barkley, R.A., Fletcher, K.E. et al. The stability of dimensions of behavior in ADHD and normal children over an 8-year followup. J Abnorm Child Psychol 21, 315–337 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00917537
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00917537