Abstract
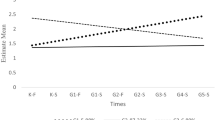
An epidemiological sample of 936 Dutch children originally aged 4–11 years was assessed at 2-year intervals over a 6-year period. Parents completed the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) on all four occasions. Stability coefficients computed for eight CBCL syndromes, Internalizing and Externalizing dimensions, and total problems revealed considerable long-term stability. There was no significant difference in the 6-year stability of internalizing vs. externalizing scores. This finding was at odds with reports of considerably lower stability of internalizing behavior, and was consistent with findings suggesting that the stability of internalizing problems should not be underestimated. The magnitude and specificity of the long-term stability of internalizing and externalizing scores lends support to the validity of these behavioral dimensions as tapped by the CBCL. No significant sex or age differences in the stability of problem behaviors were found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991a).Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M. (1991b).Manual for the Teacher's Report Form and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M. (1991c).Integrative guide for the 1991 CBCL/4-18, YSR, and TRF Profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M., Conners, C. K., & Quay, H. C. (1983).The ACQ Behavior Checklist. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M., Verhulst, F. C., Baron, G. D., & Akkerhuis, G. W. (1987). Epidemiologic comparisons of American and Dutch children: I. Behavioral/emotional problems and competencies reported by parents for ages 4 to 16.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 26, 317–325.
Cairns, R. B., Cairns, B. D., Neckerman, H. J., Ferguson, L. L., & Gariepy, J. L. (1989). Growth and aggression: I. Childhood to early adolescence.Developmental Psychology, 25, 320–330.
Cohen, J. (1977).Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (Revised ed.). New York: Academic Press.
Fischer, M., Rolf, J. E., Hasazi, J. E., & Cummings, L. (1984). Follow-up of a preschool epidemiological sample: Cross-age continuities and predictions of later adjustment with internalizing and externalizing dimensions of behavior.Child Development, 55, 137–150.
Gersten, J. C., Langner, T. S., Eisenberg, J. G., Simcha-Fagan, O., & McCarthy, E. D. (1976). Stability and change in types of behavioral disturbance of children and adolescents.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 4, 111–127.
Ghodsian, M., Fogelman, K., Lambert, L., & Tibbenham, A. (1980). Changes in behaviour ratings of a national sample of children.British Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 19, 247–256.
Graham, P., & Rutter, M. (1973). Psychiatric disorder in the young adolescent: A follow-up study.Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine, 66, 1226–1229.
Kagan, J., Reznick, J. S., & Snidman, N. (1988). Biological bases of childhood shyness.Science, 240, 167–171.
Kellam, S. G., Branch, J. D., Agrawal, K. C., & Ensminger, M. E. (1975).Mental health and going to school. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Kohn, M., & Rosman, B. L. (1972). A social competence scale and symptom checklist for the preschool child: Factor dimensions, their cross-instrument generality and longitudinal persistence.Developmental Psychology, 6, 430–444.
Loeber, R. (1982). The stability of antisocial and delinquent child behavior: A review.Child Development, 53, 1431–1446.
Macfarlane, J. W., Alien, L., & Honzik, M. P. (1962).A developmental study of the behavior problems of normal children between twenty-one months and fourteen years. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
McConaughy, S. H., Stanger, C., & Achenbach, T. M. (1992). Three-year course of behavioral/emotional problems in a national sample of 4- to 16-year-olds: I. Agreement among informants.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 31, 932–940.
McGee, R., Williams, S., Bradshaw, J., Chapel, J., Robins, A., & Suva, P. (1985). The Rutter scale for completion by teachers: Factor structure and relationships with cognitive abilities and family adversity for a sample of New Zealand children.Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 26, 727–739.
Offord, D. R., Boyle, M. H., Szatmari, P., Rae-Grant, N. I., Links, P. S., Cadman, D. T., Byles, J. A., Crawford, J. W., Blum, H. M., Byrne, C., Thomas, H., & Woodward, C. A. (1987). Ontario Child Health Study: II. Six-month prevalence of disorder and rates of service utilization.Archives of General Psychiatry, 44, 832–836.
Olweus, D. (1979). Stability of aggressive reaction patterns in males: A review.Psychological Bulletin, 86, 852–875.
Quinton, D., Rutter, M., & Gulliver, L. (1990). Continuities in psychiatric disorders from childhood to adulthood in the children of psychiatric patients. In Robins, L. N., & Rutter, M. (Eds.),Straight and devious pathways from childhood to adulthood. Cambridge University Press.
Richman, N., Stevenson, J. E., & Graham, P. J. (1982).Preschool to school: A behavioural study. London: Academic Press.
Rutter, M. (1967). A children's behaviour questionnaire for completion by teachers: preliminary findings.Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 8, 1–11.
Rutter, M. (1981). Longitudinal studies: A psychiatric perspective (pp. 326–336). In Mednick, S. A., & Baert, A. E. (Eds.),Prospective longitudinal research: An empirical basis for the primary prevention of psychosocial disorders. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Rutter, M., Graham, P., Chadwick, O. F. D., & Yule, W. (1976). Adolescent turmoil: Fact or fiction?Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 17, 35–56.
Steiger, J. H. (1980). Tests for comparing elements of a correlation matrix.Psychological Bulletin, 87, 245–251.
Van Westerlaak, J. M., Kropman, J. A., & Collaris, J. W. M. (1975).Beroepenklapper. Nijmegen, Holland: Instituut voor Toegepaste Sociologie.
Verhulst, F. C., & Akkerhuis, G. W. (1989). Agreement between parents' and teachers' ratings of behavioral/emotional problems of children aged 4–12.Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 30, 123–136.
Verhulst, F. C., & Althaus M. (1988). Persistence and change in behavioral/emotional problems reported by parents of children aged 4–14: An epidemiological study.Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica (Suppl. 339),77.
Verhulst, F. C., & Koot, J. M. (1991). Longitudinal research in child and adolescent psychopathology.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 30, 361–368.
Verhulst, F. C., & van der Ende, J. (1991a). Four-year follow-up of teacher reported problems.Psychological Medicine, 21, 965–977.
Verhulst, F. C., & van der Ende, J. (1991b). Assessment of child psychopathology: Relationships between different methods, different informants and clinical judgment of severity.Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 84, 155–159.
Verhulst, F. C., & van der Ende, J. (1992). Six-year developmental course of problem behaviors.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 31, 924–931.
Verhulst, F. C., & van der Ende, J. (in press) “Comorbidity” in an epidemiological sample.Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.
Verhulst, F. C., Akkerhuis, G. W., & Althaus, M. (1985a). Mental Health in Dutch children: I. A cross-cultural comparison.Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica (Suppl. 323), 72.
Verhulst, F. C., Berden, G., & Sanders-Woudstra, J. A. R. (1985b). Mental Health in Dutch children: II. Prevalence of psychiatric disorder and relationships between measures.Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica (Suppl. 324) 72.
Verhulst, F. C., Koot, J. M., & Berden, G. F. M. G. (1990). Four-year follow-up of an epidemiological sample.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 29, 440–448.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verhulst, F.C., van der Ende, J. Six-year stability of parent-reported problem behavior in an epidemiological sample. J Abnorm Child Psychol 20, 595–610 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00911243
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00911243