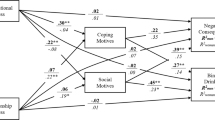
Abstract
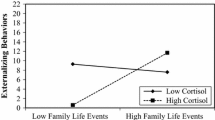
This study examined alcohol use among seventh graders in relation to life events, daily hassles, the supportive quality of the family environment, coping, and anxiety. Four hundred twenty-five students participated, 228 girls and 197 boys. Stepwise regression and discriminant function analyses indicated that the students reported more alcohol use if they also reported more life events, more daily hassles, and more conflict in the family. A stress-buffering effect of low family conflict on life events could not be substantiated for extent of alcohol use. The results are discussed in the context of the developmental transitions of adolescence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, G. M. (1981). Adolescent alcohol use and other problem behaviors: Their relationship and common parental influences.J. Youth Adoles. 13: 329–348.
Billings, A. G., and Moos, R. H. (1981). The role of coping responses and social resources in attenuating the stress of life events.J. Behav. Med. 4(2): 139–157.
Braucht, G. N. (1980). Psychosocial research on teenage drinking: Past and future. In Scarpetti, F. R., and Datesman, S. K. (eds.),Drugs and the Youth Culture, Sage, Beverly Hills, Calif., pp. 109–143.
Brook, J. S., Whiteman, M., Gordon, A. S., and Brook, D. W. (1984). Identification with parental attributes and its relationship to the son's personality and drug use.Dev. Psychol. 20: 1111–1119.
Bruns, C., and Geist, C. S. (1984). Stressful life events and drug use among adolescents.J. Hum. Stress 10: 135–139.
Coddington, R. D. (1984). Measuring the stressfulness of a child's environment. In Humphrey, J. H. (ed.),Stress in Childhood, AMS Press, New York (Series AMS Studies in Modern Society: Political and Social Issues, No.17).
De Longis, A., Coyne, J. C., Dakof, G., Folkman, S., and Lazarus, R. (1982). Relationship of daily hassles, uplifts, and major life events to health status.Health Psychol. 1(2): 119–136.
Greene, J. W., Walker, L. S., Hickson, G., and Thompson, J. (1985). Stressful life events and somatic complaints in adolescents.Pediatrics 75(1): 19–22.
Heller, K., and Swindle, R. W. (1983). Social networks, perceived social support and coping with stress. In Feiner, R. D., Jason, L. A., Moritsugu, J. N., and Farber, S. S. (eds.),Preventive Psychology: Theory, Research and Practice, Pergamon, New York.
Hetherington, E. M., and Camara, K. A. (1984). Families in transition: The processes of dissolution and reconstitution. In Parke, R. D. (ed.),Review of Child Development Research Vol. 7. The Family, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Jessor, R., and Lessor, S. L. (1977).Problem Behavior and Psychosocial Development: A Longitudinal Study of Youth, Academic Press, New York.
Kanner, A. D., Coyne, J. D., Schaefer, C., and Lazarus, R. S. (1981). Comparison of two modes of stress management: Daily hassles and uplifts versus major life events.J. Behav. Med. 4: 1–39.
Lazarus, R. F., and Folkman, S. (1984).Stress, Appraisal, and Coping, Springer, New York.
McLaughlin, R. J., Baer, P. E., Burnside, M. A., and Pokorny, A. D. (1985). Psychosocial correlates of alcohol use at two age levels during adolescence.J. Stud. Alcohol 46: 212–218.
Mechanic, D. (1983). Adolescent health and illness behavior: Review of the literature and a new hypothesis for the study of stress.J. Hum. Stress 9: 4–13.
Miller, M. J., Tobacyk, J. J., and Wilcox, C. T. (1985). Daily hassles and uplifts as perceived by adolescents.Psychol. Rep. 56: 221–222.
Moos, R. H., Insel, P. M., and Humphrey, B. (1974).Family, Work, and Group Environment Scales Manual, Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, Calif.
Murray, D. M., and Perry, C. L. (1985). The prevention of adolescent drug abuse: Implications from etiological, developmental, behavioral, and environmental models. In Battjes, R., and Williams, S. (eds.),Etiology of Drug Abuse: Implications for Prevention, National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, Md.
Neff, J. A. (1984). The stress-buffering role of alcohol consumption: The importance of symptom dimension.J. Hum. Stress 10: 35–42.
Newcomb, M. D., Huba, G. F., and Bentler, P. M. (1981). A multidimensional assessment of stressful life events among adolescents: Derivation and correlates.J. Health Soc. Behav. 22: 400–415.
Paykel, E. S. (1983). Methodological aspects of life event research.J. Psychosom. Res. 27(5): 341–352.
Peterson, A. (1982). Adolescents and stress. In Goldberger and Breznitz, S. (eds.),Handbook of Stress: Theoretical and Clinical Aspects, Free Press, New York, pp. 515–528.
Pohorecky, L. A., and Brick, J. (1982).Stress and Alcohol Use: Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Stress and Alcohol Use, Elsevier Biomedical, New York.
Rutter, M. (1983). Stress, coping, and development: Some issues and some questions. In Rutter, M., and Garmezy, N. (eds.),Stress, Coping & Development in Children, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Schroeder, D. H., and Costa, P. T. (1984), Influence of life event stress on physical illness: Substantative effects or methodological flaws (National Institute of Health; Johns Hopkins).J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 46(4): 853–863.
Spielberger, C. D., Gorsuch, R. L., and Lushene, R. E. (1970).Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory, Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, Calif.
Stern, M., Northman, J. E., and Van Slyck, M. R. (1984). Father absence and adolescent “problem behaviors”: Alcohol consumption, drug use and sexual activity.Adolescence 19(74): 301–312.
Swearingen, E. M., and Cohen, L. H. (1985). Measurement of adolescents' life events: The junior high life experiences survey.Am. J. Commun. Psychol. 13(1), 69–85.
Zimmerman, M. (1983). Weighted versus unweighted life event scores-Is there a difference?J. Hum. Stress 9: 30–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baer, P.E., Garmezy, L.B., McLaughlin, R.J. et al. Stress, coping, family conflict, and adolescent alcohol use. J Behav Med 10, 449–466 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00846144
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00846144